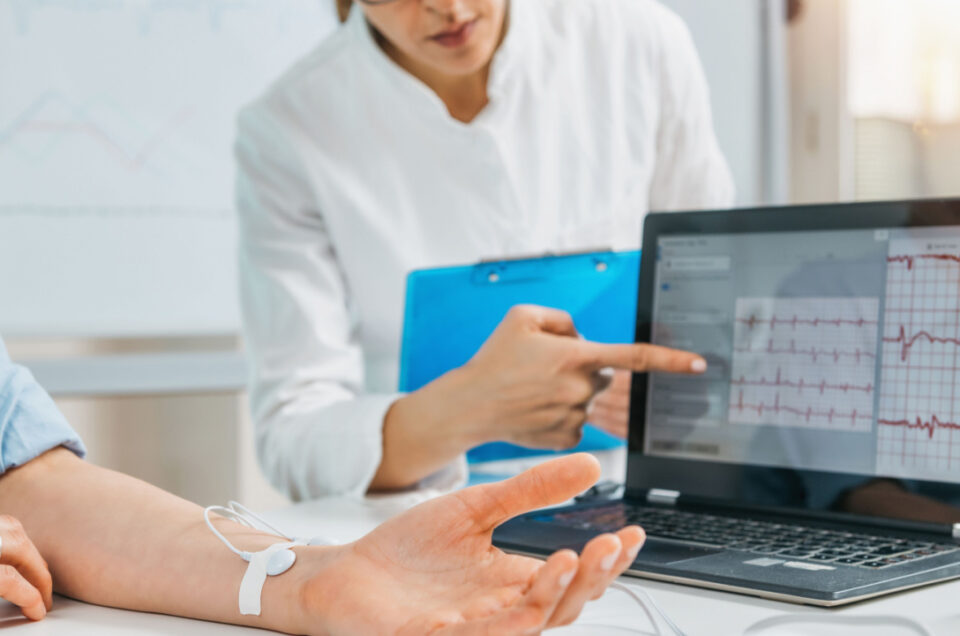
Heart rate variability (HRV) is an important aspect of athletic performance, as it can give valuable insights into an athlete’s physical and mental well-being. HRV measures the variation in time between consecutive heartbeats and is considered a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness, stress levels, and recovery. In the athletic world, monitoring HRV can help athletes optimize their training, avoid overtraining and injury, and improve overall performance. Here, we aim to explore the significance of HRV monitoring in athletes and how it can help them achieve their athletic goals.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
HRV is a measure of the variation in time between consecutive heartbeats. It reflects the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which control the body’s fight-or-flight response and rest-and-digest response, respectively. A high HRV indicates a healthy balance between these two systems and a low heart rate variability can indicate stress, fatigue, or overtraining.
Why is HRV important for Athletes?
Monitoring HRV can provide athletes with valuable insights into their physical and mental well-being. It can help them to optimize their training, prevent injury, and improve performance.
-
Optimizing Training
Athletes are constantly looking for ways to improve their performance and reach their goals. One of the most important factors in achieving these goals is effective training. HRV can help athletes to optimize their training by providing insight into how their body is responding to different types of training.
HRV can be used to determine the optimal intensity and volume of training. This is important because overtraining can lead to injury and reduce performance. By monitoring HRV, athletes can see how their body is responding to different types of training, such as high-intensity interval training or endurance training, and adjust their training accordingly. This can help to prevent overtraining (ref. link) and ensure optimal performance.
-
Preventing Injury
Injuries can have a significant impact on an athlete’s performance and career. HRV can help athletes to avoid injury by providing early warning signs of fatigue or overtraining. A sudden drop in HRV can indicate that the body is under too much stress and needs rest. By monitoring HRV, athletes can take steps to prevent injury before it occurs.
-
Improving Performance
HRV can be used to improve performance by identifying the best times to train. For example, if an athlete’s HRV is high, it may indicate that they are well-rested and ready to train. On the other hand, if an athlete’s HRV is low, it may indicate that they need more rest before training. By monitoring HRV, athletes can ensure that they are training at the right times to optimize performance.
-
Improving Recovery and Adaptation
Recovery is an essential part of the training process. It is during recovery that the body adapts to the demands of training and improves performance. HRV can be used to monitor the body’s ability to recover from training and injury.
HRV is becoming one of the most popular monitoring tools for training and recovery (ref. link) in sport sciences By monitoring HRV, athletes can identify the most effective recovery methods and track the body’s adaptation to training and stress. HRV is becoming one of the most popular monitoring tools for training and recovery in sport sciences.
-
Understanding the effects of stress and lifestyle on HRV
Stress and lifestyle can have a significant impact on an athlete’s performance and overall well-being. HRV can be used to identify the impact of stress (ref. link)and lifestyle on an athlete’s body. By monitoring HRV, athletes can implement strategies to maintain HRV and overall well-being.
-
Monitoring the overall state of mind and physical well-being
Mental and physical well-being is crucial for athletes to perform at their best. HRV can be used to understand the impact of physical and mental stress on an athlete’s body. By monitoring HRV, athletes can identify the signs of burnout, depression, and other mental health issues. By improving overall well-being, athletes can perform at their best.
Factors Affecting HRV :
-
Stress levels
Stress has a significant impact on HRV, and high levels of stress can reduce HRV and lead to overtraining and injury. Monitoring HRV can help athletes and coaches understand the impact of stress on an athlete’s physical and mental well-being and make necessary adjustments to training programs to avoid overtraining.
-
Sleep quality
Sleep is critical for athletic performance and recovery, and poor sleep quality can negatively impact HRV. Monitoring HRV can help athletes and coaches understand the impact of sleep quality on an athlete’s performance and make necessary adjustments to improve sleep quality and optimize performance.
-
Nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in athletic performance and recovery, and poor nutrition can negatively impact HRV. Monitoring HRV can help athletes and coaches understand the impact of nutrition on an athlete’s performance and make necessary adjustments to improve nutrition and optimize performance.
-
Age and fitness level
HRV can be affected by an individual’s age and fitness level, and it is essential to monitor HRV regularly to ensure that the training program is appropriate for the individual’s current state.
How to Monitor HRV in Athletes?
Methods for Measuring HRV are :
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This is the most accurate method of measuring HRV, but it also requires expensive equipment and trained personnel to interpret the results.
Chest-strap heart monitor: These are the easiest and most convenient methods for measuring HRV with comparable accuracy and precision, but they must be paired with a fitness app for data analysis.
Smartphone apps: There are also several smartphone apps that can measure HRV using the camera and microphone on the phone. These apps may not be as accurate as ECG or heart rate monitors, but they are convenient and accessible to most people.
Heart rate variability is an important tool that can help athletes monitor their physical and mental well-being, optimize training, and prevent injury. By monitoring HRV, athletes can gain valuable insights into how their body is responding to different types of training and adjust their training accordingly. There are several methods for measuring HRV, including ECG, heart rate monitors, and smartphone apps. By understanding the importance of HRV and how to measure it, athletes can take steps to improve performance and prevent injury.
Frequently Asked Questions :
1. Why is monitoring HRV important in athletes?
HRV can be used as an objective marker of fatigue and recovery, helping to guide training intensity and avoid overtraining. It can also be used to identify potential injury risks and predict athletic performance.
2. How is HRV measured?
HRV can be measured using a heart rate monitor or other wearable device that tracks heart rate, such as a fitness tracker or smartwatch.
3. What does a low HRV score indicate in athletes?
A low heart rate variability score can indicate that an athlete is fatigued or in a state of stress, which may increase the risk of injury or negatively impact performance.
4. What steps can athletes take to improve their HRV scores?
Athletes can improve their HRV scores by incorporating adequate rest and recovery, reducing stress, and engaging in physical activity and healthy habits.
5. Can HRV be used to prevent injury in athletes?
Yes, HRV can be used to identify potential injury risks and allow athletes to take preventative measures to reduce the risk of injury.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
AFib Prevention | AFib Management With Medication | Covid Antibodies | Long Covid and Heart Attack | Meditation and Heart Health | Vitamin D For Heart Health | High Cholestrol and Heart Health | Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acid | Dietary Changes for Atrial Fibrillation | Heart Rate Variability and Sleep
Frontier X2:
Heart Rate Monitor USA | ECG Monitors in India | ECG Heart Monitor UK
Stress is an inevitable part of life, but when left unmanaged, it can take a toll on our physical and mental health. One of the most important areas that stress can affect is our heart health. Chronic stress can lead to a variety of heart problems, including high blood pressure, heart attacks, and stroke. However, by managing stress effectively, we can protect our heart and overall well-being. We will explore the link between stress and heart health, and provide practical tips and strategies for managing stress and promoting good heart health.
Stress Management via Meditation
Meditation is a practice that helps to reduce stress by promoting relaxation and calming the mind. As such, a growing body of research has shown that regular meditation practice can have a positive impact on heart health. It works by training the mind to focus on the present moment and let go of worrying thoughts and stressful emotions.
When we meditate, we focus our attention on something specific, such as our breath, a word, a phrase, or a sound. This helps to quiet the mind and reduce the constant chatter of negative thoughts that can lead to stress. By focusing the mind in this manner, we become more aware of our thoughts and emotions, and can learn to recognize when we are becoming stressed.
Additionally, meditation can also help with stress by changing the way we react to stress. Regular meditation practice can help to change the way the brain processes information and emotions, and can alter the activity in certain brain regions associated with stress. This can lead to a reduction in the perception of stress and an increase in emotional regulation.
Meditation also helps to reduce stress by slowing down the physiological response to stress. Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension. When we meditate, we activate the relaxation response, which counteracts the physiological effects of stress. This can help to lower blood pressure, slow the heart rate, and relax the muscles.
Another significant physiological response to stress has to do with the metric labelled ‘Heart Rate Variability’.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between successive heartbeats. It is typically measured in milliseconds and is used to assess the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for activating the body’s fight-or-flight response, which increases heart rate and blood pressure. The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, activates the body’s rest-and-digest response, which slows down the heart rate and lowers blood pressure.
When the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are in balance, the heart rate varies naturally and regularly, resulting in a higher HRV. When the sympathetic nervous system is dominant, the heart rate becomes less variable, resulting in a lower HRV.
HRV is considered a marker of the adaptability of the autonomic nervous system and is commonly used as an indicator of stress and relaxation. In general, higher HRV is associated with greater relaxation and lower HRV is associated with higher stress. It is also used to evaluate the overall health of the cardiovascular system and to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Can Heart Rate Variability be used to Assess Meditation Quality?
In short, yes.
This should be relatively straightforward given the association of HRV with levels of stress in the body. One of the main purposes of meditation is to relax and calm a person down, and if HRV is a measure of how relaxed or calm a person is, measuring it before, during, and after a session of meditation will tell you exactly how the act impacted your physiological markers for stress.
According to Harvard Health Publishing (ref. link), many studies have shown that regular meditation practice is associated with increased HRV. In fact, one study from 2013 found that even people who did only 5 minutes of mediation per day for 10 days showed better HRV as compared to control groups. Another study found that after eight weeks of mindfulness meditation, participants had a significant increase in HRV compared to a control group.
It’s worth noting that HRV is just one metric, and it should not be used alone to assess the quality of meditation. Other factors such as self-reported stress, emotional states, and cognitive functioning, should also be considered.
How should I record my Heart Rate Variability?
To get the most accurate insight regarding the impact of your mediation, you would need to use a smart heart monitor that can continuously record your Heart Rate Variability. The Frontier X2 is a revolutionary device that gives you access to not only your Heart Rate Variability, but also your Breathing Rate, Strain, Heart Rate, Training Load, Cadence, Distance Travelled, and Pace.
Additionally, the Frontier X app will soon allow you to choose ‘Meditation’ as an activity to record. Choosing this option will give you the ability to personalize your meditation to best fit your needs, before beginning the meditation and recording your heart health data as you calm your mind and body.
Managing stress is becoming one of the most important ways to take care of your physical health, so ensure you are dealing with it as best you can by paying attention to your Heart Rate Variability data as provided by your Frontier X2.
Frequently Asked Questions :
Q: What is heart rate variability and how does it relate to meditation?
A: Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between heartbeats. It is believed that a high HRV is associated with good cardiovascular health and increased resilience to stress. Research has suggested that meditation can increase heart rate variability, by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
Q: How do I measure my heart rate variability?
A: There are a few ways to measure heart rate variability, including using a heart rate monitor or a smartwatch with HRV tracking features, or an electrocardiogram (ECG) machine.
Q: How long does it take to see the benefits of meditation on heart rate variability?
A: The effects of meditation on HRV can vary depending on the individual and the frequency and duration of the practice. Some studies have shown that regular meditation practice can lead to increased HRV within just a few weeks.
Q: Are there any specific types of meditation that are more effective for increasing heart rate variability?
A: There is some evidence that certain types of meditation, such as mindfulness and transcendental meditation, may be more effective for increasing HRV than others.
Q: Can meditation be used to treat heart conditions or other medical issues?
A: While meditation has been shown to have beneficial effects on HRV and other health markers, it should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. Please consult your doctor before using meditation as a treatment for any medical condition.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore :
Heart Rate Variability Training | Stress Relief Exercises | Antioxidants and Heart Health | Mediterranean Diet Benefits | Heart Arrhythmia Symptoms | Yoga For Heart Health | Ventricular Tachycardia Symptoms | Low Heart Rate Variability | Heart Rate Monitor Device
Frontier X2 :
Wearable Heart Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Heart Monitor in UK
If you suffer from atrial fibrillation (AFib), you know how disruptive and uncomfortable an episode can be. Luckily, there are some steps that can help stop an AFib episode in its tracks. First and foremost, it’s important to stay calm during a flare-up of symptoms. Stress or anxiety can actually make your heart rate increase further, making the episode worse than it needs to be. Take a few deep breaths and focus on relaxing your body as much as possible while waiting for medical attention if necessary.
AFib and Stress: What Is The Connection?
Intense emotions like stress and anger can affect heart rhythm. Incorporating stress management strategies, like deep breathing, relaxation, and yoga, can minimize the chance of an AFib episode. A 2015 Journal of Arrhythmia study (Ref. Link) showed that AFib patients who did yoga twice a week for 3 months saw significant decreases in blood pressure and heart rate.
AFib Medication: What Are The Medicines To Be Kept Handy
Antiarrhythmic medications like amiodarone or flecainide may help slow down the heart rate back into normal rhythm again without needing to go to the hospital right away; however this should only be done with supervision from a doctor who is familiar with treating arrhythmias like AFib episodes specifically for you since these drugs have potential side effects when used incorrectly or too often over time.
Additionally, electrical cardioversion – which involves shocking the chest area with electricity – has been known to work quickly in stopping episodes of arrhythmia including AFib but requires more intensive medical care either at home or within 24 hours after administration so please seek out professional advice before trying any new treatment methods yourself.
AFib and Healthy Lifestyle: Why It Matters
Finally remember that lifestyle changes such as reducing alcohol consumption/smoking cessation along with regular exercise have all been proven helpful in managing chronic conditions like Atrial Fibrillation. However, when you are in the middle of an AFib attack, use any of these ways to stop an episode.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can lead to palpitations. Avoid alcohol, caffeine-rich drinks, and soft drinks with phosphorus that depletes magnesium. Drink a glass of water.
- Consume potassium: AFib can result from a low potassium diet due to high salt intake. Eat a banana or drink low-sodium V8, tomato, prune, or orange juice. Avoid high-salt juices. Use potassium supplements but avoid calcium-containing ones.
- Boost magnesium: A normal heartbeat requires magnesium. Eat pumpkin seeds or other magnesium-rich foods (brazil nuts, almonds, cashews, pine nuts, etc.).
- Take potassium or magnesium supplements: Take potassium gluconate powder or magnesium supplements without calcium for relief during an episode.
Valsalva Maneuver For AFib
The Valsalva maneuver is a technique of blowing air to pop the ears and stimulate the vagus nerve to regulate heart rate in case of fast beating during AFib. To perform this, close your mouth and hold your nose, then try to exhale the air to equalize pressure.
Deep breathing for AFib
Deep, mindful breathing is an effective way to slow heart rate during an AFib episode. Find a quiet place, sit down, close your eyes, and focus on inhaling and exhaling slowly. Pay attention to the movement of your diaphragm during breathing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
A: Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related problems.
Q: What are the symptoms of AFib?
A: Symptoms of AFib include palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, and lightheadedness.
Q: What causes AFib?
A: Causes of AFib can include high blood pressure, heart disease, alcohol consumption, lung disease, stress, and certain medications.
Q: How is AFib diagnosed?
A: AFib is diagnosed through an electrocardiogram (ECG), which measures the electrical activity of the heart, or through a heart monitor worn for an extended period of time.
Q: What are the treatment options for AFib?
A: Treatment options for AFib include medications to control the heart rate and rhythm, electrical cardioversion to restore a normal heartbeat, and procedures such as catheter ablation to destroy areas of the heart causing the irregular rhythm.
Q: Can AFib be prevented?
A: AFib can often be prevented by controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption and stress.
Q: How can I manage my AFib episode?
A: To manage an AFib episode, it’s important to stay calm, avoid caffeine and alcohol, drink plenty of water, and try to relax. If the symptoms are severe or persistent, seek medical attention promptly.
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
The training of a professional athlete is very different from the training an average person engages in. There’s the obvious difference in physical capacity, but the difference we are pointing to is that of technology and medicine. Top sporting franchises and clubs spend massive amounts of money on sports medicine and technology to help their athletes reach or maintain their peak athletic performance. And it works. But the great news is, now it can work for you too.
The entrance of wearable medical technology into the mainstream has meant that we are able to analyse the impact of our physical activity much more accurately than before. Training using heart rate zones, in relation to your breathing rate, as per your body shock – these have all become more and more common practices in recent times. But the newest heart health metric that has gained attention in training circles is Heart Rate Variability. So, let’s look into it.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between consecutive heartbeats. It refers to the fluctuations in the interval between heartbeats and is used as an indicator of the autonomic nervous system activity, which regulates the body’s functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. These variations are very small, fluctuating by a fraction of a second between beats, and are undetectable except with the use of specialized devices.
What does Heart Rate Variability tell us about our Body?
As mentioned earlier, Heart Rate Variability is considered to be an indicator of the activity of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates various physiological functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. HRV is used to assess the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response, and it increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “rest and digest” response and it decreases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. A healthy individual typically exhibits a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, leading to HRV values within a certain range.
Essentially, HRV is an indicator of the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system and can provide insights into an individual’s stress levels, recovery from physical activity, and overall health status.
High vs Low Heart Rate Variability
A high HRV means that there is a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system. When the parasympathetic branch dominates, the body is in a relaxed state and the heart rate slows down, leading to higher HRV values. High HRV is associated with improved recovery from stress and physical activity, better sleep quality, and overall better health status.
On the other hand, low heart rate variability is considered a negative indicator and can indicate various physiological imbalances and health problems. Low HRV values suggest that the sympathetic branch is dominant and the body is in a state of stress or arousal. This can be due to overtraining, stress, sleep deprivation, or other health issues. Low HRV is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease, poor recovery from physical activity, and decreased overall health status.
Types of Physical Training and how the improve Heart Rate Variability
Improving Heart Rate Variability (HRV) can be achieved through a combination of physical activity and lifestyle changes. Here are some ways to train to improve HRV:
- Aerobic Exercise: Aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, and swimming can help improve heart rate variability by increasing blood flow, strengthening the heart, and improving cardiovascular function. Regular aerobic exercise can also help reduce stress and improve recovery from physical activity.
- Resistance Training: Resistance training such as weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, and resistance band exercises can help improve HRV by increasing muscle strength and endurance. Resistance training can also help reduce stress and improve recovery from physical activity.
- Mind-Body Exercise: Mind-body exercise such as yoga, tai chi, and meditation can help improve HRV by reducing stress, improving relaxation, and reducing inflammation. Mind-body exercise can also help improve sleep quality and overall health status.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with periods of rest. HIIT can help improve HRV by increasing cardiovascular function and improving recovery from physical activity.
It’s important to note that while physical activity can help improve HRV, it’s equally important to incorporate lifestyle changes such as getting adequate sleep, managing stress, and eating a healthy diet to maintain and improve HRV.
Tips for integrating HRV training into your routine
We know it isn’t easy for everybody to commit to a training regimen even if we’ve always known how beneficial it can be. That being said, the value added by incorporating any kind of training into your routine is so high, that we must give our best shot at doing so.
Here are some tips for those who struggle with setting a workout regimen.
- Make a Plan: Create a plan that outlines your goals, what types of physical activity you want to incorporate, and when and where you will complete your training. Having a plan in place can help make training a more structured and manageable part of your routine.
- Start Small: If you’re just starting out, start with short, simple exercises that you can do anywhere, such as stretching, push-ups, or jumping jacks. Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your training as you progress.
- Find a Training Buddy: Having a training partner can make training more enjoyable and help keep you accountable. Find a friend or family member who is interested in training and make plans to train together.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic and achievable goals that align with your current fitness level and lifestyle. Celebrate your progress and accomplishments along the way to help keep you motivated.
- Be Consistent: Consistency is key when incorporating training into your routine. Try to set aside time each day or each week for physical activity, even if it’s just for a few minutes. Over time, you can gradually increase the duration of your training sessions.
- Use Technology: There are many apps and devices available that can help make training more accessible and convenient. Using a device like the Frontier X2 smart heart monitor will give you unprecedented access to heart health metrics including your Heart Rate Variability.
With the level of data that we now have access to, it has become easy to improve and tailor our training to fit our exact needs. Understanding and using metrics like Heart Rate Variability will help you most efficiently achieve the goals you set for yourself. Purchase the Frontier X2 smart heart monitor to get access to your Heart Rate Variability data from while you are training to stay on top of your heart health!
FAQ’s
What is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
HRV is the variation in time between successive heartbeats, and is a measure of the body’s ability to respond to stress and recover from physical activity.
What is considered a good HRV score?
A good HRV score depends on many factors, including age, gender, and physical fitness. Generally, a higher HRV score is considered better, as it indicates a more resilient and adaptive cardiovascular system.
What type of physical activity is best for improving HRV?
A variety of physical activities can improve HRV, including aerobic exercise, resistance training, mind-body exercise, and high-intensity interval training. The best type of physical activity for improving HRV is the one that you enjoy and can maintain over the long-term.
Is it possible to have too high of an HRV score?
Although a high HRV score is generally considered better, it is possible to have too high of an HRV score. This can indicate overtraining or overexertion, and it’s important to monitor HRV levels regularly and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
There are a number of factors that influence our cardiac health, and what we consume is one of the most significant ones. It is also often highlighted because making changes to one’s eating habits is generally seen as simpler than some other lifestyle changes that promote heart health.
Heart Rate Variability is a specific heart health metric that tells us a significant amount about the functioning of our heart, but before we get into that, we must understand the principles of how diet and nutrition are linked to your cardiovascular system.
Linking Diet and Nutrition to Cardiac Health
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in maintaining good heart health. A well-balanced diet can help prevent heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health. Here are some ways in which diet and nutrition impact heart health:
- Cholesterol: A diet high in saturated and trans fats can raise blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Eating a diet low in saturated and trans fats, and high in unsaturated fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can help lower blood cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Blood Pressure: A diet high in sodium can increase blood pressure, putting added stress on the heart and blood vessels. A diet low in sodium and high in potassium, magnesium, and calcium can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Body Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for heart health. A diet high in processed and high-calorie foods, along with a sedentary lifestyle, can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease. A diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, along with regular physical activity, can help maintain a healthy weight and improve heart health.
- Inflammation: A diet high in refined carbohydrates and unhealthy fats can contribute to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, help protect the heart and blood vessels from oxidative damage. Eating a diet that includes a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and seeds, can help provide the body with ample antioxidants and improve heart health.
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Now that we’ve established the manner in which different nutrients impact the cardiovascular system, we must understand what Heart Rate Variability is, and what it indicates about your heart health.
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between consecutive heart beats. It is calculated by analyzing the intervals between heartbeats and can provide valuable information about the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and overall cardiac health.
HRV reflects the balance between the sympathetic nervous system, which regulates the “fight or flight” response, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which regulates the “rest and digest” response. A high HRV indicates a strong, healthy autonomic nervous system and a good balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. A low HRV can indicate an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system and a higher risk of heart disease.
HRV is important because it provides insight into the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which controls important functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. By measuring HRV, healthcare providers can assess an individual’s cardiac health and detect potential problems before they develop into more serious conditions.
What is the relationship between Heart Rate Variability and Diet?
As we can tell from the descriptions in both the previous sections, diet and nutrition have a significant impact on your heart health, and Heart Rate Variability is a metric that gives insight into the specifics of your cardiac function. Therefore, it should be clear that the influence of your diet can be assessed in some form using the Heart Rate Variability metric. Below are examples of how your diet can impact your Heart Rate Variability.
- Inflammation: A diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugar can increase inflammation in the body, which can negatively impact HRV. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help reduce inflammation and improve heart rate variability.
- Oxidative Stress: A diet high in sugar and processed foods can increase oxidative stress, which can harm the heart and reduce HRV. A diet high in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help reduce oxidative stress and improve HRV.
- Weight: A diet high in unhealthy fats and sugar can contribute to weight gain, which can increase the risk of heart disease and negatively impact HRV. A diet focused on whole, nutrient-dense foods can help manage weight and improve HRV.
- Hydration: Proper hydration is important for maintaining HRV, and adequate fluid intake is essential for overall heart health. Drinking enough water and eating hydrating foods, such as fruits and vegetables, can help maintain HRV.
Using a variety of heart health metrics to get a holistic understanding of your cardiac functioning is one of the best things you can do for your heart. Heart Rate Variability is a relatively new metric that has found its way into the mainstream, and provides a new angle of insight that is invaluable to us. Using a smart heart monitor like the Frontier X2 gives you access to your Heart Rate Variability, as well as a number of other metrics, allowing you to personally take charge of your heart health based on accurate clinical level data. Measure what matters with the Frontier X2!
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
One of the most fundamental activities that humankind engages in, the importance of sleep is not something to be underestimated. Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health and well-being as it allows the body to recharge and rejuvenate. When you’re asleep, the body works to repair tissues, consolidate memories, and regulate hormones. Poor sleep quality and chronic sleep deprivation have been linked to a variety of health problems, including increased risk of obesity, diabetes, depression, and cardiovascular disease. The relationship between sleep and heart health is particularly strong, as poor sleep has been shown to increase blood pressure, promote inflammation, and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. For these reasons, it is important for individuals to prioritise getting adequate sleep and to make sleep a priority in their daily routines. By doing so, they can improve their heart health and overall well-being.
Explaining the science: The relation between Sleep and Heart Health
Sleep and heart health are interlinked in a multitude of ways, as described below.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. When we are sleep-deprived, our blood pressure tends to be higher, putting increased stress on the heart. Adequate sleep can help to regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension, a leading cause of heart disease.
- Inflammation: Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to increased levels of inflammation in the body. Inflammation has been linked to cardiovascular disease, as it can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Hormonal Balance: Sleep is essential for maintaining hormonal balance. During sleep, the body produces hormones that regulate appetite, metabolism, and blood sugar levels. Disruptions in sleep patterns can lead to imbalanced hormones, which can contribute to heart disease.
- Stress Response: Sleep is important for regulating the stress response. Chronic stress has been linked to increased risk of heart disease, and sleep deprivation can amplify the effects of stress on the heart. Getting adequate sleep can help to reduce stress and improve overall heart health.
How to improve the quality of my Sleep?
Here are several tips for improving sleep to improve heart health:
- Create a sleep-conducive environment: The environment in which we sleep can greatly affect our sleep quality. To promote good sleep, create a dark, cool, and quiet sleep environment. Keep electronic devices out of the bedroom and use a comfortable mattress and pillow.
- Establish a consistent sleep routine: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can help regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and improve sleep quality. Aim to maintain a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Limit exposure to screens before bedtime: The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with the production of the sleep hormone melatonin and disrupt sleep. To improve sleep, limit exposure to screens for at least an hour before bedtime and consider using a blue light filter on devices.
- Engage in physical activity: Regular physical activity has been shown to improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep disorders. Aim to engage in moderate physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Manage stress: Stress can interfere with sleep and exacerbate the risk of heart disease. To manage stress, consider practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Seeking support from friends and family, and engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of calm can also help to manage stress and improve sleep.
What to avoid consuming before Sleep?
The food and drink you consumed through the day can have an impact on the quality of your sleep. Here are a few things to avoid so as to improve your sleep quality.
- Late-night caffeine consumption: Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with sleep by making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. To improve sleep, it is recommended to avoid consuming caffeine in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Late-night meals: Eating a heavy meal close to bedtime can interfere with sleep by causing discomfort and acid reflux. To improve sleep, it is recommended to finish eating at least two to three hours before bedtime.
- Alcohol consumption: Although alcohol may initially help you fall asleep, it can interfere with sleep later in the night and lead to fragmented, poor-quality sleep. To improve sleep, it is recommended to limit alcohol consumption and avoid drinking before bedtime.
Improving sleep quality is crucial for maintaining good heart health. Sleep plays a vital role in regulating the body’s systems, including cardiovascular function, and poor sleep has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. By prioritizing sleep and taking steps to improve sleep quality, individuals can promote good heart health and improve overall well-being.
Finally, improve your sleep quality using all the information above, and pair this movement towards better heart health with the use of a smart heart monitor. Using a product like the Frontier X2, one of the only wearables you can have on through the night, gives you access to a variety of heart health metrics so that you can assess your cardiac functioning as closely and accurately as possible. Purchase the Frontier X2, and be on your way to a healthier tomorrow!
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
The experience of any major medical problem can have a significant impact on the life of the patient even once they have survived it. This is especially true for patients who have experienced a Heart Attack in the past. A heart attack often puts human mortality into perspective and can be a life-altering experience that leaves you feeling scared and unsure of how to move forward. That is completely understandable. Still, moving on from a major life event like this is necessary so as to not let it continue to impair your quality of life.
Fortunately, making certain simple lifestyle changes can greatly improve your chances of a full recovery and reduce the risk of future cardiac events. Whether it’s adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, or managing stress, small changes can make a big impact on your heart health.We will explore the various lifestyle changes that heart attack survivors can make to optimize their recovery and take control of their heart health. By incorporating these changes, you can reclaim control of your health and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
The best lifestyle changes to make to optimise your recovery from a Heart Attack
Eating a Heart Healthy diet
Diet plays a critical role in heart health as it can greatly impact your risk of developing heart disease. In general, a heart-healthy diet should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods that provide the nutrients needed for optimal heart health, while also limiting foods that can increase the risk of heart disease.
So, what are the foods that increase the risk of heart disease?
- Saturated and trans fats: Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fatty meats, butter, and baked goods, can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Refined carbohydrates: Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, sugary drinks, and processed snacks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to high insulin levels and increased risk of heart disease.
- Sodium: Consuming high levels of sodium, which is often found in processed foods and restaurant meals, can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Added sugars: Foods high in added sugars, such as candy, desserts, and sugary drinks, can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease.
These foods can be harmful to heart health because they can contribute to the development of cardiovascular risk factors, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and obesity. By limiting these foods and replacing them with heart-healthy options, individuals can improve their heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Foods that are good for heart health include:
- Fruits and vegetables: These are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals and can help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
- Whole grains: Whole grains are high in fiber and can help lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Lean protein: Foods like fish, poultry, and beans are good sources of protein and can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are high in healthy fats and can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.
- Olive oil: Olive oil is a good source of monounsaturated fats, which can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.
Engaging in regular physical activity
Exerting yourself and testing your heart after a heart attack can be a difficult process. That’s why it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase physical activity after a heart attack, under the guidance of a doctor. A combination of aerobic exercise and strength training can be particularly helpful for improving heart health.
Below are the reasons physical activity helps optimise your recovery from a Heart Attack:
- Improves cardiovascular fitness: Regular exercise can help improve cardiovascular fitness, which can help the heart pump blood more efficiently and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
- Lowers blood pressure: Physical activity can help lower blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
- Improves cholesterol levels: Exercise can help raise levels of good cholesterol (HDL) and lower levels of bad cholesterol (LDL), which can improve heart health.
- Reduces stress: Exercise has been shown to reduce stress, which is a major contributor to heart disease.
- Increases blood flow: Regular physical activity can help improve blood flow, which can help speed up the healing process after a heart attack.
Quitting Smoking
Smoking cigarettes is possibly one of the worst things you can do for your heart health. Therefore, quitting smoking leads to a variety of positive outcomes that make you healthier, and keep you protected. Smoking is a major cause of cardiovascular disease, and it increases the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries, which can lead to blockages and subsequent heart attacks. By quitting, the body is able to heal more effectively, and the risk of complications and long-term damage to the heart is reduced. Quitting smoking is beneficial for heart attack recovery because it reduces the risk of having another heart attack, improves blood flow to the heart, lowers blood pressure and reduces stress on the heart.
Managing your Stress
Stress management is important for recovering from a heart attack because stress can increase the heart rate, blood pressure, and the risk of having another heart attack. Chronic stress can also weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, which can negatively affect the healing process. Additionally, stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating, smoking, and alcohol consumption, which can further strain the heart and impede recovery.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support from loved ones can help the heart to heal and reduce the risk of further heart problems. Engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of calm can also promote overall well-being and contribute to a successful recovery.
Changing lifestyle habits after a heart attack is crucial for leading a happy and healthy life. Making positive changes such as quitting smoking, eating a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help to reduce the risk of another heart attack, improve heart function, and enhance overall well-being. These lifestyle changes can also have a positive impact on mental health and reduce the risk of depression, which is common after a heart attack. By making these changes, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of future heart problems. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for recovery and ensure that these lifestyle changes are sustainable over time
Finally, pair your new recovery plan with the use of a heart monitoring device to know exactly how you’re impacting your heart. Purchase the revolutionary Frontier X2 to get access to detailed data on your cardiac functioning and be on your way to a healthier tomorrow!
The prevalence of stress in modern day society has made the management of that same stress one of the most pertinent up and coming fields of research. Exercise, or generally any physical activity, has always rightfully been touted to us as one of the easiest ways to improve our physical health, but we’re starting to see its impact on our mental health too. For any of us that consistently lift weights, go for runs, or play a sport, we’re well aware of the uplift that comes after the activity. So, how exactly does this work, and is exercise truly an effective stress management practice?
Stress and it’s specific impact on Heart Health
Before looking into the impact of exercise on stress, let’s look at why it is pivotal that we manage that stress effectively.
Stress and heart health are closely related. Chronic stress can have a negative impact on heart health by increasing the risk of several heart-related conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. When a person experiences stress, the body releases stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which cause the heart rate to increase, blood vessels to narrow, and blood pressure to rise. This can increase the workload on the heart and cause damage over time. Therefore, it’s important to manage stress effectively to maintain overall heart health and reduce the risk of heart-related conditions, which are the leading cause of death worldwide.
Mechanisms by which Exercise helps manage Stress
Exercise provides stress relief through several mechanisms, including:
- Release of endorphins: Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers and mood boosters that can help improve feelings of well-being and reduce stress levels. Endorphins interact with the brain to reduce the perception of pain and increase feelings of pleasure, providing a natural high that can help improve mood and reduce stress.
- Reduction of physical symptoms: Exercise can also help reduce the physical symptoms of stress, such as an increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure, by improving cardiovascular health. Regular exercise can help regulate the cardiovascular system, reducing the physical effects of stress and improving overall heart health.
- Improved sleep: Exercise can also help improve sleep, which is important for managing stress. Physical activity can help reduce feelings of anxiety and improve sleep quality, providing a sense of calm that can help reduce stress levels.
- Mental distraction: Exercise can also provide a mental distraction, providing an escape from the stressors of daily life and improving mood. The physical and mental demands of exercise can help redirect focus and provide a sense of accomplishment, reducing feelings of stress and anxiety.
- Mind-body connection: Exercise can also help reduce stress by improving the mind-body connection. Some types of exercise, such as yoga, tai chi, and meditation, are specifically designed to promote relaxation and reduce stress by focusing on breathing, mindfulness, and movement.
Different Types of Exercise and how they help with Stress
Each of these types of exercise release endorphins, improve your sleep, and provide a mental distraction. In this section we will outline the unique ways in which each of these types of physical activity help manage stress.
-
Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise is a type of physical activity that increases the heart rate and breathing rate to provide oxygen to the body’s muscles. Examples of aerobic exercise include running, cycling, swimming, jumping rope, and brisk walking. The goal of aerobic exercise is to maintain an elevated heart rate for an extended period of time, improving cardiovascular fitness and overall health.
How it helps with stress management.
- Increased heart rate: Aerobic exercise increases the heart rate, which can help reduce the physical symptoms of stress. Regular aerobic exercise can help regulate the cardiovascular system, reducing the physical effects of stress and improving overall heart health.
-
Resistance Training
Resistance training, also known as strength training, is a type of exercise that involves working against resistance to build strength, muscle mass, and improve overall physical fitness. This can be achieved through the use of weights (such as dumbbells or barbells), resistance bands, or body weight exercises. Examples of resistance training exercises include bench press, bicep curls, squats, lunges, and push-ups. Resistance training is beneficial for building strength, improving bone density, and increasing overall physical fitness.
How it helps with stress management.
- Increased muscle mass and bone density: Regular resistance training can also help increase muscle mass and bone density, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall physical health. The physical benefits of resistance training can provide a sense of strength and stability, reducing feelings of stress and anxiety.
- Improved self-esteem and confidence: Resistance training can help increase self-esteem and confidence, which can help reduce feelings of stress. The physical and mental benefits of resistance training, such as increased strength and improved body composition, can provide a sense of accomplishment and improve self-image, reducing feelings of stress and anxiety.
-
Mind-Body Exercise
Mind-body exercise is a type of physical activity that involves the integration of physical movements with mental focus, breathing techniques, and mindfulness. The goal of mind-body exercise is to improve physical and mental well-being through the practice of self-awareness and stress reduction. Examples of mind-body exercise include yoga, tai chi, meditation, and Pilates. Mind-body exercise can improve physical fitness, flexibility, balance, and reduce stress and anxiety levels.
How it helps with stress management.
- Reduced muscle tension and stress: Mind-body exercise can also help reduce muscle tension and stress. The physical and mental demands of mind-body practices, such as deep breathing and relaxation techniques, can help reduce physical symptoms of stress, such as muscle tension, headaches, and fatigue.
- Improved focus and concentration: Mind-body exercise can help improve focus and concentration, reducing feelings of stress and anxiety. Mind-body practices, such as yoga and tai chi, can help improve mental clarity and focus, reducing distractions and improving overall mental well-being
- Improved self-awareness and stress management skills: Mind-body exercise can also help improve self-awareness and stress management skills. The physical and mental demands of mind-body practices can help individuals better understand and manage their stress levels, reducing the risk of developing stress-related health problems.
Exercise can play a vital role in reducing stress and improving heart health. Whether it’s through aerobic exercise, resistance training, or mind-body exercise, each form of exercise has unique stress-relieving benefits that can contribute to a healthy heart. Regular physical activity can also help lower the risk of heart disease and stroke, boost mood, improve sleep quality, and promote overall physical and mental well-being. To gain the maximum benefits, it is recommended to engage in regular exercise, including a combination of aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercises for a balanced approach to stress relief and heart health.
Finally, pair your new understanding of exercise as a stress management technique with the use of a heart monitoring device to know exactly how you’re impacting your heart. Purchase the revolutionary Frontier X2 and be on your way to a healthier tomorrow!
Frontier X2 :
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Medical emergencies can occur at any time, and having the knowledge or expertise to assist in such situations can be vital. This is why First Aid is one of the most universally taught skills. Running cold water over a burn, giving the heimlich manoeuvre when someone’s choking, or even performing CPR when the situation calls for it – these are all examples of First Aid practises one is expected to be familiar with.
So, why aren’t we as familiar with the response to other serious, life-threatening medical emergencies. In the US alone 805,000 people experience a heart attack per year (ref.link). In the UK 1 person is admitted to the hospital due to a heart attack every 5 minutes. These are staggering numbers, not meant to induce fear but to reflect the need to be prepared for such an event.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, is a medical emergency in which the blood supply to a part of the heart muscle is blocked. This usually occurs when there is a buildup of fatty deposits in the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle, that partially or completely blocks the flow of blood. This results in the heart muscle not receiving enough oxygen and nutrients from the blood, leaving it susceptible to severe damage.
Responding as quickly as possible is pivotal in dealing with cardiac issues because time is a critical factor in preserving heart function. Prompt treatment can help minimise the risk of permanent damage to the heart muscle and greatly increase the chances of a favourable outcome, reducing the risk of life-threatening complications.
The Most Common Signs/Symptoms of a Heart Attack
- Chest pain or discomfort: This can feel like pressure, fullness, squeezing, or pain in the centre or left side of the chest that can last for more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
- Shortness of breath: This can occur with or without chest pain and may be a sign that the heart is not getting enough blood and oxygen.
- Arm, jaw, neck, back, or stomach pain: This can be felt in one or both arms, the jaw, neck, back, or stomach and can be accompanied by chest pain.
- Nausea and vomiting: This can be a sign of a heart attack, especially if it is accompanied by chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: This can occur when the heart is not pumping enough blood, causing a drop in blood pressure and a lack of oxygen to the brain.
It’s important to note that not everyone will experience the same symptoms, and some people may have no symptoms at all.
How to Provide Assistance When Someone is Having a Heart Attack
If someone is experiencing a heart attack, it’s important to take the following steps:
- BEFORE ANYTHING ELSE Call for emergency medical services: Dial 911 or the local emergency number immediately. Do not wait to see if the symptoms go away, because as mentioned earlier, every second counts when it comes to treating a heart attack.
- Chew and swallow an aspirin: If the person is able to take aspirin safely, have them chew and swallow a low-dose aspirin. Aspirin can help reduce the risk of further heart damage.
- Provide comfort: Stay with the person and try to keep them calm. Encourage them to sit or lie down and rest, and help them loosen any tight clothing that may be restricting their breathing.
- Administer oxygen, if available: If you have access to oxygen, help the person use it to breathe. This can help increase the amount of oxygen in their blood and reduce the stress on their heart.
- Monitor vital signs: Keep track of the person’s breathing, pulse, and blood pressure, if possible.
- Prepare for the ambulance: Gather any relevant medical information, including any medications they are taking, and be ready to provide details of their symptoms.
Once again, it is of the utmost importance to remember that a heart attack can be a life-threatening emergency, and prompt medical attention is necessary to minimize the risk of permanent damage to the heart muscle. If someone is experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, do not hesitate to call for emergency medical services.
How to take care of yourself after surviving a Heart Attack
The recommended care following a heart attack depends on several factors, including the severity of the attack, the underlying cause, and the person’s overall health. However, some general guidelines for post-heart attack care include:
- Medications: A person may be prescribed medications to help reduce the risk of future heart attacks and improve heart function, such as aspirin, blood thinners, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, can help reduce the risk of future heart attacks and improve overall heart health.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation is a program that includes exercise, education, and support to help a person recover and improve their heart health following a heart attack.
- Follow-up care: Regular follow-up care with a doctor is important to monitor the person’s progress, adjust medications as needed, and identify any potential complications.
- Monitoring symptoms: A person should be aware of any changes in their symptoms and report any new or worsening symptoms to their doctor promptly.
It’s important to note that the specific recommended care for each individual will vary based on the specifics of their heart attack and overall health. Working closely with a healthcare provider to create a personalised care plan is essential for optimal recovery and reducing the risk of future heart problems.
The idea of anyone experiencing a heart attack is a scary one, but hopefully with the information you’ve picked up here you can now respond from a place of knowledge rather than one of fear.
As mentioned in the article, monitoring your symptoms, both before or after experiencing a heart attack, can be the best way to be aware of any irregularities in cardiac function. We keep reiterating that the quicker you act, the less harmful a heart attack (or really any other cardiac issue) will be. Purchase the revolutionary Frontier X2 smart heart monitor which gives you access to a multitude of vital heart health metrics as well as a continuous ECG. Monitoring your heart has never been this easy and this accurate, so go ahead and ensure that you are always on top of your heart health!
If you’ve been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AFIB), it can be a daunting task to figure out how to manage your condition. But don’t worry, there are plenty of ways you can keep AFIB under control, including medications and lifestyle changes. Here are some tips on how to best manage your AFIB so that you can live life without fear or discomfort.
AFib treatment: Work with your doctor for a treatment plan
First off, let’s talk about medication. AFib treatment is never a one-size-fits-all. Your doctor may prescribe one or more drugs for controlling the rate and rhythm of your heart beat as well as reducing symptoms like palpitations and chest pain associated with AFIB episodes. It is important to remember that these medications should only be taken exactly as prescribed by a healthcare professional in order for them to work properly – never change dosages yourself.
AFib lifestyle changes: Keep an eye on obesity, stress and more
In addition to taking prescription meds, making healthy lifestyle choices is key when it comes to managing afib effectively over time. This includes regular exercise such as walking or swimming; eating nutritious foods rich in fiber; avoiding alcohol consumption; quitting smoking if applicable; getting enough sleep each night (7-9 hours); managing stress levels through relaxation techniques like yoga/meditation/deep breathing exercises etc.; monitoring heart health with the help of a smart heart monitor such as the Frontier X2, all of which will help reduce the risk factors associated with developing this condition further down the line too.
Dietary changes can lead to weight loss and better blood sugar control for those with diabetes. Adopting a healthier diet can be difficult, but reducing processed foods and increasing fresh fruits and vegetables is a great first step. Focus on breaking unhealthy habits like mindless snacking and aim to transition to a Mediterranean diet, which is known to aid weight management and regulate blood sugar or a DASH diet that is known to regulate blood pressure.
Lastly but most importantly – make sure that you stay up-to-date on any new developments related specifically towards treating afib since medical research continues even today into better understanding this complex disorder so we have more options available than ever before now when it comes tackling its effects head-on successfully over the long term. As per this article (Ref. Link) on US Cardiology Review, AFib patients can look forward to improvements in catheter-based ablative techniques, the development of a more effective standalone surgical method, the availability of effective atrial antiarrhythmic drugs, the implementation of better methods to prevent thromboembolic events, and the introduction of innovative pharmacologic and genetic approaches that will drive advancements in preventing AFib.
Summarizing the tips detailed above, you need to:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle – exercise regularly, eat a healthy diet, manage stress, and avoid triggers like alcohol and caffeine.
- Control other health conditions – high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and obesity can contribute to AFib, so work with your doctor to manage these conditions.
- Take medications as prescribed – follow your doctor’s instructions for taking medications to control heart rate and rhythm.
- Monitor symptoms – keep track of symptoms and report any changes to your doctor.
- Keep medical appointments – see your doctor regularly to monitor your condition and discuss any changes in treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the warning signs of afib?
The warning signs of Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) include: irregular heartbeat or palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort, lightheadedness or dizziness, weakness or fatigue. You might also experience sweating, fainting, confusion or memory loss.
How to stop afib episode?
There are several ways to stop an Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) episode including medications, deep breathing and relaxation, and cardioversion. Triggers like alcohol, caffeine, and stress can worsen AFib episodes, so avoiding them can help to reduce the frequency and duration of episodes.
What is the best wearable afib monitor?
The best wearable Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) monitor is subjective and depends on individual needs and preferences. Visit fourthfrontier.com and read about the Frontier X2 and monitor your heart health during any activity.
Can acid reflux trigger afib?
Acid reflux can trigger Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) in some people. AFib is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly, and research has shown that people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a common form of acid reflux, are at increased risk of AFib. This is because the acid reflux can irritate the heart and trigger an AFib episode. If you have both acid reflux and AFib, it’s important to manage the acid reflux effectively to reduce the risk of AFib episodes.