You’re sitting quietly — watching TV, reading, or lying in bed — and suddenly, your heart flutters. It skips. It races. The episode lasts just a few seconds, maybe a minute, and then it vanishes like it never happened.
You go to the doctor. They run a 12-lead ECG. Maybe even a 24-hour Holter test.
The results? “Normal.”
But what you felt was real. So why didn’t the test catch it?
The Mystery of “Normal” Test Results
Many people who experience occasional palpitations—sudden thuds, flips, or rapid beats—are told that their hearts are perfectly fine. For some, that’s comforting. For others, it’s frustrating, especially when the symptoms continue.
The truth is, standard heart tests often miss intermittent arrhythmias. If your heart rhythm disturbance doesn’t occur during the short monitoring window, the ECG will appear normal. It’s like trying to catch a lightning strike with a snapshot, while we need a CCTV camera.
Why Short-Term ECGs Aren’t Always Enough
A standard ECG records your heart’s electrical activity for a few seconds. A Holter monitor might capture 24 to 48 hours. But what if your palpitations show up once a week? Or once a month? Or only at night? In these cases, standard tests can easily miss rhythm disturbances that may cause palpitations
Not all palpitations are created equal. Some represent harmless irregularities, while others may signal more serious electrical instability in the heart. The following are common rhythm disturbances that can cause fluttering, skipped beats, or pounding sensations, often transient and missed in standard ECGs:
- Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): These are short-lived episodes of atrial fibrillation that come and go unpredictably, often lasting minutes to hours and stopping on their own without treatment. Because they’re intermittent and may not cause overt symptoms, paroxysmal AF can go undiagnosed for years, despite significantly increasing stroke risk over time.
- Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs) and Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): These are early beats originating in the atria or ventricles. While they’re usually benign, frequent PACs or PVCs can cause noticeable palpitations or a feeling of a skipped heartbeat. In some cases, especially when very frequent, they may be associated with structural heart disease or contribute to cardiomyopathy.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): SVT refers to a group of arrhythmias that start in the atria and cause sudden-onset, fast heart rhythms — often described as a rapid, pounding sensation in the chest. Episodes may last seconds to hours and can terminate spontaneously. While often not life-threatening, recurrent SVT can significantly impair quality of life and may require intervention if it is frequent.
- Atrial Flutter: Similar to AFib, this arrhythmia involves rapid electrical activity in the atria but in a more organized, cyclical pattern. It may present with a fast, regular rhythm and is often associated with symptoms like fatigue or breathlessness. Atrial flutter is frequently seen in patients with structural heart disease or post-ablation AF recurrence.
- Ventricular Arrhythmias: While rare in healthy individuals, arrhythmias like ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF) are more serious and potentially life-threatening. Occasional ventricular ectopy (i.e., isolated PVCs) is common and benign, but sustained or frequent runs — particularly during exertion or in people with structural heart disease — warrant immediate investigation.
Even serious heart rhythm irregularities can go undetected if they don’t occur during the test.
Read More: Monitoring Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation With The Frontier X Plus
But If It’s Infrequent, Should You Worry?
Yes — and here’s why.
Palpitations might seem benign, especially if they’re rare or go away quickly. But even occasional or “silent” episodes can be early warning signs of more serious conditions. Some possibilities include:
- Atrial fibrillation (AF), especially the paroxysmal kind, which often starts intermittently before becoming persistent
- Tachycardias that could increase in frequency or duration over time
- Heart failure risk, if arrhythmias disrupt blood flow long-term
- Stroke risk, particularly from undiagnosed AF, even without symptoms
Studies show that around one-third of those with AFib may not experience symptoms. So occasional flutters shouldn’t be ignored, especially if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
What Does a Palpitation Actually Feel Like?
Patients describe them in different ways:
- “It felt like my heart skipped a beat.”
- “It was fluttering in my chest for a few seconds.”
- “My heart pounded out of nowhere.”
- “There was a thud, then a pause.”
Sometimes the flutter is followed by dizziness, fatigue, anxiety, or a brief sense of breathlessness. These signs matter. They could be clues to underlying cardiovascular arrhythmias, not just stress or overexertion.
The Role of Continuous ECG Monitoring In Managing Heart Health
This is where continuous, long-term ECG monitoring fills the gap. Unlike traditional tools, these devices are worn for days or even weeks. They:
- Track your heart 24/7, even while you sleep, work out, or rest
- Capture rare and unpredictable events that standard ECGs miss
- Allow symptom tagging, so you can mark when you feel something off
- Record high-fidelity data across all daily activities
The key is remote monitoring, letting your physician review real-time ECG data from your device, sometimes with cloud-based storage and alerts for irregularities.
This means that even one-off flutters, short AF episodes, or infrequent PVCs can be caught and reviewed, giving your care team a full picture of your sinus rhythm and any deviations from it.
What Happens After the Data Is Captured?
Once the ECG data is collected:
- Cardiologists analyze the pattern, timing, and frequency of irregularities.
- They look for heart arrhythmias, prolonged QT intervals, abnormal beats, or signs of AF heart rhythm.
- Based on the findings, they may recommend treatment (medications, ablation), further testing, or lifestyle changes.
Importantly, long-term monitors provide insight into when the problem happens, such as during stress, after meals, or at night, which helps tailor both diagnosis and treatment.
When Should You Consider Continuous Monitoring?
You might benefit from long-term ECG tracking if:
- You feel fluttering, skipping, pounding, or irregular beats occasionally
- You’ve had normal tests but persistent symptoms
- You experience dizziness, fatigue, chest discomfort, or breathlessness without explanation
- You’re monitoring the effects of medications or post-ablation outcomes
- You have a family history or risk factors for arrhythmias or AF
Final Thoughts: Don’t Dismiss the Flutters
Just because a quick test comes back normal doesn’t mean your heart is behaving normally all the time. Heartbeat arrhythmias can be elusive; they may hide for days, only to show up when you’re not looking. Remote, continuous ECG monitoring empowers you and your doctor to detect hidden issues, uncover patterns, and start treatment early. So, the next time your heart flutters, don’t ignore it. Listen closely. If needed, track it. And give your heart the attention it deserves.
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) are early, extra heartbeats that start in the heart’s lower chambers (the ventricles), disrupting the heart’s normal rhythm for a moment. They are relatively common in 3% to 20% of the general population and are often detected during evaluations for palpitations or incidentally on routine electrocardiograms (ECGs). They often show no symptoms and require no special treatment. But for some, these contractions can cause uncomfortable sensations, and anxiety, or even signal an underlying cardiac problem. Let’s first understand what PVCs are and then discuss everything you need to know about them.
What are PVCs?
PVC is short for Premature Ventricular Contractions. They are also called Ventricular premature beats and Ventricular extrasystoles. In a normal, synchronized heart rhythm, your heart beats in a smooth, steady rhythm thanks to a natural electrical system. It all starts in a small area called the sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the upper right part of your heart. This is your heart’s natural pacemaker — it sends out a signal that tells the top chambers (the atria) to contract and push blood into the lower chambers (the ventricles).
Next, the signal passes through a checkpoint called the atrioventricular (AV) node, which briefly slows things down to give the ventricles time to fill with blood. Then the signal travels down special pathways to the bottom of the heart, making the ventricles contract and pump blood to the lungs and the rest of your body.
But sometimes, things don’t go as planned. In a condition called Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs), the signal starts too early, and it comes from the bottom chambers (the ventricles) instead of the top. This early signal can throw off the heart’s normal rhythm, leading to a feeling of a skipped or extra beat. You might feel them as a flutter in the chest, a missed beat, a strong thump, or a momentary pause in your heartbeat
Most PVCs are harmless, especially in individuals with healthy hearts. But in some cases, they may reflect or contribute to heart dysfunction, especially when they occur frequently.
What PVCs Feel Like: Common Symptoms
If you have PVC, you may or may not feel the symptoms. You may discover them only during a routine ECG or check-up. When symptoms do occur, they can include:
- A sensation of skipped or irregular heartbeats
- Chest fluttering
- Chest Thumping,
- Lightheadedness
- Fatigue and mild shortness of breath.
It is necessary to contact your healthcare professional if you have symptoms like fainting.
What Causes PVCs?
PVCs can occur in healthy individuals without any clear reason. However, several triggers and risk factors have been associated with their occurrence.
1. Lifestyle and Non-Cardiac Triggers
Certain daily practices, habits, or conditions that are not directly related to the heart can trigger PVCs. Here are some common triggers:
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Tobacco use
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleep deprivation
- Medications (like decongestants or asthma medications)
2. Medical Conditions
Pre-existing medical conditions can trigger PVCs. Here are a few triggers:
- Electrolyte imbalances (low potassium, magnesium, or calcium)
- Anemia
- High blood pressure
- Structural heart disease (like cardiomyopathies or valve disorders)
- Acute events such as heart attacks or myocarditis
PVCs can also occur more frequently with age. Males, African Americans, and individuals with hypertension or bundle branch block are statistically more prone to developing PVCs.
Understanding the risks of PVC
In healthy individuals, occasional PVCs are generally not dangerous. However, their impact depends on several factors, including frequency, symptoms, and underlying heart health.
- Occasional PVCs in healthy individuals are usually benign and don’t require treatment.
- Frequent PVCs (e.g., >10% of total heartbeats in 24 hours) may impair cardiac function.
- Persistent high PVC burden can lead to PVC-induced cardiomyopathy, causing heart muscle weakening and left ventricular dysfunction.
- Nonsustained VT occurs when ≥3 PVCs appear consecutively but resolve within 30 seconds.
- Sustained VT is a serious condition where a rapid heartbeat lasts >30 seconds and may cause syncope or sudden cardiac arrest.
- Symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or breathlessness alongside PVCs require further clinical evaluation.
- Frequent or symptomatic PVCs should prompt cardiology referral, especially in those with underlying heart disease.
Close Monitoring Needed:
Those with a high PVC burden or preexisting heart conditions need regular follow-ups. Early detection and appropriate management can help reverse damage and significantly improve the quality of life. Continuous ECG monitors can help track PVC burden over time and evaluate treatment effectiveness, especially in individuals at risk of PVC-induced cardiomyopathy.
How Are PVCs Diagnosed?
If you feel unusual heartbeats, your doctor may recommend:
12-lead Electrocardiogram (ECG) – to detect abnormal heartbeats
Holter monitor – a 24 to 48-hour device to track your heart rhythm
Echocardiogram – to check for structural heart problems
Exercise Stress testing – to evaluate how your heart behaves under physical exertion.
Wearable ECG devices – Portable, wearable monitors that continuously track your heart rhythm over days or weeks for irregularities
These tests help rule out underlying heart disease, which is critical in determining if your PVCs are benign or a sign of something more serious.
The Role of Wearable ECG Devices
Recent advancements in FDA-cleared wearable continuous ECG monitors have made it easier to detect both symptomatic and silent PVCs. These devices offer continuous, real-time heart monitoring outside of clinical settings, making it possible to track irregular beats over days or weeks and identify high-burden PVCs that may go unnoticed during short ECGs or clinic visits.
Unlike wrist-based devices or traditional Holter monitors that require periodic clinic visits, patchless, chest-worn, medical-grade, continuous ECG monitors like the Frontier X Plus can capture continuous, high-fidelity ECG waveforms in real time for up to 24 hours (or as long as the clinician prescribes), with just an hour of chargingIt enables remote access to ECG data by physicians for early diagnosis, reducing the need for repeated in-clinic testing. Additionally, detailed ECG reports can be downloaded and easily shared with healthcare providers for follow-up, second opinions, or long-term heart health management.
By integrating seamlessly into daily life, the Frontier X Plus offers high-fidelity continuous ECG recording that can aid physicians in early detection of arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation, as well as ongoing evaluation and treatment planning. While the Frontier X Plus does not detect PVCs directly, the ECG data it captures can be reviewed by physicians to assess rhythm patterns. In patients with a known high PVC burden, this data may support long-term monitoring of treatment effectiveness, lifestyle changes, or outcomes post-catheter ablation, with appropriate clinical oversight.
Read More: Continuous ECG Monitoring to Detect Asymptomatic Heart Arrhythmias During Sleep
How Are PVCs Treated?
Treatment is not always necessary for people with no symptoms and low-frequency PVCs.
What can help?
- Lifestyle changes can help manage PVCs:
- Reduce or avoid caffeine and alcohol
- Get adequate sleep
- Manage stress and anxiety
- Avoid stimulants and certain decongestants
2. Medications may be prescribed if symptoms are bothersome:
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (in selected cases)
3. If lifestyle changes and medicines don’t have an effect, radiofrequency catheter ablation may be recommended.
Summary
PVCs are common and often harmless, especially in healthy individuals. However, frequent or symptomatic PVCs can indicate underlying cardiac issues and warrant evaluation. With advanced continuous ECG monitoring, you can take charge of your heart health from the comfort of home.
Whether you’re evaluating palpitations or managing a diagnosed arrhythmia, understanding your heart rhythm is the foundation for peace of mind and proactive care.
FAQs
1. Are PVCs life-threatening?
In most healthy individuals, PVCs are harmless. However, in people with heart disease or very frequent PVCs, they can lead to complications if untreated.
2. Do PVCs require lifelong treatment?
Not always. Many people outgrow them, or they reduce with lifestyle changes. Medications or ablation may be needed in persistent or high-burden cases.
3. Is exercise safe with PVCs?
Generally, yes, especially if you don’t have structural heart disease. Still, consult your healthcare professional before starting a workout routine if you have frequent PVCs.
4. Can I monitor PVCs at home?
No. Wearable ECG monitors like the Frontier X Plus allow users to record their heart rhythm continuously. While the device can detect atrial fibrillation, it does not detect PVCs. To identify PVCs or other irregularities, the recorded ECG data must be reviewed by a physician.
5. Can anxiety cause PVCs?
Yes. Stress and anxiety are common triggers. Learning stress-management techniques may help reduce their frequency.
6. When should I see a doctor about PVCs?
If you feel dizzy, faint, have chest pain, or notice frequent irregular heartbeats, you should see a healthcare provider for evaluation.
When it comes to heart rhythm disorders, atrial flutter (AFL) and atrial fibrillation (AF) are two of the most common – and often confused – conditions. Both can lead to serious health risks, including stroke and heart failure, but understanding how they differ is critical for early detection, effective management, and peace of mind.
In this blog, we’ll break down the differences between atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation, why these arrhythmias matter, and how modern continuous ambulatory monitoring can help you and your healthcare team stay ahead of silent or intermittent episodes.
What Are Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are types of supraventricular arrhythmia, meaning they originate in the heart’s upper chambers (atria). Both result in abnormal electrical activity that disrupts normal heartbeat patterns.
Atrial Flutter
- Atrial flutter is characterized by rapid but regular electrical signals in the atria.
- The atria may beat at rates of about 300 beats per minute, but the ventricles (the lower chambers) usually beat at a regular, normal rate.
- On an ECG, atrial flutter often produces a classic sawtooth pattern.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
- AF involves chaotic, disorganized electrical signals in the atria.
- The atria quiver instead of contracting effectively.
- Ventricular response is typically irregular and faster than normal.
- On ECG, Atrial Fibrillation presents with the typical narrow complex “irregularly irregular” pattern with no distinguishable P-waves
What Causes These Arrhythmias?
Both conditions share overlapping risk factors:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disorders
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart valve disorders
- Excessive alcohol use
- Sleep apnea
However, atrial flutter is more often linked to scarring in the atria (e.g., after heart surgery), while AFib tends to be associated with age-related atrial changes or a family history of heart disease.
Symptoms: How Do They Feel?
Both atrial flutter and AFib can cause:
- Palpitations (sensation of a racing or fluttering heart)
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest discomfort
- Fatigue
AFib is often more unpredictable because of its irregular rhythm. Atrial flutter, despite being fast, may feel steadier but can still lead to serious complications like blood clots.
Read More: Preventing Complications from AFib: What You Need to Know
Why Does It Matter?
Stroke Risk
Both arrhythmias allow blood to pool in the atria, increasing the risk of clots that can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. People with AFib have a slightly higher stroke risk, but AFL also demands prompt medical attention.
Heart Failure
Untreated AFib and flutter can weaken the part of the heart responsible for pumping blood, leading to heart failure over time.
Different Treatments
- Atrial flutter treatment often involves catheter ablation, as the abnormal pathway can usually be targeted precisely.
- AFib treatment is more complex, requiring a combination of atrial fibrillation medication, rate or rhythm control strategies, and sometimes ablation.
In both conditions, blood thinners are commonly prescribed to prevent clots. When medication is needed, doctors may use drugs for atrial flutter and AFib, such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or antiarrhythmics to control the rate or rhythm.
Prevention Tips for Atrial Flutter & Atrial Fibrillation
-
Maintain a heart-healthy diet
Focus on a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. This supports cardiovascular function and reduces inflammation.
-
Stay physically active
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly to improve circulation and heart rhythm stability.
-
Limit alcohol and caffeine
Excessive intake of stimulants can trigger arrhythmias. Stick to moderation or avoid them altogether if you’re prone to irregular rhythms.
-
Manage chronic conditions
Proper control of hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnea, and thyroid disorders can lower your arrhythmia risk.
-
Avoid smoking
Tobacco use increases your risk of heart disease and rhythm disorders. Quitting has immediate cardiovascular benefits.
-
Monitor your heart rhythm proactively
Use long-term ECG monitors if you’re at risk or symptomatic. Early detection allows early intervention.
-
Routine check-ups and screenings
Especially important if you have a family history of arrhythmia or genetic predisposition. Early screening can prevent complications.
Read More: Healthy Lifestyle Changes for Managing AFib: Tips for Living with Atrial Fibrillation
| Feature | Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) | Atrial Flutter |
| Rhythm | Irregular | Regular |
| Atrial Rate | 100 to 175 bpm disorganised | Up to 300 bpm organized |
| Ventricular Response | Irregular | May be regular or slower than the atria |
| ECG Appearance | No distinct P waves; chaotic baseline | “Sawtooth” pattern |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, fatigue, dizziness, breathlessness | Similar symptoms, sometimes less pronounced |
| Stroke Risk | High | Also elevated, but generally slightly lower than AFib |
| Common Causes | Hypertension, heart disease, thyroid disorders, and alcohol | Same as AFib; often coexists with AFib |
Continuous ECG Technology: Why It’s Critical
One of the biggest challenges is that both arrhythmias can occur intermittently or silently. In fact, people may have episodes of AFib or flutter that they never feel until a complication like a stroke happens.
This is where continuous ECG technology becomes essential:
- It records your heart rhythm around the clock – during work, rest, or exercise.
- It captures both silent and symptomatic arrhythmias that could be missed during short clinic ECGs.
- It helps your doctor decide whether you need an atrial fibrillation medication, a procedure, or simply close follow-up.
Can Atrial Flutter and AFib Coexist?
Yes. Up to half of patients with atrial flutter will eventually develop AFib.
This overlap is important because it can influence your treatment plan. If you’re being evaluated for atrial flutter treatment, your care team will also consider strategies to prevent or manage AFib.
When Should You Seek Medical Advice?
You should speak to a doctor if you experience:
- An irregular or rapid heartbeat at rest
- Shortness of breath or unexplained fatigue
- Dizziness or fainting
- Chest discomfort
If you have risk factors such as high blood pressure, sleep apnea, or a family history of arrhythmias or heart disease, monitoring your heart rhythm proactively can help prevent complications.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation is key to reducing your risk of stroke, heart failure, and other complications. Both conditions can be managed effectively with the right mix of atrial fibrillation medication, drugs for atrial flutter, procedures, and lifestyle changes – but early detection is critical.
Continuous ECG-based heart monitors are valuable tools that help you and your healthcare team detect these arrhythmias before they cause harm, offering clarity and control over your heart health.
About The Frontier X Plus
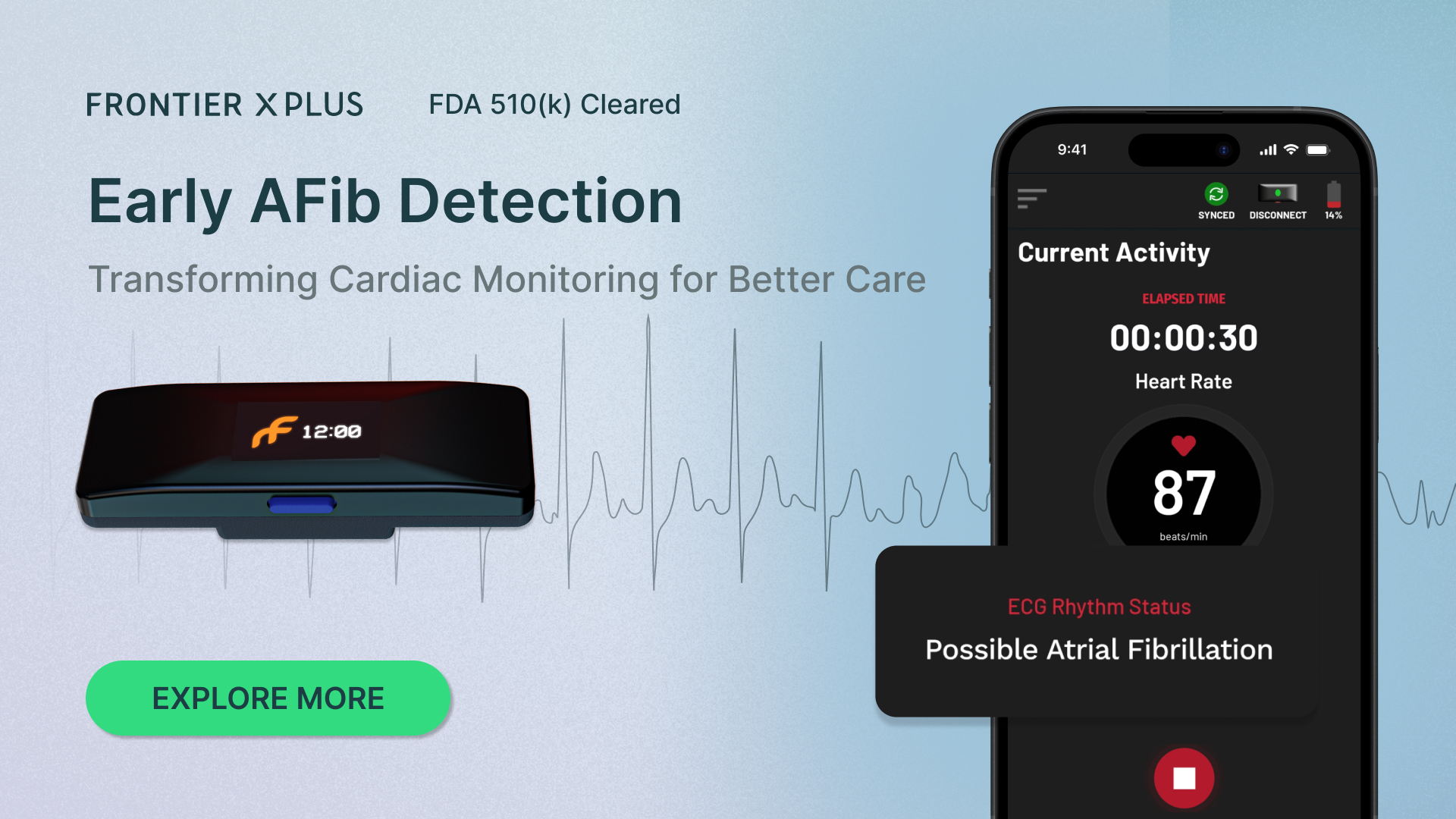
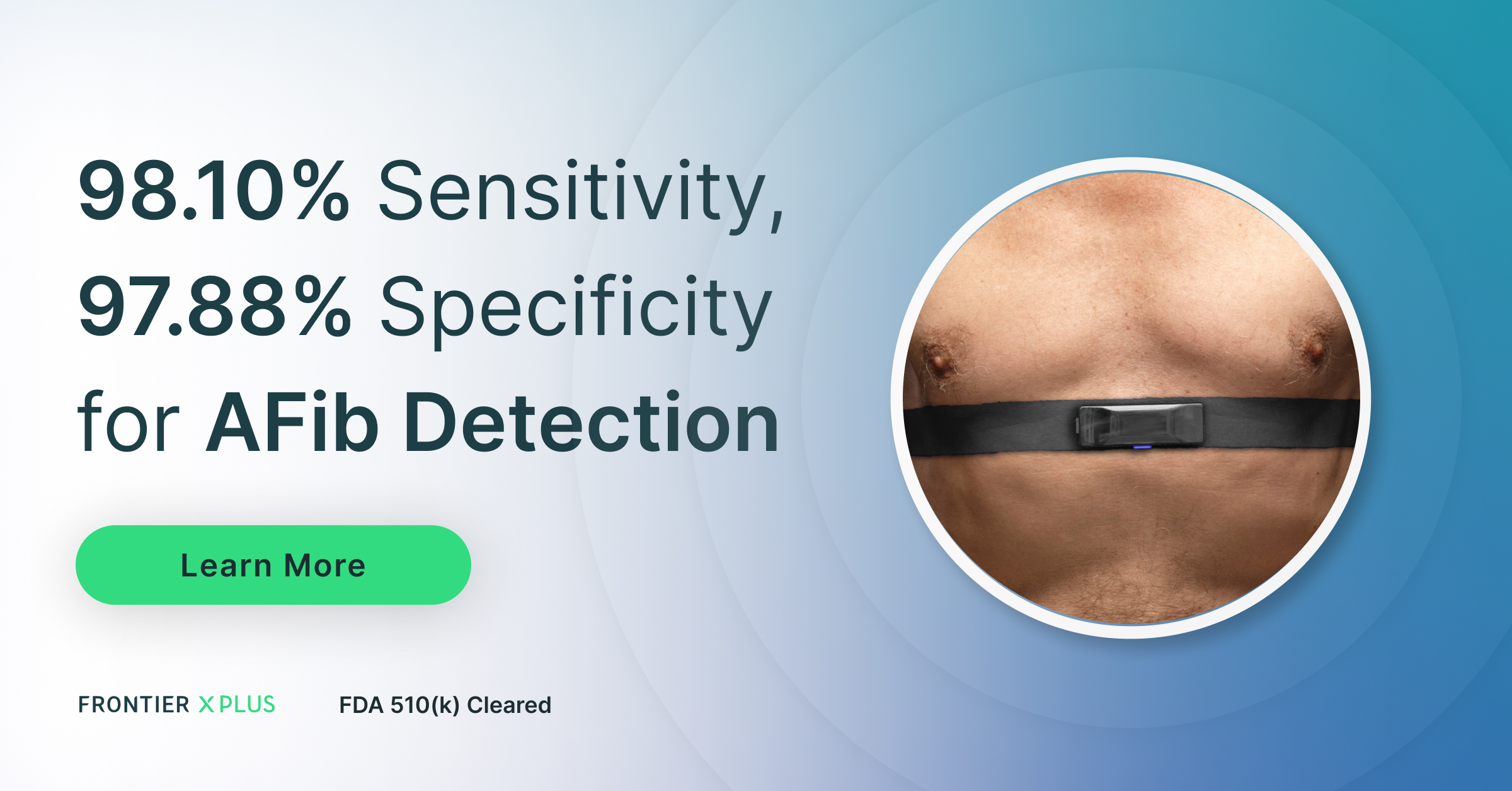
The Frontier X Plus is an FDA 510(k)-cleared prescription-only medical device offering single-channel ECG monitoring through a comfortable chest-worn design, and can be used continuously for 24 hours between recharges. Built for healthcare professionals, patients with cardiac concerns, and health-focused individuals, it enables early detection of Afib and other irregular heart rhythm analysis, all without wires, adhesives, or hospital visits.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs: Atrial Flutter vs. Atrial Fibrillation
Is atrial flutter more dangerous than atrial fibrillation?
Both conditions carry a risk of stroke and heart failure if untreated. AFib generally has a higher stroke risk because of the irregular blood flow, but atrial flutter is also serious and requires medical evaluation.
What is the treatment for atrial flutter?
Common atrial flutter treatment includes catheter ablation, which targets the abnormal electrical pathway, and medications like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to control heart rate. Blood thinners are often prescribed to prevent stroke.
What medications are used for atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation medication can include rate-control drugs (e.g., beta-blockers), rhythm-control drugs (e.g., flecainide, amiodarone), and blood thinners (e.g., apixaban, warfarin) to reduce stroke risk.
Can drugs for atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation be the same?
Often yes – both may use rate-control medications and blood thinners. However, rhythm-control strategies and decisions about procedures like ablation may differ.
How can I tell if I have AFib or atrial flutter at home?
It’s difficult to tell without an ECG. Long term ECG monitoring devices can help detect irregular patterns and assist physicians in detection.
Does atrial flutter always require ablation?
Not always. Some patients are managed with medication first. But ablation is highly effective for atrial flutter treatment, especially when medications don’t work or cause side effects.
Have you ever felt your heart flutter, skip a beat, or suddenly pound for a moment? For many people, this fleeting sensation is caused by something called a Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) — a common type of irregular heartbeat. While PACs are often harmless, frequent or persistent PACs can sometimes indicate deeper cardiac issues, making awareness and monitoring crucial.
Here, we’ll explore:
- What PACs are
- What do they feel like
- What causes them
- When they may become serious
- How continuous ECG can help
What Are Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)?
PACs are early heartbeats that originate in the atria, the heart’s upper chambers, before the heart’s natural pacemaker (the sinoatrial node) fires. This disrupts the normal rhythm — often followed by a brief pause — which may feel like a skipped or extra-strong heartbeat.
Real-World Example: When PACs Are More Than Just a Nuisance
In a recent case published in HeartRhythm Case Reports, a 38-year-old woman experienced persistent palpitations due to an unusually high burden of premature atrial contractions (PACs). Despite initial conservative treatment, her symptoms worsened, and imaging revealed impaired left ventricular function. Electrophysiological evaluation confirmed the PACs as the underlying cause. She underwent catheter ablation, after which her heart function and symptoms significantly improved, highlighting that frequent PACs, while often benign, can sometimes lead to reversible cardiomyopathy if left untreated.
This example underscores why it’s essential to understand and track your heart rhythm, especially if symptoms persist.
What Do PACs Feel Like?
PACs can vary in how they’re experienced:
- A fluttering sensation
- A skipped or forceful heartbeat
- Shortness of breath or anxiety
- Or no sensation at all
They’re often more noticeable when lying down or at rest. While many people live with occasional PACs without concern, frequent PACs can signal underlying instability in the heart’s electrical system.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors
PACs may be caused or worsened by:
- Caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine
- Stress, anxiety, or lack of sleep
- Electrolyte imbalances (like low potassium or magnesium)
- Dehydration
- Certain medications
- Underlying heart or lung conditions (like COPD or heart failure)
You’re more likely to experience PACs if you’re older, sedentary, pregnant, have high blood pressure, low HDL (“good”) cholesterol, or live with chronic illness.
When Should You Be Concerned?
PACs are generally benign, but medical evaluation is recommended if:
- They happen frequently or in clusters
- You feel dizzy, faint, fatigued, or have chest discomfort
- You have a history of atrial fibrillation (AFib) or other arrhythmias
- Your quality of life or sleep is affected
High PAC burden (i.e., frequent PACs) is associated with:
- Increased risk of AFib
- Greater likelihood of ischemic stroke
- Progression to heart failure or reduced cardiac output
Diagnosing and Monitoring PACs
PACs are often missed during routine ECGs since they may not occur during a short snapshot. That’s where continuous or ambulatory ECG becomes valuable.
Key Tools Used to Diagnose PACs:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Holter monitor (24–48 hours)
- Echocardiogram
- Blood tests (to check electrolytes or thyroid function)
But even Holters can miss intermittent Premature Atrial Complexes. For better detection and diagnosis, long-term, wearable ECG devices offer a major advantage.
Why Continuous Monitoring Matters
With continuous ECG-based heart rate monitors, you and your doctor can:
- Catch early signs of arrhythmias
- Track patterns or triggers (like stress or caffeine)
- Reduce anxiety by understanding what’s happening with your heart
- Avoid unnecessary clinic visits through remote medical review
- Make informed decisions about lifestyle changes or treatments
Read more: 24×7 Continuous ECG: The Future of Personalized Heart Health Management
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help
You should seek urgent care if Premature Atrial Complexes are accompanied by:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Persistent shortness of breath
- Fainting or extreme fatigue
- A rapid or irregular heartbeat lasting over 30 minutes
Even if PACs are usually harmless, it’s better to rule out serious conditions early.
Final Thoughts
Premature Atrial Contractions are often a normal part of your heart’s rhythm, but if they become frequent or symptomatic, they deserve attention. With modern continuous ECG monitoring technology, you can take control of your heart health from the comfort of your own home.
Whether you’re investigating palpitations or managing a known arrhythmia, understanding your heart’s rhythm is the first step toward peace of mind and proactive care.
Keywords:
If you take your heart health seriously – whether due to a known condition, family history, or unexplained symptoms – you’ve probably wondered whether a smartwatch is enough to keep tabs on your heart. While smartwatches are great for general wellness, they’re not built for clinical-grade monitoring.
Smartwatches emerged as part of a growing trend towards self-quantification and everyday health awareness. As people sought more control over their fitness, sleep, and heart rate data, tech companies responded with increasingly capable wrist-worn devices that delivered instant feedback. These tools made heart monitoring more accessible to the general public, offering ECG spot checks and irregular rhythm alerts. But despite their innovation, smartwatches were never designed for continuous, medical-grade monitoring. That’s where the Frontier X Plus sets a new standard – giving you and your doctor a much clearer, continuous view of your heart.
In this article, you’ll understand how the Frontier X Plus compares to a typical smartwatch, other available smart watches, and why it’s a better choice if you’re looking for reliable, actionable insights about your heart health.
1. Clinical-Grade ECG vs. Wellness Tracking
Your smartwatch might let you take a 30-60-second ECG reading here and there, usually when you voluntarily remember to check. It may be useful, but not enough if you have symptoms that are intermittent, or if you’re being evaluated for a condition like Atrial Fibrillation.
The Frontier X Plus, however, is an FDA-cleared, prescription device designed for continuous ECG monitoring. You wear it on your chest, and it captures accurate data as you live your life — whether you’re at work, walking the dog, or asleep.
2. Continuous Monitoring That Fits Into Your Life
Unlike a smartwatch, which only records ECGs when you tell it to, Frontier X Plus works in the background, continuously. It records your ECG for up to 24 hours on a single charge, and because it’s designed for daily wear with a quick one-hour recharge, you can use it for days at a time.
If you’ve ever had symptoms that vanish before you could open your watch app, this device is for you.
3. Made for Medical Insight, Not Just Fitness Goals
Smartwatches are great for counting steps and reminding you to stand up, but when it comes to real heart monitoring, they fall short. If your doctor needs to understand your rhythm over time, your smartwatch won’t cut it. The Frontier X Plus is built for exactly that. It’s used in cardiac rehab, post-operative care, and remote patient monitoring, and the data it collects can be reviewed securely by your physician, often without you needing to return to the clinic.
4. Better Accuracy, Less Guesswork
Let’s face it: wrist-based ECGs can be inconsistent. Sweat, movement, or how tight your band is can affect results, sometimes showing false positives or inconclusive data.
The Frontier X Plus sits securely on your chest, providing stable, high-quality ECG signals. If the signal isn’t good, the system flags it, so your doctor only sees clinically reliable data.
5. From Data to Diagnosis, Faster
If your smartwatch tells you something might be off, your next step is usually a referral for further testing. That means waiting, worrying, and possibly wearing a Holter monitor later.
With the Frontier X Plus, you skip the guesswork. Your device collects the data your doctor needs, and a full report, including heart rate trends, arrhythmia flags, and symptom correlations, is generated at the end of your monitoring period.
6. Peace of Mind for People Who Need More Than Alerts
If you’ve been diagnosed with AFib, experience irregular heartbeats, or are just trying to understand concerning symptoms, you deserve better than “maybe” alerts. You deserve clear answers.
The Frontier X Plus gives you confidence that every beat is being tracked, even while you are asleep. That kind of peace of mind simply doesn’t come from a smartwatch.
Read More- Frontier X Plus: The Best Ambulatory ECG Monitor for AFib Detection
The Frontier X Plus vs Smartwatch: At a Glance
| Feature | Frontier X Plus | Smartwatch |
| ECG Type | Continuous, clinical-grade | Intermittent, user-initiated |
| Accuracy | FDA-cleared, validated vs 12-lead ECG | Moderate, lifestyle-grade accuracy |
| Monitoring Duration | 24 hrs per charge, multi-day use | 30–60 sec spot checks |
| Data Access | Cloud dashboard for clinicians | Consumer-facing app only |
| Use Case | Medical-grade monitoring, rehab, IDTFs, extended Holter | Wellness, fitness tracking |
| Comfort | Chest strap, patchless | Wrist-based, less stable for ECG |
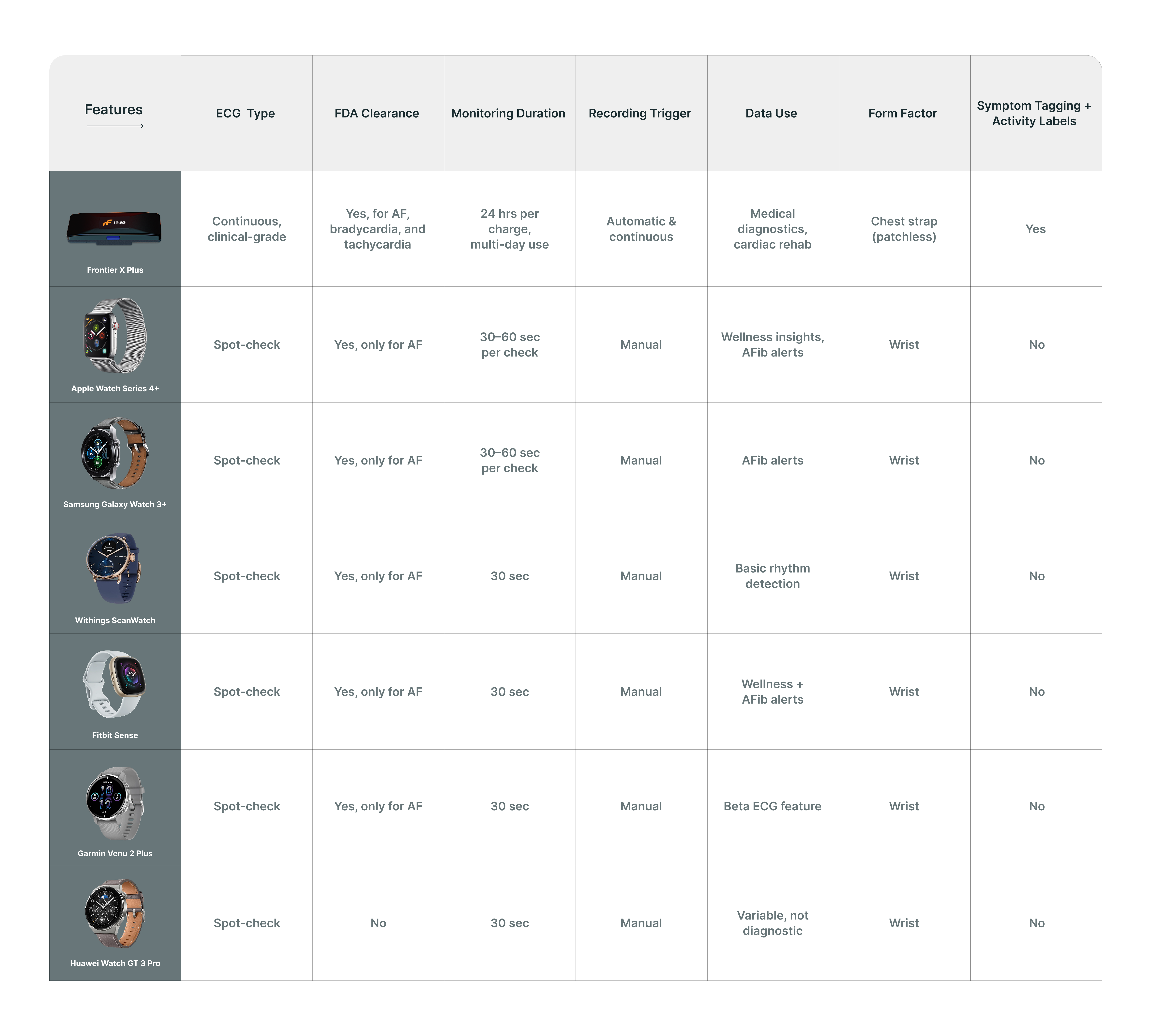
How the Frontier X Plus Compares to Popular Smartwatch Heart Monitors
Final Thoughts
Smartwatches are great wellness companions, but they aren’t made for clinical-level heart monitoring. If your health — or your doctor’s recommendations — demand more than a snapshot, it’s time to consider the Frontier X Plus.
You deserve clarity, accuracy, and continuous insight — and that’s exactly what this device delivers.
To learn more about how the Frontier X Plus supports remote cardiac monitoring, visit Fourth Frontier’s Professional Page.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of arrhythmia affecting millions globally, yet it often goes unnoticed. More than 59 million individuals lived with AF in 2019. Many people live with what’s called asymptomatic AF or silent AF, where irregular heart rhythms occur without any obvious symptoms. While the absence of symptoms might seem like a relief to you, if left unchecked, silent AF raises the risk of serious complications like stroke. That’s where the Frontier X Plus, a patchless continuous ECG monitoring device, comes to your rescue.
Moreover, after your cardiac procedure, monitoring for silent or asymptomatic AF becomes especially important. These irregular heart rhythms, which often occur without symptoms, can significantly increase the risk of stroke if left undetected. Continuous, clinical-grade ECG monitoring with devices like the Frontier X Plus ensures that these hidden episodes are caught early, enabling timely medical intervention during this critical recovery phase.
In this blog, you will explore how the Frontier X Plus enables you and your clinician to detect and manage silent AFs through continuous, real-time, remote heart monitoring — all while you go about your daily routine.
What Is Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation/Silent AF?
Asymptomatic AF is when you experience episodes of Atrial Fibrillation without feeling any noticeable symptoms. Unlike typical AF, which can cause palpitations, fatigue, or dizziness, asymptomatic AF may occur silently for months or even years. Yet, it poses the same elevated risks of blood clots, stroke, and heart failure.
According to studies, nearly 27% of AF cases are asymptomatic, and undetected AF is responsible for up to one-third of all strokes. That’s why routine ECG monitoring at home — with a clinically validated device like Frontier X Plus — is essential.
Why Traditional Monitoring Often Falls Short
Standard devices, such as Holter monitors and smartwatches, are not designed to detect intermittent or silent episodes. Holters usually record for only 24–48 hours, which may miss an AFib event entirely, and their bulky design with adhesive electrodes and wires often causes skin irritation and disrupts sleep. Smartwatches, while convenient, rely on short, 30 to 60-second user-initiated ECG recordings and frequently deliver inconclusive or inaccurate results due to poor signal quality or motion. Their wrist-based placement can also lead to signal interruptions during daily movement, reducing reliability for clinical use.
When you’re not feeling symptoms, you likely won’t think of initiating a recording, which is exactly why Frontier X Plus is different.
Read more: Frontier X Plus vs. Holter Monitor: The Future of AFib Detection at Home
The Frontier X Plus: Always-On ECG Monitoring at Home
The Frontier X Plus is an FDA 510(k)-cleared, chest-worn, patchless ECG monitor that captures your heart’s electrical activity continuously throughout the day — even when you’re not aware of anything unusual.
Key features include:
- Continuous ECG monitoring for up to 23 hours per hour of charge, as long as your clinician prescribes, serving as an extended Holter
- Real-time and retrospective ECG data review – Your heart data can be checked both as it’s happening and after the recording is done
- Secure cloud storage accessible by your clinician – Your heart recordings are safely stored online, so your doctor can review them anytime
- Symptom tagging and activity labeling for context – You can note how you’re feeling and what you’re doing during recordings, so your doctor gets the full picture
This makes it ideal for catching asymptomatic AF that may otherwise be missed by short-term or user-activated devices.
Monitoring That Blends Into Your Lifestyle
You don’t need to visit a clinic or stay wired to bulky equipment to take an ECG. With the Frontier X Plus, you simply wear a lightweight, patchless device on your chest using a soft strap. It syncs effortlessly to a companion mobile app, where your data is uploaded to a secure dashboard.
You can go about your routine — working, exercising, sleeping, driving, riding — while your device handles the heart hustle behind the scenes. If something concerning is detected, your physician can review the data and intervene early.
Clinically Actionable Data That Doctors Trust
The Frontier X Plus isn’t just a wellness gadget — it’s a prescription-based tool used in cardiac rehab, remote patient monitoring, and arrhythmia diagnostics. Its advanced algorithms detect:
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Bradycardia
- Tachycardia
- Normal sinus rhythm
At the end of your monitoring period, your doctor receives a detailed report outlining heart rate trends, rhythm breakdowns, and any arrhythmic episodes, giving them the insight they need to make informed treatment decisions.
Peace of Mind Without the Guesswork
Living with asymptomatic AF can feel like living in the dark. The Frontier X Plus shines a light on your heart’s rhythm — even when you don’t feel a thing. Whether you’re being screened for AF due to family history, managing an existing condition, or recovering from a cardiac procedure, this device offers the clarity and confidence you deserve.
Final Thoughts
If you’re at risk of silent arrhythmias like asymptomatic AF, don’t wait for symptoms to appear. With the Frontier X Plus, you get continuous, clinical-grade ECG monitoring — all from the comfort of your own place. Unlike smartwatches or Holters, the Frontier X Plus gives you and your care team the full picture, helping detect AF early and intervene sooner.
Your heart doesn’t sleep when you do — and for millions, that’s when the danger begins. Many individuals experience asymptomatic heart arrhythmias during sleep, including serious conditions like atrial fibrillation (AF), atrial flutter, SVT arrhythmia, and ventricular tachycardia, all without any noticeable symptoms. These silent heart irregularities may only be detected with extended monitoring, and if left unchecked, they can result in life-threatening outcomes such as stroke or sudden cardiac arrest.
Thanks to the evolution of electrocardiogram monitor technology, devices like the Frontier X Plus — a clinical-grade, chest-worn, ambulatory ECG monitor — now allow for continuous, at-home tracking of cardiac rhythms. Whether you’re sleeping or plain lying down after a long day at work, this compact, patchless ECG monitor delivers accurate, high-resolution data that helps identify hidden arrhythmias and supports timely intervention.
Why Nighttime Heart Arrhythmias Go Undetected
Some of the most dangerous heart arrhythmia types — like AFib with rapid ventricular response, ventricular fibrillation (v fib), and abnormal heart rhythms — occur intermittently and often during rest. Because symptoms don’t always appear, these episodes may go unnoticed until a serious event occurs.
Traditional tools like in-clinic ECGs or 24-hour Holter monitors often fall short, missing these nighttime episodes. And while some smartwatches are FDA-cleared for AFib detection, they only capture 30 to 60-second snapshots, which means they can easily miss intermittent or nighttime episodes. Plus, let’s be honest, you don’t want to wake up in the middle of the night just to press your finger on your smartwatch for a 30-second ECG. Smartwatches don’t offer the sustained signal quality needed to pick up brief but dangerous events like flutter in the heart
This is where the Frontier X Plus becomes invaluable — offering continuous recording for up to 24 hours per charge, quick syncing via a mobile app, and seamless remote monitoring for your physician to review without delay.
Read more: Frontier X Plus vs. Holter Monitor: The Future of AFib Detection at Home
How Continuous Home ECG Monitoring Changes the Game
The Frontier X Plus enables uninterrupted ECG monitoring at home, capturing data overnight with exceptional signal clarity. This wearable cardiovascular monitor tracks sinus rhythm, flags arrhythmia in the heart, and detects abnormalities like AF, tachycardia, and bradycardia— all without requiring you to press a button or initiate a reading.
Through its cloud-based platform, the Frontier X Plus allows your healthcare provider to access daily ECG files and identify concerning patterns early, enabling intervention before symptoms even arise.
Key Advantages of Using The Frontier X Plus for Nighttime ECG/EKG Monitoring
- Early Detection of Arrhythmias: Identify silent AF, bradycardia, and tachycardia
- Clinical-Grade Data Quality: Get EKG rhythms that match the fidelity of in-clinic systems.
- Superior Comfort & Compliance: The patchless, chest-worn design supports uninterrupted use through the night.
Unlike patch-based monitors or wrist-worn devices, the Frontier X Plus uses a soft, chest-strap design that’s both patchless and wire-free, making it significantly more comfortable for overnight wear. Its secure placement ensures stable contact throughout the night, resulting in high-quality, uninterrupted ECG recordings even as you move during sleep. Where adhesive patches can irritate the skin and smartwatches often lose signal or shift position, Frontier X Plus stays firmly in place, offering clinical-grade data without compromising your rest.
Who Can Benefit from Monitoring with the Frontier X Plus?
- Individuals with known or suspected cardiovascular arrhythmia or abnormal ECG history
- Patients recovering from procedures where monitoring Atrial Fibrillation is critical
- Those at risk for medical atrial fibrillation, or abnormal heart rhythm
- People with unexplained fatigue, sleep disturbances, or nighttime flutter sensations
Final Thoughts
Many irregular heart rhythms, including AFib, bradycardia, and tachycardia, occur at night without symptoms. The only way to catch them is through continuous, high-quality monitoring. With the Frontier X Plus, you get a reliable, wearable EKG / ECG machine that empowers you and your care team to track your heart arrhythmia risks while you sleep. From identifying AF, bradycardia, and tachycardia, this device ensures nothing goes unnoticed.
If you’re concerned about your AF heart rate, sinus rhythm, or overall cardiac stability, speak to your physician about using the Frontier X Plus. Then, you can take control of your heart’s health from the comfort of home.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common types of arrhythmias, affecting millions globally. It disrupts the heart’s normal rhythm and increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other complications. However, not all AF is the same. If you’ve been diagnosed — or are trying to understand your risk — it’s essential to know the difference between persistent and paroxysmal AFib
In this blog, we’ll explain the key differences, what symptoms to look out for, and how continuous ECG monitoring using tools like the Frontier X Plus can support management.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
AF is a type of atrial arrhythmia in which the upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly and out of sync with the lower chambers (the ventricles). This irregular rhythm can cause symptoms like palpitations, fatigue, chest discomfort, or shortness of breath, though many people remain asymptomatic, especially in the early stages.
Paroxysmal AF: Comes and Goes
Paroxysmal AFib refers to AFib episodes that begin suddenly and stop on their own, usually within 7 days (often within 24 hours). These episodes may occur sporadically and be triggered by stress, exercise, sleep apnea, or alcohol consumption. For some, they happen once a year; for others, several times a week.
- Symptoms: Palpitations, fluttering, lightheadedness, or fatigue, or sometimes no symptoms at all.
- Risks: Still carries a stroke risk; even asymptomatic episodes can be dangerous if left undetected.
- Challenge: Because it’s intermittent, paroxysmal AFib is harder to catch on a standard ECG.
Persistent AF: A Lasting Rhythm Problem
Persistent AF lasts longer than 7 days and usually requires medical intervention to stop, such as electrical cardioversion or medication. Over time, persistent AF can become harder to treat and may lead to structural changes in the heart.
- Symptoms: More likely to cause ongoing fatigue, shortness of breath, or reduced exercise tolerance.
- Risks: Higher risk of stroke, blood clots, and heart failure if unmanaged.
- Management: Often involves long-term rhythm or rate control medications, and possibly ablation.
Comparing Paroxysmal AFib vs. Persistent AFib
| Feature | Paroxysmal AFib | Persistent AFib |
| Duration | < 7 days (often self-terminates) | > 7 days (requires medical intervention) |
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual or worsening |
| Symptoms | Sporadic or absent | More consistent and noticeable |
| Stroke Risk | Yes | Yes |
| Treatment Need | May not require immediate treatment | Requires active management |
| Detection Difficulty | Harder to detect due to timing | More likely to show on a standard ECG |
The Role of Continuous ECG Monitoring
Because paroxysmal AF can be unpredictable and brief, traditional methods like an in-clinic ECG or a 24-hour Holter monitor often fall short. These tools may miss intermittent episodes, especially if they don’t occur during the monitoring window.
That’s where continuous ECG monitors come in.
Devices such as the Frontier X Plus are designed to provide extended, real-time heart rhythm monitoring in everyday settings. Worn comfortably on the chest, they continuously capture high-quality ECG data across activities like sleep, exercise, and rest, making it easier to catch elusive arrhythmias.
- The Frontier X Plus is a prescription-based medical device for clinical-grade monitoring and remote physician oversight.
Both devices support:
- Continuous ECG waveform recording
- Real-time AF pattern detection
- Symptom tagging and activity labeling
- Cloud-based data access for sharing with clinicians
By giving you a window into your heart’s behavior outside the clinic, these monitors improve the odds of detecting AF early, even in asymptomatic or paroxysmal cases.
Read more about the Frontier X Plus: The Best Ambulatory ECG Monitor for AFib Detection
Why Early Detection of AFib Matters
Both persistent and paroxysmal AFib increase the risk of stroke, and that risk remains even if your symptoms are mild or infrequent. Studies show that around one-third of those with AFib may not experience symptoms, highlighting the importance of vigilance.
By using a prescription-based continuous ECG monitor like the Frontier X Plus, you can:
- Catch silent or intermittent episodes early
- Start anticoagulation or other therapy sooner if needed
- Monitor the success of treatments like ablation or medication
- Make informed lifestyle changes to reduce recurrence
Final Thoughts
Whether AF shows up occasionally or becomes a constant presence, understanding your rhythm patterns is essential. Early detection and long-term monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of complications like stroke and heart failure.
With wearable continuous ECG monitors like the Frontier X Plus, you no longer need to wait for symptoms to appear in a doctor’s office. Instead, you can continuously monitor your heart — and share accurate, actionable data with your healthcare provider — from the comfort of home.
If you’ve ever felt a flutter, skipped beat, or unexplained fatigue — even just once — it may be time to explore continuous ECG monitoring. A few extra beats of data could make all the difference.
Stay informed. Monitor smarter. And take charge of your heart health.
Heart health is more than just your pulse. With advancements in wearable technology and remote monitoring, we’re gaining deeper insights into not only how fast your heart beats but how it beats — and how consistently. Two commonly referenced yet often misunderstood concepts in this context are Heart Rate Variability (HRV) and Heart Rhythm Irregularities.
While both involve how your heart behaves between beats, they indicate very different things. Understanding the difference is crucial, especially for those tracking their cardiovascular health, managing AF (Atrial Fibrillation), or trying to distinguish between a healthy sinus rhythm and a potentially dangerous arrhythmia.
Here we’ll break down these concepts, explain how they relate to arrhythmias, and show how continuous ECG monitoring can be an effective way to uncover hidden risks.
What Is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
HRV refers to the slight variations in time between each heartbeat. Heart rate variability (HRV), the change in the time intervals between adjacent heartbeats. The normal resting sinus rhythm of the heart is highly irregular during steady-state conditions rather than being monotonously regular, which was the widespread notion for many years. A healthy heart is not a metronome.
This is where HRV can feel counterintuitive. Most people assume “irregular” equals “bad.” But in the context of HRV, more variability usually indicates better adaptability.
Here’s why: your heart is under constant control of the autonomic nervous system, which balances sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) influences. A high HRV means your body is flexibly switching between these states, allowing you to respond to stress, exercise, or recovery more effectively. Low HRV means your system is stuck and less responsive to change.
Typical HRV values
| HRV Level | Approx. Range (ms) | Interpretation |
| High HRV | > 100 ms | Generally reflects strong autonomic (ANS) adaptability |
| Moderate HRV | 50–100 ms | Suggestive of borderline or average vagal function |
| Low HRV | < 50 ms | Associated with higher health risks in population studies |
Important Caveat:
While these numeric thresholds are commonly used — and can correspond roughly to clinical insights — the PeerJ review emphasizes that
- No universally accepted HRV thresholds exist due to protocol differences peerj.com
- Thresholds must be interpreted in context: age, presence of disease, measurement conditions, and comparison to individual baseline rather than population average
What Can Affect HRV?
- Positive influences: Meditation, good sleep, aerobic exercise, balanced nutrition
- Negative influences: Stress, dehydration, alcohol, illness, overtraining
While HRV is not a direct marker of heart rhythm abnormalities, consistently low HRV over time can indicate elevated risk of cardiovascular events, especially in individuals with predisposing conditions.
Read More: What Are The Factors That Affect HRV?
What Are Heart Rhythm Irregularities?
Now let’s shift to heart rhythm irregularities, or arrhythmias. These refer to actual disturbances in the electrical signals that coordinate your heartbeat. While HRV looks at normal fluctuations, arrhythmias involve abnormal patterns in your heart’s rhythm or rate.
Common forms of heart rhythm irregularities include:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AF): A rapid, irregular heartbeat originating in the upper chambers (atria)
- Atrial Flutter: A more organized but still abnormal rhythm
- Bradycardia: Slower-than-normal heart rate
- Tachycardia: Faster-than-normal heart rate
- Premature beats: Extra heartbeats that can feel like palpitations or skipped beats
Unlike HRV, these are not subtle, beneficial changes — they’re red flags that something may be wrong with the heart’s electrical system.
HRV vs. AF and Other Rhythm Irregularities: Key Differences
| Aspect | Heart Rate Variability (HRV) | Heart Rhythm Irregularities (AF, etc.) |
| What it measures | Natural variability in time between beats | Abnormal or chaotic electrical activity in the heart |
| Normal or abnormal? | Usually normal and healthy | Usually abnormal and potentially dangerous |
| Role in diagnosis | An indicator of stress, recovery, and the nervous system | Diagnostic sign of cardiovascular arrhythmia |
| Requires medical attention? | Not unless drastically low | Yes, often requires diagnosis and treatment |
| Detectable by wearables? | Yes | Yes (with clinical-grade ECG monitoring) |
Why the Confusion Between the Two?
The rise of smartwatches and fitness trackers has popularized HRV among health-conscious users. However, these devices often do not distinguish clearly between high HRV and abnormal rhythm. A user might see “variability” on their tracker and assume it’s a problem, or worse, fail to notice when an AF heart rhythm is developing silently in the background.
That’s why medical-grade wearables with ECG capability are vital. These tools help distinguish healthy HRV patterns from dangerous heartbeat arrhythmias — something general consumer devices often cannot do with accuracy.
Remote Monitoring: Your Ally in Early Detection
Remote monitoring through continuous ECG technology has revolutionized how we manage cardiovascular health. For conditions like paroxysmal AF, which can come and go unpredictably, or for detecting subtle heart irregularities that don’t show up in a quick clinic ECG, long-term data is everything.
Wearable ECG monitors like the Frontier X2 (wellness-classified) and the Frontier X Plus (prescription-only) offer continuous tracking that captures real-time heart rhythms throughout your daily life — during sleep, exercise, stress, or relaxation.
The continuous ECG technology can help you in:
- Differentiate sinus rhythm from AF
- Detect sudden arrhythmias like tachycardia or bradycardia
- Enable symptom tagging to correlate how you feel with your rhythm
- Share data securely with physicians for early diagnosis
Why This Matters: Stroke, Heart Failure, and the Silent Threat
One of the most dangerous aspects of AF and other arrhythmias is that they can be asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. Yet they carry serious risks — especially stroke, which can occur even in those who feel perfectly fine.
Studies suggest that up to 30% of AF cases are silent, and undiagnosed AF may cause one-third of all strokes. The earlier it’s caught, the better your chances of avoiding life-altering complications.
That’s why remote monitoring with devices capable of real-time ECG is no longer just a convenience — it’s a proactive, often life-saving strategy.
Takeaway: Know the Difference. Act Early.
HRV and heart rhythm irregularities may both involve how your heart beats, but that’s where the similarity ends.
- HRV is a sign of flexibility, health, and recovery.
- AF and arrhythmias are signs of instability and may require urgent care.
By using advanced, continuous monitoring tools — and understanding what your data actually means — you can separate signal from noise, and take control of your heart health with clarity and confidence.
If you’ve ever experienced fatigue, a fluttering sensation, skipped beats, or even just want to better understand your cardiovascular system, don’t settle for guesswork. Look for wearables that monitor both HRV and ECG to give you the full picture.
Because when it comes to your heart, every beat counts.
If you’ve ever experienced unexplained palpitations, dizziness, or chest discomfort, your doctor may have recommended a Holter monitor. While this traditional device has helped many detect heart rhythm issues over the years, the future of cardiac care is shifting – and it’s moving right into your home. With the rise in wearable ECG monitoring devices like the Frontier X Plus, you now have the opportunity to take control of your heart health like never before. Here, we’ll explore how Frontier X Plus compares to Holter monitors and why ECG monitoring at home is quickly becoming the new standard in cardiac care.
A Quick Look at Holter Monitors
Holter monitors are portable ECG devices that continuously record your heart’s electrical activity over a period of 24 to 48 hours. Worn around your neck or waist with electrodes stuck to your chest, Holter monitors collect data for your physician to analyze after the device is returned.
They remain widely used — in fact, the U.S. cardiac Holter monitor market was valued at approximately USD 164.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 229.1 million by 2033, according to IMARC Group. This steady growth reflects ongoing demand, but also highlights opportunities for innovation in ambulatory ECG monitoring.
While Holters have been essential in diagnosing arrhythmias and silent heart conditions, they have limitations, especially when it comes to comfort, real-time feedback, and prolonged use.
Meet The Frontier X Plus — The Modern Alternative
Frontier X Plus is a chest-worn, FDA-510(k) cleared, prescription-based ECG monitor designed for remote heart monitoring in real-world environments. Whether you’re at rest, walking, working, or even exercising, it continuously tracks your heart rhythms throughout the day. With a quick recharge time of about an hour, you can wear the device day after day, for as long as your doctor prescribes, syncing your ECG data to the cloud each night. This enables seamless, uninterrupted multi-day monitoring – ideal for capturing intermittent symptoms and maintaining a complete view of your heart health over time.
Unlike Holters, which are typically worn once and reviewed later, Frontier X Plus allows your clinician to monitor your heart in the moment and take timely action when needed. It’s lightweight, wireless, and comfortable, making it perfect for ECG monitoring at home.
Real-Time Insight vs. Retrospective Review
With a Holter monitor, you wear the device for a day or two, return it, and then wait for your doctor to analyze the data. If your abnormal heartbeat didn’t occur during that window, it might be missed entirely.
With Frontier X Plus, you’re not stuck waiting. The device syncs ECG data through a companion app and uploads it to a secure clinician dashboard. If you’re enrolled in a monitoring program, your data is reviewed daily. Alerts are triggered if you haven’t synced in over 36 hours or if data quality is low, ensuring continuous, actionable monitoring.
This is one step towards innovation and a giant leap forward in care. If you suffer from intermittent Atrial Fibrillation, Tachycardia, and Bradycardia, real-time detection can be the difference between proactive care and a missed detection.
Comfort and Ease of Use
Holter monitors require multiple sticky electrodes, wires, and sometimes a belt or pouch. You may be told not to shower, and movement can be limited. If you’ve worn one, you know it’s not ideal for long-term monitoring or active lifestyles.
Frontier X Plus? It’s built for modern living. You strap it onto your chest like a fitness tracker. There are no wires. No gels. No bulky external units. You charge it like your phone, sync it through your app, and go about your day.
You can even livestream your ECG during setup to make sure you’re getting a clean signal — something that Holter monitors can’t do.
Designed for the Way You Live
Think about it: would you rather strap on a device that restricts your movement for 24 hours, or wear something designed to be barely noticeable as you go about your daily routine?
Frontier X Plus is built with home heart monitoring in mind. It’s comfortable under clothing and doesn’t interfere with sleep or exercise. Whether you’re managing a known heart condition or just monitoring your heart’s behavior during endurance training, this device fits into your lifestyle seamlessly.
Clinical Accuracy You Can Trust
You might be wondering, “Is it as accurate as a Holter?” The answer is yes — and in many ways, even better.
Frontier X Plus detects various cardiac rhythms, including:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Tachycardia (fast heart rate)
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
In clinical validation studies, the device demonstrated sensitivity and specificity comparable to traditional 12-lead ECGs.
READ MORE ON THE FRONTIER X PLUS: Frontier X Plus: The Best Ambulatory ECG Monitor for AFib Detection
End-of-Study Reports for Your Doctor
Once your monitoring period ends (typically 2 days), a certified cardiac physiologist or your prescribing clinician generates a full report from your ECG data. This includes breakdowns of heart rhythms, flags for abnormalities, and trend analysis.
You or your doctor receives this report within 24 hours, either via secure email or directly uploaded into your healthcare provider’s EMR system (e.g., EPIC).
This speed and depth of feedback simply isn’t available with legacy Holter workflows.
When Should You Ask About Frontier X Plus?
If you’re experiencing symptoms like:
- Fluttering or skipped beats
- Unexplained fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Fainting spells or dizziness
- Irregular pulse or chest discomfort
…talk to your physician about ambulatory ECG monitoring. Ask whether a remote heart monitoring option like Frontier X Plus might be more appropriate than a Holter monitor.
It’s especially useful if your symptoms are intermittent or occur during specific activities like sleep or exercise. With a real-time system, your clinician won’t have to guess what’s happening when you’re not in the clinic.
The Future Is on Your Chest
Holter monitors had their moment. They’re still useful in many settings. But for today’s patients — whether you’re active, managing a heart condition, or simply looking for peace of mind — Frontier X Plus represents a smarter, more responsive path forward.
The ability to monitor your heart from home, share data instantly with your doctor, and wear a device that’s truly built for your lifestyle is what makes this wearable a leader in its category.
Ask your physician about Frontier X Plus today — because the future of heart monitoring is here, and it’s wearable.