Home » Heart Health » arrhythmia » Ventricular Arrhythmias: Everything You Need to Know
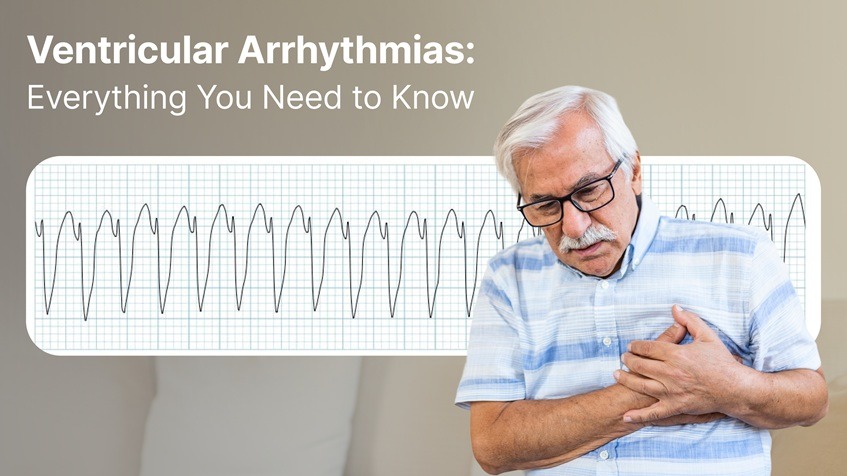
When your heart beats too fast, too slow, or erratically, it can feel like something is off. If you’ve ever thought, “My heart feels like it is racing,” or experienced a sudden, rapid heartbeat out of nowhere, you’re not alone. For many people, these sensations may be signs of ventricular arrhythmias, a group of heart rhythm disturbances originating in the lower chambers of the heart – the ventricles.
These conditions range from premature beats to potentially life-threatening rhythms like ventricular tachycardia (V Tach) and ventricular fibrillation (V Fib). Understanding these irregular rhythms is critical because early detection and management can prevent severe complications, including sudden cardiac arrest.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about ventricular arrhythmias, from their causes to treatment options and the latest in monitoring technology.
What Are Ventricular Arrhythmias?
Ventricular arrhythmias refer to abnormal electrical signals in the heart’s ventricles – the two lower chambers responsible for pumping blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. These disturbances can lead to inefficient blood flow, resulting in symptoms like dizziness, palpitations, fainting, or even cardiac arrest.
Types of Ventricular Arrhythmias
Understanding ventricular rhythm types is essential because not all ventricular arrhythmias are equally dangerous. Here’s a breakdown:
- Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): They are early, extra heartbeats that start in the heart’s lower chambers (the ventricles), disrupting the heart’s normal rhythm for a moment
- Ventricular Tachycardia (V Tach): It is a rapid heart rhythm – more than 100 beats per minute – that begins in the lower chambers of the heart. This condition prevents the heart’s chambers from filling adequately with blood, reducing the amount that is pumped to the body.
- Ventricular Fibrillation (V Fib): is a life-threatening heart rhythm where the ventricles quiver or fibrillate chaotically instead of expanding and contracting effectively. This prevents the heart from pumping out blood. Within seconds, blood flow to the brain stops, causing loss of consciousness. Without immediate treatment, usually with defibrillation, V-Fib leads to sudden cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of Ventricular Arrhythmias
Many patients describe ventricular arrhythmias as feeling like a “sudden rapid heartbeat” or an erratic heart rhythm. Other common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
- Shortness of breath
- Palpitations or fluttering sensations in the chest
- Fatigue or weakness
These symptoms often trigger a search for a heart monitor to check for arrhythmia, which helps confirm the diagnosis.
What Causes Ventricular Arrhythmias?
Several factors can lead to abnormal ventricular activity:
- Coronary artery disease
- Cardiomyopathy (weak or enlarged heart muscle)
- Heart failure
- Previous heart attack (myocardial infarction)
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Genetic conditions like arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
- Medications or stimulant abuse
- Structural heart changes
In some cases, the cause remains unknown – a condition called idiopathic ventricular arrhythmia.
Why Are Ventricular Arrhythmias Dangerous?
Ventricular arrhythmias are a leading reason for cardiac arrest, especially when they progress to V Fib. The rapid and disorganized contractions prevent the heart from pumping blood, cutting off oxygen to the brain (cardiac arrest) and other vital organs. Without immediate intervention, this can lead to death within minutes.
Even if life-threatening events are avoided, heart rhythm problems like sustained V Tach can weaken the heart over time, increasing the risk of heart failure and other complications.
Diagnosing Ventricular Arrhythmias
If you suspect a ventricular rhythm issue, healthcare providers will often recommend a combination of tests:
Common Diagnostic Tools:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG):
The first-line test to detect arrhythmias in real-time. - Medical Holter Monitor:
A portable device worn for 24 to 48 hours to catch intermittent heart rhythm disturbances. - Event Monitors & Loop Recorders:
Long-term devices for patients with infrequent but concerning symptoms. - Echocardiogram & Cardiac MRI:
Used to check for structural abnormalities contributing to arrhythmias. - Electrophysiology Study (EPS):
A specialized test to map the heart’s electrical pathways and identify the source of abnormal signals. - Exercise stress test : if symptoms occur under exertion, exercise stress tests will often be ordered to look for these conditions
Treatment Options for Ventricular Arrhythmias
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the arrhythmia, symptoms, and underlying causes.
Medications
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs:
These are prescribed to stabilize ventricular activity. Common ventricular tachycardia treatment drugs include amiodarone and lidocaine. - Beta-Blockers:
Reduce the risk of dangerous arrhythmias, especially in patients with heart disease. - Calcium Channel Blockers:
Sometimes used in specific arrhythmia cases.
Catheter Ablation
For frequent or life-threatening V Tach, doctors may recommend ventricular tachycardia ablation. This minimally invasive procedure targets and destroys the tissue responsible for the abnormal electrical signals.
Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Success Rate:
Recent studies show that catheter ablation has a success rate of around 70-80% in controlling V Tach, especially in patients with structurally abnormal hearts.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
An ICD is a device implanted under the skin that detects abnormal ventricular rhythms and delivers shocks to restore normal rhythm. ICDs are life-saving for people at high risk of sudden cardiac death.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing ventricular arrhythmias. Unlike standard ECGs that capture a snapshot in time, ECG monitors that record continuously over many hours or days, provide high-fidelity ECG to doctors, thereby enabling them to detect:
- PVC patterns
- V Tach episodes
- Irregular heartbeats that are symptomless
These devices also empower patients by providing near-real-time insights into their heart health, ensuring that erratic heart rhythms don’t go unnoticed.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While some ventricular arrhythmias are unavoidable due to genetics or prior heart damage, you can take steps to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a heart-healthy lifestyle
- Treat high blood pressure and cholesterol
- Avoid stimulant drugs and excessive caffeine
- Manage sleep apnea
- Follow your doctor’s advice if you have known heart diseases
- Follow an appropriate exercise plan
When to See a Specialist
If you’ve experienced symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or episodes where my heart feels like it is racing, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. A ventricular tachycardia specialist or electrophysiologist can help determine the cause and recommend the best treatment path.
Final Thoughts
Ventricular arrhythmias are more than just uncomfortable sensations – they can be serious indicators of underlying heart rhythm problems. From premature ventricular complexes to life-threatening V Fib, these conditions require prompt attention, proper diagnosis, and often long-term management.
With advancements in irregular heartbeat monitor technology, patients and physicians now have better tools to detect, monitor, and treat these rhythms early – before they lead to serious complications.
FAQs: Ventricular Arrhythmias
Q: What’s the difference between V Tach and V Fib?
A: In V Tach, ventricles contract in a coordinated manner but do so very rapidly. In V Fib, ventricles contract in an uncoordinated manner.
Q: What is the success rate of V Tach ablation?
A: Ventricular tachycardia ablation has a success rate of 70-80% for reducing arrhythmia episodes.
Q: How do I know if my rapid heartbeat is dangerous?
A: Persistent sudden rapid heartbeat with symptoms like fainting or chest pain requires immediate medical attention.
If you’re concerned about ventricular arrhythmias, talk to your healthcare provider about continuous monitoring options to keep your heart health a priority.
Related Posts
You might also like
-

Featured Articles
- Why Body Shock Monitoring Is Crucial for Every AthleteJanuary 7, 2026
- Frontier X2 vs Smart Ring: Which Wellness Tracker Knows...November 28, 2025
- The ROI of Investing in Frontier X2 With HSA/FSANovember 21, 2025
- Why Body Shock Monitoring Is Crucial for Every Athlete
CATEGORIES
POPULAR POSTS
-
Follow us on
Top Searches for Heart Health
Top Searches for AFib
Frontier X2 Smart Heart Devices
Top Searches for Heart Rate
VISUAL STORIES