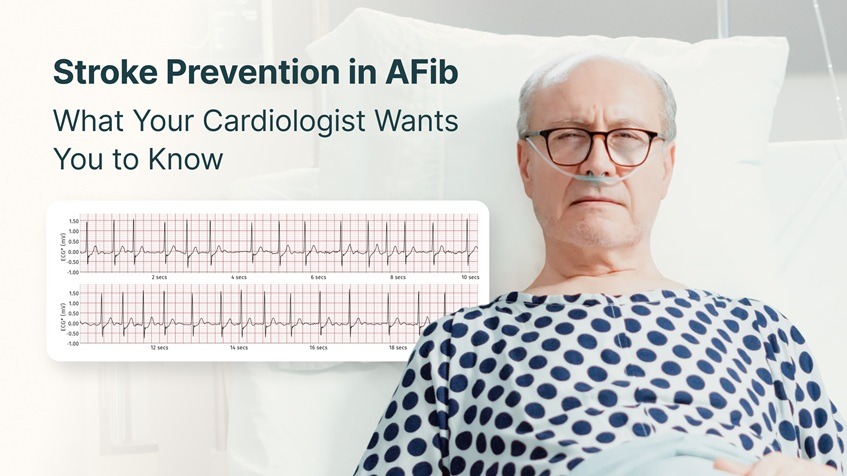
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders in the world – yet it’s also one of the most underdiagnosed. While AFib itself might not be immediately life-threatening, its greatest danger lies in what it can lead to: stroke.
In fact, AFib increases the risk of stroke by nearly fivefold. Understanding this connection and taking the right preventive steps can make a life-changing difference.
Let’s explore why AFib increases stroke risk, how cardiologists prevent it, and what you can do to protect your heart and brain health.
Understanding the AFib–Stroke Connection
To understand why AFib raises stroke risk, you need to first understand what happens during this irregular heart rhythm.
In a healthy heart, the atria (upper chambers) contract in a steady, coordinated rhythm, efficiently pushing blood into the ventricles. But during Atrial Fibrillation, electrical signals become chaotic. The atria quiver instead of contracting properly, causing blood to pool and stagnate, especially in a small pouch called the left atrial appendage.
This stagnant blood can form clots, which may travel through the bloodstream and block an artery in the brain – leading to an ischemic stroke.
Why Stroke Risk Is Higher in AFib Patients
- Irregular Blood Flow:
AFib prevents smooth blood movement, creating turbulence that promotes clot formation. - Aging and Coexisting Conditions:
People over 65, or those with hypertension, diabetes, or heart failure, are especially vulnerable. - Silent AFib Episodes:
Some people have asymptomatic AFib, meaning they don’t feel palpitations or dizziness – but stroke risk remains. - Inadequate Monitoring:
Without continuous ECG monitoring, intermittent AFib can go unnoticed for years, delaying treatment.
Recognizing AFib-Related Stroke Symptoms
A stroke caused by AFib looks like any other stroke, but it’s often more severe. Key warning signs include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body)
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Blurred or lost vision
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden, severe headache
Time is brain – if you suspect a stroke, call emergency services immediately.
How Cardiologists Prevent Stroke in AFib Patients
Stroke prevention in AFib isn’t just about treating symptoms – it’s about reducing clot formation and maintaining rhythm stability.
Here’s what your cardiologist may recommend:
1. Anticoagulant (Blood Thinning) Therapy
Medications like warfarin or newer DOACs (Direct Oral Anticoagulants) such as apixaban or rivaroxaban help prevent clot formation. Your doctor will assess your stroke risk using a scoring system like CHA₂DS₂-VASc, which considers factors like age, diabetes, heart failure, and hypertension.
Disclaimer: These medications should only be taken under the guidance and supervision of a qualified physician. Your cardiologist will determine whether anticoagulation is appropriate based on your medical history, risk profile, and current health status.
2. Rate and Rhythm Control
If your heart is racing or irregular, your cardiologist may use medications like:
- Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers (for rate control)
- Antiarrhythmics (to restore or maintain normal rhythm)
In some cases, procedures like cardioversion or catheter ablation may be considered to reset or isolate abnormal electrical pathways.
3. Left Atrial Appendage Closure
For patients who can’t tolerate long-term anticoagulants, a left atrial appendage (LAA) closure device, such as the Watchman, can physically block clot escape routes.
4. Lifestyle Changes to Support Stroke Prevention
- Manage blood pressure: High BP is a key contributor to both AFib and stroke.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases atrial strain.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine: Both can trigger arrhythmias.
- Exercise moderately: Avoid overexertion, especially if your AFib is unstable.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco accelerates vascular damage.
The Role of Long-Term ECG Monitoring in Stroke Prevention
Short-duration ECGs or smartwatch-based recordings may miss brief or nighttime AFib episodes that still contribute to stroke risk. Long-term ECG monitoring offers a more complete rhythm picture by tracking heart activity over extended periods.
Devices such as the medical-grade Frontier X Plus and the wellness-grade Frontier X2 allow users to record ECG data during daily routines, rest, and exercise. Unlike optical sensors found in many wrist-worn devices, these chest-worn tools capture electrical signals directly from the chest, providing clearer ECG waveforms with visible P-waves. This can support users and their healthcare providers in reviewing rhythm patterns and understanding overall heart-performance trends more effectively.
For individuals seeking to lower AFib-related stroke risk, long-term ECG monitoring can help:
- Reveal rhythm irregularities that short-term tests might overlook
- Track heart rhythm stability following therapy or lifestyle changes
- Provide ECG trend data that assists healthcare professionals in clinical assessment and decision-making
By offering long-term rhythm insights, these tools support a shift toward more informed and proactive heart health management.
When to Talk to Your Cardiologist
You should discuss AFib and stroke prevention if you experience:
- Frequent palpitations or skipped beats
- Unexplained fatigue or shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- A family history of stroke or heart rhythm disorders
Even if your symptoms seem mild, early detection through ECG-based evaluation can significantly lower your long-term stroke risk.
Living Confidently with AFib
AFib doesn’t have to dictate your future. With proper management – medications, lifestyle optimization, and consistent heart rhythm monitoring – you can dramatically reduce the risk of stroke and maintain an active, fulfilling life.
Many cardiologists now recommend combining clinical follow-ups with wearable ECG monitoring, ensuring that rhythm irregularities are caught before they cause harm.
When patients understand their heart rhythm patterns, they become empowered to make informed decisions – and that’s the essence of modern cardiac care.
FAQs
1. How does AFib cause a stroke?
AFib causes the upper chambers of the heart to beat irregularly, allowing blood to pool and form clots. These clots can travel to the brain and block arteries, resulting in an ischemic stroke.
2. Can AFib-related strokes be prevented?
Yes. With the right combination of anticoagulants, lifestyle changes, and rhythm management, most AFib-related strokes can be prevented.
- What are the best treatments for stroke prevention in AFib?
Your cardiologist may prescribe blood thinners, rate or rhythm management medications, or recommend catheter ablation. Long-term ECG monitoring can provide valuable heart rhythm data over time, helping physicians assess treatment effectiveness and make informed adjustments. - Can wearable ECG devices help detect AFib early?
Devices like the medical-grade Frontier X Plus and the wellness-grade Frontier X2 allow users to record ECG data over extended periods. This long-term rhythm information can support physicians in identifying irregular trends that may warrant further clinical evaluation.
5. Is AFib always permanent?
No. AFib can be paroxysmal (intermittent), persistent, or permanent. Early intervention improves chances of maintaining normal sinus rhythm.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders worldwide, affecting millions of people – but when it comes to women, AFib behaves differently. While men are statistically more likely to develop AFib, women tend to experience more severe symptoms, a higher risk of complications, and are often underdiagnosed.
Understanding the unique AFib triggers in women – from hormonal fluctuations and stress to underlying health conditions – is essential for early detection and prevention. With the help of long-term ECG monitoring through advanced wearables like Frontier X Plus, women can now track subtle changes in their heart rhythm, empowering them to take charge of their cardiac health.
What Is AFib and Why It Matters
AFib is a type of atrial arrhythmia where the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat irregularly and out of sync with the lower chambers (ventricles). This irregular electrical activity can cause the heart to pump less efficiently, leading to poor circulation, blood clots, stroke, and heart failure if left untreated.
Women often experience different or atypical AFib symptoms, including:
- Unexplained fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath during mild exertion
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations or fluttering sensations
- Anxiety or sleep disturbances
While these symptoms may seem mild or be mistaken for stress or menopause-related changes, they can signal an underlying heart rhythm disorder.
Unique AFib Triggers in Women
1. Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal changes across a woman’s life – especially during menstruation, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause – can influence heart rhythm stability. Estrogen and progesterone affect autonomic balance and electrical conduction, meaning fluctuations can make women more prone to arrhythmias like AFib.
Low estrogen levels post-menopause may also contribute to increased inflammation, higher blood pressure, and reduced vascular elasticity, all of which could elevate AFib risk.
2. Stress and Emotional Health
Psychological stress and anxiety are well-known triggers of irregular heartbeats. In women, chronic stress often leads to elevated cortisol and adrenaline levels, which increase sympathetic nervous system activity – a key contributor to atrial arrhythmias.
Women are also more likely than men to experience stress-induced cardiomyopathy (Takotsubo syndrome), which can mimic or exacerbate AFib episodes.
3. Thyroid Disorders
Women have significantly higher incidence of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism than males and both conditions can disrupt normal cardiac rhythm.
- Hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolism, leading to rapid heart rate and AFib.
- Hypothyroidism can alter heart rate variability and electrical conduction.
Monitoring thyroid levels is crucial for women with recurrent palpitations or AFib-like symptoms.
4. Sleep Disturbances and Sleep Apnea
Poor sleep quality, insomnia, and sleep apnea are all linked to AFib. Hormonal transitions such as menopause often increase the prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in women.
When oxygen levels drop during sleep apnea, the heart compensates by increasing rate and pressure, which can strain the atria and trigger arrhythmia.
5. Caffeine, Alcohol, and Dehydration
While occasional caffeine intake is safe, excessive consumption of coffee, energy drinks, or alcohol can trigger AFib episodes, particularly in women sensitive to stimulants. Alcohol disrupts electrolyte balance and increases atrial excitability, while dehydration reduces blood volume, stressing the cardiovascular system.
6. Medications and Supplements
Certain over-the-counter cold medicines, weight-loss pills, or herbal supplements can act as sympathomimetic agents, raising heart rate and inducing arrhythmia. Women taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or oral contraceptives should consult their doctors if they experience palpitations or rapid heartbeats.
7. Underlying Health Conditions
Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and anemia are more likely to cause AFib in women. Chronic inflammation, fluid retention, and changes in cardiac structure from these diseases can disrupt the heart’s electrical stability.
Why Women Are Often Underdiagnosed
Women’s AFib symptoms are often atypical or intermittent, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed care. Moreover, AFib in women tends to occur later in life and often coincides with other age-related cardiac issues, compounding risk.
Because AFib episodes can come and go, traditional short-term ECGs or occasional check-ups may miss them. This is where long-term ECG monitoring becomes invaluable.
Role of Long-Term ECG Monitoring with Frontier X Plus
Modern wearable ECG tools such as the Frontier X Plus – a medical-grade, FDA-cleared, prescription-based long-term ECG monitor – enable women to record single-lead ECG and heart-rate data over extended periods, giving them and their physicians a clearer picture of how the heart behaves in daily life.
These tools can help you:
- Record long-duration ECG data, allowing you and your physician to observe overall rhythm trends across everyday activities and sleep.
- Track heart rate and changes in rhythm patterns in response to stress, exertion, and recovery.
- Review additional metrics such as breathing and body-impact, which can help you understand how physical effort relates to your cardiovascular responses.
- Share your recorded data with your physician, enabling them to review and interpret the information as part of a broader clinical evaluation when needed.
For women who experience occasional palpitations, light-headedness, or fatigue, long-term ECG recording offers a more complete picture of how the heart responds to everyday activities — insights that short-duration tests may not capture.
Prevention and Management Tips for Women with AFib
- Monitor your heart rhythm regularly using continuous ECG devices.
- Manage stress with mindfulness, yoga, or relaxation exercises.
- Balance hormones naturally through proper nutrition, exercise, and medical guidance.
- Stay hydrated and limit stimulants like caffeine and alcohol.
- Prioritize sleep and seek evaluation for sleep apnea if snoring or fatigue is persistent.
- Regular checkups for thyroid, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
- Consult a cardiologist if you notice irregular heartbeats, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue.
The Bigger Picture: Empowering Women’s Heart Health
AFib can be effectively managed with lifestyle adjustments, early detection, and data-driven monitoring. As more women embrace wearable cardiac technology, the ability to detect arrhythmias early and prevent complications is stronger than ever.
Continuous and long-term ECG monitoring empowers women to move beyond guesswork – allowing them to truly understand how stress, hormones, and sleep affect their heart rhythm.
FAQs
Q1. What are the common AFib symptoms in women?
Common AFib symptoms in women include fatigue, palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, and sleep disturbances. These may differ from the typical chest fluttering seen in men.
Q2. Can hormonal changes trigger AFib?
Yes. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone during menopause, pregnancy, or menstrual cycles can affect heart rhythm and trigger AFib episodes.
Q3. How is AFib diagnosed in women?
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is diagnosed through an electrocardiogram (ECG) performed or reviewed by a healthcare professional. Since AFib episodes can occur intermittently, long-term ECG monitoring can provide additional rhythm data between clinical assessments.Medical-grade devices such as Frontier X Plus (FDA-cleared) are designed to detect AFib, tachycardia, and bradycardia, to help users observe rhythm patterns over time.
Q4. What lifestyle changes help reduce AFib risk in women?
Managing stress, avoiding stimulants, getting quality sleep, staying hydrated, and maintaining a heart-healthy diet all lower AFib risk.
Q5. Can AFib be prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, early detection, regular heart monitoring, and controlling contributing conditions like hypertension and thyroid disorders can significantly reduce risk.
Key Takeaways
- AFib affects women differently, with unique hormonal and stress-related triggers.
- Symptoms are often subtle and may go unnoticed without continuous ECG tracking.
- Frontier X Plus provides reliable, long-term ECG insights that support heart health awareness, early detection of irregular patterns, and better management in consultation with healthcare professionals.
- Empowering women with data-driven heart monitoring leads to early detection and better outcomes.
Can Changes in Temperature or Altitude Trigger AFib?
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) – the most common sustained heart rhythm disorder – is often linked to stress, exertion, and heart disease. But did you know that changes in temperature or altitude can also affect how your heart beats? Whether it’s the heat of summer, the chill of winter, or the thin air of high-altitude regions, these environmental factors can impact heart rate, oxygen delivery, and electrical activity, potentially triggering atrial arrhythmia in susceptible individuals.
Let’s explore how environmental shifts can influence your heart’s rhythm, what signs to look out for, and how continuous ECG monitoring can help detect early changes.
Understanding AFib: When the Heart’s Electrical System Goes Offbeat
Atrial Fibrillation occurs when the atria (the upper chambers of the heart) beat chaotically and out of sync with the ventricles. This irregular rhythm reduces the efficiency of blood flow and can lead to clots, stroke, and heart failure if left untreated.
In a normal heart rate, electrical signals travel in an orderly way through the heart. But in AFib, those signals become erratic – resulting in a fast, irregular heartbeat that feels like fluttering or pounding in the chest. While genetics, hypertension, and cardiac conditions are well-known causes, environmental stressors like temperature extremes and altitude can also act as triggers.
How Temperature Affects Heart Rhythm
1. Heat and Dehydration
When temperature rises, your body works harder to stay cool. Blood vessels dilate, and your heart pumps faster to push more blood toward the skin for cooling. This increased heart rate can strain the cardiovascular system, especially in people with underlying atrial arrhythmia or heart issues.
Moreover, dehydration – common during hot weather or exercise – can cause electrolyte imbalances (like low potassium or sodium), which disrupt electrical conduction in the heart. Studies show that electrolyte depletion and heat stress can elevate the risk of AFib episodes.
Key takeaway: During heat exposure or workouts in hot climates, staying hydrated and avoiding excessive exertion helps maintain a normal heart rhythm.
2. Cold Temperatures and Vasoconstriction
Cold weather has the opposite effect. Low temperatures cause blood vessels to constrict (tighten), raising blood pressure and increasing the heart’s workload. This sudden cardiac strain can elevate the risk of heart arrhythmias and even heart attacks in predisposed individuals.
Research indicates that winter months see a spike in AFib incidence, possibly due to the combination of high blood pressure, thicker blood viscosity, and increased sympathetic nervous system activity. People with existing heart arrhythmia or AFib history should be cautious about abrupt exposure to cold temperatures.
Pro tip: Warm up gradually before outdoor exercise in winter and wear temperature-appropriate layers to avoid abrupt cardiovascular stress.
Altitude and AFib: The Role of Oxygen Levels
1. Low Oxygen and High Heart Rate
At higher altitudes – generally above 2,500 meters – the oxygen concentration in the air decreases. To compensate, your heart beats faster and pumps harder to deliver enough oxygen to the body. This increased heart rate and cardiac workload may trigger atrial fibrillation or other atrial arrhythmias, especially in individuals with a prior history of heart rhythm disorders.
Hypoxia (low oxygen levels) also affects ion channel activity in cardiac cells, potentially disturbing the heart’s electrical conduction. In extreme cases, the body’s compensatory response (including higher adrenaline levels) can further raise heart rhythm instability.
2. The “Altitude Acclimatization” Period
During the first few days at high altitude, your body adapts to reduced oxygen through faster breathing, elevated heart rate, and increased red blood cell production. However, this adaptation phase is a time when AFib may be more likely to occur. Even healthy individuals sometimes experience palpitations, lightheadedness, or chest discomfort as their cardiovascular system adjusts.
Preventive tip: Ascend gradually if possible, stay well-hydrated, and avoid overexertion during early altitude exposure.
Exercise, Altitude, and Atrial Fibrillation: A Delicate Balance
Many endurance athletes train or compete at altitude to improve aerobic efficiency. But intense exercise combined with hypoxia and dehydration can overstimulate the sympathetic nervous system, potentially triggering AFib or flutter.
In such cases, continuous ECG monitoring is invaluable for understanding how your heart responds to environmental stressors. It helps detect patterns like increased heart rate at rest, nocturnal arrhythmias, or sudden spikes during exertion, which may otherwise go unnoticed in standard checkups.
The Role of Long-Term ECG Monitoring: Frontier X Plus
Traditional heart monitoring methods like Holter tests provide only short-duration insights – typically 24 to 48 hours – and may not reflect how your heart behaves during daily routines or physical activity. That’s where wearable, chest-based ECG devices such as Frontier X Plus (medical-grade, FDA-cleared, prescription-based) and Frontier X2 (wellness) extend the value of continuous heart tracking.
Frontier X Plus provides medical-grade, long-term ECG monitoring, cleared by the FDA to detect Atrial Fibrillation (AFib), Tachycardia, and Bradycardia. It enables physicians and users to assess heart rhythm trends under various conditions for diagnostic and follow-up purposes. Frontier X2, on the other hand, is designed for wellness and performance insights. It records continuous ECG and heart rate during activities such as exercise, altitude training, and sleep, helping users understand their heart rhythm patterns and physiological responses over time.
Both devices are patchless and chest-based, offering accurate, motion-resistant ECG recording that supports long-term tracking of heart rhythm dynamics and physical performance.
By correlating environmental factors such as temperature, altitude, and exertion with long-term ECG and heart rate data, these tools provide valuable insights into how external stressors influence cardiac performance – supporting informed lifestyle decisions and personalized training optimization.
Practical Tips to Reduce AFib Risk at Different Temperatures and Altitudes
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration increases heart rate and electrolyte imbalance – both can trigger AFib.
- Avoid Sudden Temperature Changes: Allow your body to acclimate gradually to heat or cold.
- Acclimatize Before Intense Activity: Especially at altitude, give your cardiovascular system time to adjust.
- Monitor Your Heart Continuously: Use reliable ECG devices like Frontier X Plus to spot irregularities early.
- Maintain Electrolyte Balance: Replace lost minerals during prolonged workouts or high-heat exposure.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, or breathlessness after temperature or altitude changes warrant medical review.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical advice if you experience:
- Persistent heart fluttering or rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness, fainting, or shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort or fatigue unrelated to exertion
These could be early signs of AFib, heart arrhythmia, or oxygen-related cardiac stress.
FAQs
1. Can altitude trigger AFib?
Yes. High-altitude environments with low oxygen levels can increase heart rate and cardiac strain, sometimes triggering AFib or atrial arrhythmia, especially in individuals with prior heart rhythm issues.
2. Why does my heart race when it’s hot or cold?
Both heat and cold stress the heart differently. Heat causes dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, while cold increases blood pressure and heart workload – either can elevate heart rate and trigger arrhythmias.
3. Can exercise at altitude cause AFib?
Intense workouts at high altitude may increase sympathetic activation and oxygen demand, occasionally leading to AFib episodes. Monitoring ECG continuously during such training is highly recommended.
4. What is the best way to monitor my heart for AFib?
Continuous ECG monitors like Frontier X Plus (medical grade) provide accurate, long-duration ECG data to detect atrial fibrillation and heart rhythm abnormalities during daily activities or sleep.
5. How can I prevent AFib related to temperature or altitude?
Gradual acclimatization, hydration, electrolyte balance, and avoiding extreme exertion are key preventive steps. Long-term ECG monitoring can help detect changes before they escalate.
Understanding Angina: A Warning Sign from the Heart
Chest pain is one of the most alarming symptoms anyone can experience. While not every instance of chest pain means a heart attack, it should never be ignored – especially when it’s angina.
Angina pectoris, commonly called angina, is not a disease itself but a symptom of underlying heart disease, typically coronary artery disease (CAD). It occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood, often due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries.
When the oxygen supply is insufficient, the heart sends distress signals in the form of chest discomfort, pressure, or pain. Recognizing and addressing these signs early can be the key to preventing a serious cardiac event.
What Does Angina Feel Like?
Angina pain is often described as:
- Tightness or pressure in the chest
- Burning, squeezing, heaviness, or even shooting or stabbing discomfort that may radiate to the jaw, neck, shoulders, arms, or back. This discomfort may not only spread to these areas but can also originate from them. However, individuals with diabetic autonomic neuropathy may not experience any of these sensations due to reduced pain perception.
- A feeling of fullness or discomfort, especially during exertion
- Shortness of breath, nausea, or fatigue are common, particularly in women and older adults. However, some women, especially older women, may not experience these typical symptoms. Instead, they may present with atypical signs such as subtle changes in cognitive function or symptoms that mimic other conditions, like a urinary tract infection.
The discomfort usually lasts a few minutes and eases with rest or medication like nitroglycerin. However, persistent or worsening pain should always be evaluated immediately – as it could indicate a heart attack.
Types of Angina
Angina is classified into several types, each reflecting a different underlying mechanism or risk level:
1. Stable Angina
The most common form, stable angina occurs predictably with physical exertion, stress, or cold weather and subsides with rest. It signals partial blockage of coronary arteries but indicates a chronic, manageable condition if treated properly.
2. Unstable Angina
This is a medical emergency. Unstable angina occurs at rest or with minimal exertion and may last longer than a few minutes. It often means a plaque rupture or clot has significantly reduced blood flow – a warning sign of an impending heart attack.
3. Variant (Prinzmetal’s) Angina
Caused by spasms in the coronary arteries rather than plaque buildup, this form of angina can occur at rest, often at night or early morning. It may cause severe pain and temporary ECG changes but usually resolves with vasodilators.
4. Microvascular Angina
Sometimes referred to as cardiac syndrome X, this type involves dysfunction of the small blood vessels of the heart. It is more common in women, and traditional angiograms may appear normal despite ongoing ischemia (low blood flow).
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Angina
Angina arises primarily due to reduced coronary blood flow, but several factors increase the risk:
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol levels
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Family history of heart disease
Each of these contributes to damage or narrowing of the coronary arteries, making it harder for the heart to receive sufficient oxygen during times of increased demand.
When Chest Pain Should Not Be Ignored
While not every chest discomfort is heart-related, angina-like symptoms should always prompt evaluation. Seek immediate help if:
- Chest pain occurs at rest or during minimal activity
- Pain spreads to the arms, back, neck, or jaw
- It is accompanied by sweating, nausea, or breathlessness
- The discomfort persists for more than 5–10 minutes despite rest
In these cases, call emergency services – it could be unstable angina or a heart attack requiring urgent medical care.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Angina
Diagnosing angina involves a combination of clinical assessment, ECG monitoring, and imaging tests. Common diagnostic approaches include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects abnormalities in heart rhythm and ischemic changes.
- Stress Test: Monitors ECG during physical exertion to assess blood flow under stress.
- Continuous ECG Monitoring: Tracks real-time heart rhythm patterns and transient ischemic changes that may occur outside of clinical settings.
- Echocardiogram: Evaluates heart function and blood flow.
- Coronary Angiography (CT and invasive): Visualizes arterial blockages through X-ray imaging.
Continuous ECG or wearable heart monitors can detect short-lived ischemic episodes that may go unnoticed in routine clinic tests, providing deeper insights into daily heart performance.
Treatment for Angina: Restoring Blood Flow and Relieving Pain
The goal of angina treatment is to improve blood flow to the heart, reduce symptoms, and prevent future cardiac events.
Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3s
- Exercise regularly, under medical supervision
- Manage stress and maintain healthy body weight
- Control diabetes, cholesterol, and blood pressure
Medications
(Important: The medications listed below are for general awareness only. Treatment should always be determined by a qualified physician. Never start, stop, or adjust any medication without consulting your healthcare provider.)
- Nitrates (e.g., Nitroglycerin): Dilate blood vessels to improve blood flow and relieve pain
- Beta-blockers: Slow the heart rate, reducing oxygen demand
- Calcium channel blockers: Relax arteries and lower blood pressure
- Antiplatelet agents (e.g., Aspirin): Prevent clot formation
- Statins: Lower cholesterol and stabilize arterial plaques
Medical Procedures
If medication alone isn’t enough, doctors may recommend:
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: To open narrowed arteries
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): To reroute blood flow around blockages
Long-Term ECG Monitoring and the Role of Frontier X Plus
For individuals experiencing recurrent chest discomfort or suspected angina episodes, long-term ECG monitoring provides valuable insights into heart rhythm patterns.
Devices like Frontier X Plus allow users to record extended ECG waveforms and heart rate, with the option for live viewing during daily activities or workouts. This enables clinicians and users to understand how the heart responds under stress, exertion, and rest.
Long-term ECG monitoring can:
- Capture transient changes in heart rhythm that short ECGs may miss
- Track heart rate variability and rhythm patterns
- Help clinicians correlate symptoms, such as chest discomfort, with recorded ECG trends
For patients with stable angina or undergoing post-treatment follow-up, Frontier X Plus provides a non-invasive way to observe ongoing heart activity in relation to daily lifestyle, supporting continuous evaluation and proactive heart health management.
Living with Angina: Managing and Preventing Recurrence
Angina can be a lifelong condition, but it doesn’t have to limit your life. The key is vigilant management and consistent monitoring:
- Follow your medication regimen carefully.
- Track your heart rate and ECG using advanced wearables.
- Maintain regular follow-ups with your cardiologist.
- Stay attentive to warning signs and avoid triggers like overexertion and emotional stress.
With early detection and smart monitoring, most patients with angina can lead active, fulfilling lives while reducing their risk of heart attack.
Key Takeaways
- Angina is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
- It signals underlying coronary artery disease and can precede a heart attack.
- Stable angina occurs with exertion; unstable angina can appear at rest and is an emergency.
- Diagnosis involves ECG, stress testing, and sometimes angiography.
- Long-term ECG monitoring devices, such as Frontier X Plus, record extended heart rhythm data, allowing clinicians and users to observe transient changes in cardiac activity and support ongoing heart health evaluation.
FAQs
Q1: What causes angina chest pain?
Angina occurs when reduced blood flow through narrowed coronary arteries limits oxygen supply to the heart muscle, causing pain or discomfort.
Q2: How do I know if my chest pain is angina or a heart attack?
Angina usually improves with rest or medication, while heart attack pain is more severe, lasts longer, and may include nausea, sweating, and breathlessness. Always seek emergency help if uncertain.
Q3: What is the treatment for angina?
Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications like nitrates or beta-blockers, and in severe cases, angioplasty or bypass surgery to restore blood flow.
Q4: Can angina be detected on ECG?
Yes. Angina-related ischemia often shows ST-segment or T-wave changes on ECG. Continuous ECG monitoring can detect transient episodes missed in short tests.
Q5: How can continuous ECG monitoring help angina patients?
Long-term ECG devices like the Frontier X Plus record continuous heart rhythm data and allow live viewing of ECG signals. This enables users and clinicians to review heart activity during episodes of chest discomfort and understand how the heart responds to exertion or stress, supporting further clinical evaluation and personalized management.
Understanding POTS: When Standing Up Triggers a Rapid Heartbeat
Have you ever felt your heart racing or your head spinning the moment you stand up from sitting or lying down? This could be a sign of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) – a condition that affects blood flow and the body’s ability to regulate heart rate and blood pressure when changing positions.
POTS is a form of dysautonomia, meaning it involves dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) – the part of the nervous system that controls automatic functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and blood vessel constriction.
When a healthy person stands up, blood briefly pools in the legs due to gravity, and the ANS quickly compensates by tightening blood vessels and slightly increasing the heart rate to maintain adequate blood flow to the brain. If you have POTS, this regulation doesn’t work efficiently. Your heart rate may increase by more than 30 bpm or exceed 120 bpm within 10 minutes of standing without a corresponding drop in blood pressure, causing symptoms like lightheadedness, palpitations, fatigue, or even fainting.
Key Symptoms of POTS
POTS can manifest differently among individuals, but common signs may include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness upon standing
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) – often >110 bpm while upright
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance
- Palpitations or “pounding” heartbeat
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or GI discomfort
- Cold or blotchy hands and feet
These symptoms tend to worsen with heat, dehydration, prolonged standing, or sudden postural changes.
Types of POTS
Researchers recognize several subtypes of POTS based on the dominant underlying mechanism:
- Neuropathic POTS:
Caused by peripheral nerve damage that impairs blood vessel constriction in the legs, leading to excessive blood pooling. - Hyperadrenergic POTS:
Marked by an overactive sympathetic nervous system and elevated norepinephrine levels, resulting in high heart rate, tremors, and anxiety-like symptoms. - Hypovolemic POTS:
Characterized by low blood volume, which can worsen dizziness and heart rate instability. - Secondary POTS:
Develops as a consequence of another condition, such as autoimmune disorders, diabetes, long COVID, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS), or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Why Does POTS Cause Dizziness When Standing?
The hallmark dizziness or “head rush” in POTS arises from reduced blood flow to the brain upon standing. When you rise quickly, gravity causes about 500–1000 ml of blood to pool in the lower body. In healthy individuals, the ANS corrects this within seconds. But in POTS patients, the blood vessels fail to constrict efficiently, and the heart compensates by beating faster – often exceeding 120 bpm at rest or early in standing posture.
Despite this rapid heart rate, the brain may still receive less oxygenated blood, leading to symptoms like dizziness, blurred vision, or near-fainting episodes.
Common Triggers and Causes of POTS
While the exact cause of POTS remains multifactorial, several triggers and risk factors have been identified:
- Viral infections (including COVID-19)
- Autoimmune conditions such as lupus or Sjögren’s syndrome
- Deconditioning or prolonged bed rest
- Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in young women
- Genetic predisposition
- Low blood volume or hypovolemia
- Chronic stress or anxiety disorders
Emerging research also indicates that POTS is more common in women aged 15–50, possibly linked to hormonal influences on autonomic regulation.
Diagnosis: How Is POTS Identified?
Diagnosing POTS often involves ruling out other conditions that cause similar symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, low blood pressure, anemia, or dehydration.
Common diagnostic steps include:
- Tilt Table Test:
The gold standard for POTS diagnosis. The patient is strapped to a table that tilts upright, and continuous ECG and blood pressure monitoring assess changes upon standing. - Active Stand Test:
Heart rate and blood pressure are recorded while lying down, then after standing for 10 minutes. A heart rate rise ≥30 bpm (or ≥40 bpm in teens) without hypotension suggests POTS. - Blood Volume and Norepinephrine Levels:
These may be measured to identify hypovolemic or hyperadrenergic subtypes. - Continuous ECG Monitoring:
Continuous or wearable ECG devices help track abnormal heart rate patterns in daily life, distinguishing between episodic tachycardia and persistent autonomic imbalance.
Treatment Options for POTS
There’s no single cure for POTS, but symptoms can be managed effectively with lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medications.
Lifestyle and Non-Pharmacologic Strategies
- Increase Fluid and Salt Intake: Boosting blood volume can help stabilize blood pressure.
- Compression Garments: Support stockings reduce blood pooling in the legs.
- Gradual Exercise Programs: Recumbent cycling and swimming build tolerance.
- Avoid Prolonged Standing, Sitting or Heat Exposure.
- Elevate the Head of the Bed: Reduces overnight fluid shifts.
Medical Treatments
- Beta-blockers to reduce heart rate
- Fludrocortisone to increase fluid retention
- Midodrine to constrict blood vessels
- Ivabradine (in selective cases) for heart rate control
- SSRIs or SNRIs to modulate autonomic function
Each treatment plan is individualized based on symptom patterns and POTS subtype.
The Role of Long-Term ECG Monitoring in POTS Management
Devices like the FDA-cleared, medical grade Frontier X Plus allow long-term ECG monitoring, enabling patients and clinicians to visualize heart rate fluctuations and rhythm changes throughout the day – especially during posture shifts, exercise, or recovery.
Unlike standard Holter monitors that capture data for only 24 hours, the Frontier X Plus enables long-term ECG (24 h per 30 min of charge) and heart rate tracking over extended periods. It is cleared for detecting cardiac rhythm irregularities such as atrial fibrillation (AFib), tachycardia, and bradycardia, while also helping users and clinicians observe physiological patterns – such as heart rate changes during posture shifts – that may warrant further evaluation.
By combining ECG trends with activity and posture data, users gain a deeper understanding of how daily habits and triggers influence their heart’s autonomic response, allowing better management and lifestyle adjustment.
Living with POTS: Adapting and Thriving
While POTS can initially feel overwhelming, understanding the condition empowers individuals to take control of their symptoms. With the right combination of hydration, diet, gradual exercise, and continuous monitoring, many people with POTS can return to full activity levels.
The key lies in tracking your body’s signals – both mechanical (through posture and activity) and electrical (through ECG and heart rate) – to manage the delicate balance of your autonomic system.
Key Takeaways
- POTS is a form of autonomic dysfunction causing excessive heart rate increase upon standing.
- Common symptoms include dizziness, palpitations, and fatigue.
- Diagnosis relies on tilt table tests and continuous ECG monitoring.
- Hydration, salt intake, compression, and graded exercise are first-line treatments.
- Devices like Frontier X Plus enable long-term ECG tracking to personalize therapy and identify triggers.
SEO-Optimized FAQs
Q1: What causes POTS syndrome?
POTS occurs when the autonomic nervous system fails to regulate blood flow properly upon standing, often due to neuropathy, low blood volume, or an overactive sympathetic response.
Q2: Why does my heart rate increase when I stand up?
Standing causes blood to pool in the lower body. In POTS, blood vessel constriction is impaired, forcing the heart to beat faster to maintain blood flow to the brain.
Q3: How is POTS diagnosed?
A tilt table test or active stand test measuring heart rate and blood pressure changes helps confirm POTS. Continuous ECG monitoring can support diagnosis by tracking heart rate patterns in real life.
Q4: What is the treatment for POTS?
Treatment includes lifestyle adjustments like increasing fluid and salt intake, wearing compression garments, and in some cases, medications such as beta-blockers or fludrocortisone.
Q5: Can long-termECG monitoring help with POTS?
Yes. Devices like Frontier X Plus continuously track heart rate and rhythm changes, offering insights into postural responses and helping optimize treatment plans.
Our hearts are remarkable organs, tirelessly pumping blood to sustain life. But sometimes, the heart beats faster than normal, even at rest. This condition, known as tachycardia, can be alarming if left unchecked. Understanding its signs, causes, and treatment options is essential to maintain heart health and prevent complications.
What Is Tachycardia?
Tachycardia is defined as a heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute (bpm) in adults at rest. For some individuals, even a heart rate of 110 at rest can indicate mild tachycardia. While occasional increases in heart rate can occur due to exercise, stress, or caffeine, persistent tachycardia may signal an underlying heart problem that requires attention.
Tachycardia can be classified based on its origin:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): Starts in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT): Begins in the lower chambers (ventricles) and can be more serious.
- Sinus tachycardia: A faster-than-normal heart rate originating from the sinus node, usually triggered by stress, fever, or other non-cardiac causes.
Signs and Symptoms of Tachycardia
Tachycardia may present subtly or with noticeable symptoms. Common signs include:
- Rapid heartbeat at rest: Feeling your heart racing when you are not physically active.
- Palpitations: Awareness of irregular or forceful heartbeats.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Reduced blood flow to the brain and body due to the heart not filling properly
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty in breathing as the heart struggles to pump efficiently.
- Chest pain or discomfort: Can indicate the heart is under stress.
- Fatigue or weakness: Reduced oxygen delivery to muscles and organs.
Some individuals may have mild tachycardia with minimal symptoms, making early detection difficult. Persistent or unexplained episodes warrant a medical check-up.
Common Causes of Tachycardia
Understanding the underlying cause is key to effective treatment. Causes can be cardiac or non-cardiac.
Cardiac Causes
- Heart-related conditions:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Heart failure
- Heart valve disease
- Previous heart attack
- Arrhythmias:
Conditions like atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter can trigger abnormal rapid heartbeats.
Non-Cardiac Causes
- Lifestyle and physiological factors:
- Stress, anxiety, or panic attacks
- Excess caffeine, nicotine, or alcohol
- High fever or infection
- Medical conditions:
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Medications:
Certain medications, including decongestants and stimulants, can elevate heart rate.
Diagnosing Tachycardia
Accurate diagnosis is critical to determine the right treatment for rapid heart rate or treatment for fast heartbeat. Doctors may use:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Holter or long-term ECG monitoring: Devices like Frontier X Plus can track heart rhythm continuously for 24 hours, capturing intermittent episodes that standard ECGs may miss. Continuous monitoring helps clinicians understand the frequency, duration, and triggers of tachycardia.
- Blood tests: To check for thyroid function, electrolyte levels, and anemia.
- Echocardiogram: Assesses the heart’s structure and pumping efficiency.
Treatment for Tachycardia
The approach depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause. Treatments range from lifestyle changes to medications and medical procedures.
Lifestyle Modifications
For mild tachycardia triggered by lifestyle factors:
- Limit caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine
- Practice stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation
- Maintain regular exercise routines (under medical supervision if necessary)
- Ensure proper hydration and sleep
Medications
Several drugs can help regulate heart rate, often prescribed depending on the type of tachycardia:
- Beta-blockers: Slow down the heart rate and reduce workload.
- Calcium channel blockers: Help control rhythm in certain arrhythmias.
- Antiarrhythmic medications: Used in more persistent or serious arrhythmias.
Medical Procedures
In cases where medications are insufficient:
- Cardioversion: A controlled electrical shock to restore normal rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: A procedure to destroy small areas of heart tissue causing abnormal signals.
- Pacemaker implantation: For cases of brady-tachy syndrome or conduction problems.
Emergency Situations
Rapid or sustained ventricular tachycardia, chest pain, fainting, or severe shortness of breath requires immediate medical attention.
When to See a Doctor
Seek professional care if you experience:
- Persistent rapid heartbeat at rest
- Chest pain or pressure
- Fainting or severe dizziness
- Shortness of breath not related to exertion
Early diagnosis can prevent complications like stroke, heart failure, or cardiac arrest.
The Role of Long-term ECG Monitoring
Traditional in-office ECGs provide a snapshot of your heart’s rhythm but may miss intermittent episodes. Long-term ECG monitoring with devices like Frontier X Plus offers near real-time data on heart rate and rhythm for extended periods. This technology allows doctors to detect mild or transient tachycardia, assess triggers, and tailor treatment for fast heartbeat effectively. By capturing subtle changes in heart activity, patients gain proactive insights into heart health and timely interventions.
Preventing Tachycardia
While some forms are unavoidable due to underlying heart conditions, you can reduce risk factors:
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
- Maintain a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Exercise regularly, avoiding overexertion
- Avoid stimulants like caffeine or nicotine in excess
- Monitor your heart rate periodically, especially if you have risk factors
Tachycardia can be intimidating, but with awareness, monitoring, and timely intervention, it is manageable. Understanding the signs, causes, and solutions allows you to take proactive steps to protect your heart. Continuous ECG monitoring, medications, lifestyle modifications, and professional care together provide a comprehensive approach to managing a fast or irregular heartbeat. Don’t ignore persistent rapid heartbeats—your heart health depends on timely action.
FAQs About Tachycardia
Q1: Is a heart rate of 110 at rest dangerous?
A heart rate above 100 bpm at rest is classified as tachycardia. Occasional spikes may be harmless, but persistent readings of 110 bpm or more should be evaluated by a doctor.
Q2: Can mild tachycardia resolve on its own?
Yes, mild tachycardia caused by stress, caffeine, or temporary conditions may subside once triggers are removed. However, recurrent episodes warrant medical assessment.
Q3: What is the best medicine for tachycardia?
Treatment depends on the type and cause. Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs are commonly prescribed. Only a cardiologist can determine the most appropriate medication.
Q4: Can tachycardia be prevented?
Lifestyle modifications, stress management, avoiding stimulants, and monitoring heart health can reduce risk. Regular check-ups are crucial for early detection.
Q5: How does Long-term ECG monitoring help?
Long-termECG monitoring captures intermittent episodes, even when you are at rest, helping doctors identify triggers and tailor treatment for fast heartbeat or rapid heart rate effectively. Devices like Frontier X Plus make long-term monitoring convenient and precise.
Q6: Is tachycardia always a sign of heart disease?
Not always. While tachycardia can indicate underlying cardiac conditions, it may also result from stress, caffeine, fever, or hormonal imbalances. Proper evaluation is necessary.
Understanding Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD), also known as Coronary Heart Disease, remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. It develops when the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup – a process known as atherosclerosis.
When these arteries are partially or completely blocked, the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen. This reduced blood flow – known as cardiac ischemia or myocardial ischemia – can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, discomfort in the arms, neck, jaw and back, or even lead to a heart attack. Over time, chronic ischemia can also result in ischemic heart failure, where the heart weakens and struggles to pump effectively.
What Causes Ischemic Heart Disease?
The root cause of IHD lies in plaque formation – fatty deposits that accumulate on the arterial walls. These plaques are made up of cholesterol, calcium, and other cellular waste products. When they harden and narrow the arteries, blood flow to the heart becomes restricted, leading to coronary artery disease (CAD)
Several factors increase the risk of developing IHD, including:
- High cholesterol levels and high blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet high in saturated fats and trans fats
- Chronic stress
- Family history of heart disease (non-modifiable risk factors)
Over time, these risk factors damage the inner lining of arteries, making it easier for plaque to accumulate and cause clogged arteries – the hallmark of ischemic heart disease.
Symptoms of Ischemic Heart Disease
The symptoms of IHD can range from mild discomfort to severe cardiac events. However, many people experience silent ischemia, where reduced blood flow occurs without noticeable symptoms. For others, the signs may be more evident.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Chest pain (Angina):
A classic sign of ischemia, angina feels like pressure, squeezing, or burning in the chest. It often occurs during exertion or stress and improves with rest. - Shortness of breath:
Reduced oxygen supply to the heart can make even mild activity feel exhausting. - Fatigue and weakness:
The heart’s inability to pump sufficient blood can cause persistent tiredness, even without exertion. - Palpitations or irregular heartbeat:
Disrupted blood flow can trigger cardiac arrhythmias, increasing the risk of complications. - Pain in arms, jaw, neck, or back:
These referred pain symptoms often accompany angina and can indicate heart ischemia. - Nausea, sweating, or dizziness:
These are particularly common in women or older adults experiencing ischemic cardiac episodes.
Note: In individuals with diabetic autonomic neuropathy or older women, ischemic heart disease may present atypically. Classic chest pain may be absent due to nerve dysfunction, leading to silent ischemia. Symptoms can include fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, palpitations, nausea, and non-chest discomfort. Awareness is key for timely diagnosis
If chest discomfort persists or worsens despite rest, it could signal a heart attack (myocardial infarction) – a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Types of Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease is not a single condition but an umbrella term encompassing several related disorders:
1. Stable Angina
This occurs when the heart’s oxygen demand temporarily exceeds supply – typically during exercise or emotional stress. Symptoms are predictable and improve with rest or medications such as nitroglycerin.
2. Unstable Angina
A more serious condition, unstable angina can occur even at rest and may not respond to usual treatment. It indicates a high risk of an impending heart attack due to a ruptured plaque or sudden clot formation.
3. Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
When a coronary artery is completely blocked, part of the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, leading to tissue death. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical to limit heart damage and prevent heart failure.
4. Silent Ischemia
Not all ischemic episodes cause pain or noticeable symptoms. Silent ischemia is often detected only through ECG monitoring, stress tests, or cardiac imaging.
5. Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Chronic ischemia weakens the heart muscle over time, leading to ischemic heart failure – characterized by reduced ejection fraction and fluid buildup.
How Is Ischemic Heart Disease Diagnosed?
Early and accurate CAD diagnosis plays a key role in preventing severe complications. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects electrical abnormalities that indicate ischemia or past heart attacks.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to assess heart structure and function.
- Stress Testing: Monitors ECG changes during exercise or medication-induced stress.
- Coronary Angiography: Provides detailed imaging of coronary arteries to locate blockages.
- CT Coronary Angiogram: A non-invasive scan to visualize plaques and arterial narrowing.
- Blood Tests: Check for cardiac biomarkers and cholesterol levels.
Effective Treatments for Ischemic Heart Disease
Treatment depends on the severity of blockage and symptoms but generally aims to restore blood flow, reduce symptoms, and prevent future cardiac events.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Engaging in regular physical activity (after physician clearance)
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through mindfulness or yoga
These foundational steps can significantly slow the progression of atherosclerosis.
2. Medications
Doctors may prescribe:
- Antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel) to prevent clot formation
- Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers to reduce heart workload
- Statins to lower LDL cholesterol and stabilize plaque
- Nitrates to relieve angina
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs for blood pressure and cardiac protection
3. Medical Procedures and Surgery
- Angioplasty and Stenting: A balloon-tipped catheter opens the blocked artery, often followed by stent placement.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure that redirects blood flow around severely blocked arteries using grafts from other vessels.
These interventions can dramatically improve blood flow and quality of life in advanced CAD.
Role of continuous ECG in Ischemic Heart Disease
Traditional tests capture heart activity at specific moments, but many rhythm changes or ischemic episodes occur unpredictably – during daily activities, stress, or sleep.
Continuous ECG devices like Frontier X2 enables individuals to record heart trends in near real time, helping both users and clinicians observe variations that may correlate with symptoms such as palpitations, breathlessness, or chest discomfort.
By providing long-duration ECG data, these tools support clinician review, assist in monitoring recovery, and offer insights into how the heart responds during everyday life. This continuous tracking can complement standard clinical assessments and promote more personalized heart health awareness.
Preventing Ischemic Heart Disease
While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices have the greatest impact.
Preventive steps include:
- Regular check-ups for cholesterol, blood pressure, and glucose levels
- Staying physically active and avoiding prolonged sitting
- Eating a balanced, Mediterranean-style diet
- Using wearable ECG devices to understand heart rhythm patterns and exercise responses
- Consulting a doctor promptly for any chest discomfort
Consistent self-awareness and early medical guidance can help manage risk and maintain long-term heart health.
FAQs on Ischemic Heart Disease
- What is the main cause of ischemic heart disease?
Atherosclerosis – plaque buildup in coronary arteries that restricts blood flow. Risk factors include high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressure. - How do I know if I have blocked arteries?
Common signs include chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Some individuals may have silent ischemia, detected only through clinician-ordered tests such as ECG or imaging. - Can ischemic heart disease be reversed?
Plaque cannot be completely removed, but its progression can be slowed or stabilized through lifestyle changes, medication, and medical management. - What’s the difference between ischemic heart disease and heart failure?
IHD is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle; if left unmanaged, it can lead to heart failure, where the heart’s pumping ability declines. - How can continuous ECG devices help?
Devices like Frontier X2 provide long-duration ECG recording, helping individuals and clinicians observe variations that can inform further evaluation or treatment discussions.
Final Thoughts
Ischemic Heart Disease remains a major global health concern, but it is also highly manageable with early awareness and the right interventions.
Combining lifestyle changes, medical therapy, and continuous ECG for heart insight empowers individuals to stay proactive about their heart health.
Your heart drives every moment of your life – protect it through knowledge, prevention, and consistent care.
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and heart failure (HF) are two of the most common – and closely connected – cardiovascular disorders worldwide. It is often uncertain whether heart failure leads to atrial fibrillation or develops as a result of it, since both conditions share complex, interdependent mechanisms. This interplay can create a vicious cycle that profoundly affects heart function, quality of life, and overall survival. Recognizing and understanding the connection between AFib and heart failure are essential for early detection, prevention, and effective management.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
Atrial fibrillation is a type of cardiac arrhythmia – an irregular and sometimes rapid heart rhythm. In AFib, the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat chaotically and out of sync with the lower chambers (ventricles). This irregular rhythm can cause poor blood flow, palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, or fatigue.
AFib affects millions globally, and its prevalence increases with age and conditions like hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and coronary artery disease. What makes AFib particularly concerning is its association with major complications such as stroke and heart failure.
What Is Heart Failure?
Heart failure doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working. It means the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. There are two main types:
- Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF): The heart’s pumping ability is weakened.
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF): The heart’s pumping strength is normal, but stiffness prevents proper filling.
Both types can occur in patients with AFib, often worsening symptoms and complicating treatment.
The Two-Way Relationship Between AFib and Heart Failure
AFib and heart failure often coexist – and each condition can worsen the other through distinct mechanisms:
- AFib leading to Heart Failure
When the atria beat irregularly and rapidly, the ventricles may also beat too fast. This persistent tachycardia can strain the heart muscle, leading to tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy – a reversible form of heart failure caused by sustained rapid heart rates.
AFib also reduces atrial contraction, which normally contributes up to 30% of ventricular filling. Without it, the heart’s pumping efficiency drops, increasing the risk of fluid buildup, shortness of breath, and fatigue. - Heart Failure leading to AFib
In heart failure, increased pressure and stretching of the atria can disrupt the heart’s electrical system. This remodeling creates the perfect environment for AFib to develop. High levels of stress hormones, inflammation, and fibrosis further damage cardiac tissue, perpetuating arrhythmia risk.
Together, these processes form a feedback loop – where some industry experts believe that AFib may worsen heart failure and that heart failure may increase AFib risk
How Common Is the Overlap?
Studies suggest that up to 40% of people with newly diagnosed heart failure had AFib at some stage of their illness. The presence of both conditions is associated with worse outcomes, including more frequent hospitalizations, reduced exercise capacity, and higher mortality rates.
Symptoms: How to Tell When AFib or Heart Failure Is Getting Worse
Many symptoms overlap, making it challenging to distinguish which condition is responsible. Common signs include:
- Shortness of breath (especially during activity or lying down)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest discomfort
- Rapid weight gain from fluid buildup
Because AFib can come and go (paroxysmal AFib), symptoms may fluctuate – making continuous rhythm monitoring crucial.
The Hidden Dangers: Stroke and Sudden Worsening
AFib increases the risk of stroke by five times. In heart failure patients, this risk is even higher because blood flow is already compromised. AFib can also worsen heart failure suddenly, causing fluid accumulation in the lungs – a condition known as acute decompensated heart failure, which requires emergency treatment.
Why Detecting AFib Early Matters in Heart Failure Prevention
Early recognition and management of AFib can prevent structural heart damage. Continuous monitoring allows for detection of asymptomatic (“silent”) AFib, which may otherwise go unnoticed but still poses a high stroke and heart failure risk.
In several studies, AFib episodes lasting greater than 5 minutes were associated with an increased likelihood of stroke and progression to sustained AFib. Early rhythm control strategies – such as medications or catheter ablation – can prevent cardiac remodeling and delay or reverse heart failure progression.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify AFib and Heart Failure
A thorough evaluation includes:
- 12-lead Electrocardiogram (ECG): To identify irregular rhythm.
- Echocardiogram: To assess heart function, chamber size, and ejection fraction.
- Holter or Continuous Single Lead ECG Monitoring: To detect intermittent or exercise-induced AFib.
- Blood tests: To check for thyroid, kidney, and electrolyte abnormalities.
- Cardiac MRI or CT scan: In selected cases to evaluate structural disease.
Treatment Strategies: Managing Both AFib and Heart Failure Together
Treating AFib in the context of heart failure requires balancing rhythm control, rate control, and stroke prevention.
1. Rate Control
The goal is to maintain a manageable heart rate (typically below 100 bpm at rest) using medications such as:
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers (in select patients)
- Digoxin (for additional control in heart failure)
2. Rhythm Control
Restoring and maintaining normal sinus rhythm can improve symptoms and heart function. Options include:
- Antiarrhythmic medications
- Electrical cardioversion
- Catheter ablation, which isolates arrhythmic foci in the atria – especially effective in patients with symptomatic AFib and reduced ejection fraction.
3. Stroke Prevention
Anticoagulation is essential. The CHA₂DS₂-VASc score helps assess stroke risk and guide therapy with agents like apixaban, rivaroxaban, or warfarin.
4. Heart Failure Optimization
Medications such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors not only improve heart function but also lower the risk of recurrent AFib episodes.
Lifestyle Modifications That Benefit Both Conditions
- Maintain a healthy weight and control blood pressure.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine, both of which can trigger AFib.
- Get regular physical activity – but avoid overexertion as advised by physician/doctor.
- Prioritize sleep quality, as sleep apnea worsens both AFib and HF.
- Manage stress, which can increase arrhythmia risk.
The Role of Long-Term ECG Monitoring
One of the key challenges in managing AFib and heart failure is the intermittent nature of symptoms. Long-term ECG monitoring – through advanced tools like the Frontier X Plus – bridges this gap by providing long-term rhythm data during rest, activity, and sleep.
Unlike smartwatches that rely on optical sensors, the Frontier X Plus offers medical-grade chest-based ECG accuracy, validated against traditional 12-lead ECGs. It continuously captures heart rhythm patterns, helping identify silent AFib episodes, sustained tachycardia, or bradycardia – all vital indicators of cardiac strain.
For individuals with AFib, heart failure, or both, using long-term ECG monitoring empowers proactive management, allowing physicians to adjust medications or recommend interventions before complications develop.
Prognosis: Can You Live Well with AFib and Heart Failure?
Absolutely – with timely detection, consistent monitoring, and lifestyle management. Advances in ablation therapy, new-generation anticoagulants, and wearable ECG technology mean patients can maintain excellent quality of life while reducing their risk of stroke or hospitalization.
The key lies in personalized care – knowing your rhythm, understanding your triggers, and partnering with your healthcare provider to stay ahead.
FAQs on AFib and Heart Failure
- Can AFib cause heart failure even if I have no symptoms?
Yes. Silent AFib can lead to structural heart damage and impaired pumping function over time – making early detection crucial. - Which comes first – AFib or heart failure?
It varies. AFib can trigger heart failure due to fast rates, and heart failure can cause AFib due to chamber stress. Often, both progress together. - Does controlling heart rate help prevent heart failure?
Yes. Keeping your heart rate within a target range reduces cardiac workload and helps preserve heart muscle function. - How can I track my AFib episodes at home?
You can monitor your heart’s activity at home using tools that record ECG over time. The Frontier X Plus is a medical-grade, FDA-cleared, long-term ECG monitor that records detailed heart rhythm data, enabling physicians to review and assess patterns that may be consistent with AFib or other rhythm irregularities. For personal wellness insights, the Frontier X2 offers ECG and heart-rate tracking during workouts or daily life, helping you observe how your heart responds to exertion and recovery – supporting more informed conversations with your healthcare provider. - What lifestyle changes lower the risk of both AFib and heart failure?
Regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, managing blood pressure, avoiding alcohol binges, and getting good sleep are proven to help.
Sleep is supposed to be restorative. But for millions of people, the night is filled with silent threats to their heart health. One of the most overlooked dangers? Sleep apnea – a sleep condition that doesn’t just disrupt breathing but can also trigger dangerous heart arrhythmias.
If you’ve ever experienced palpitations when lying down, noticed an erratic sleep heart rate, or woken up gasping for air, you might be facing more than just a bad night’s sleep. Sleep apnea and arrhythmias are closely linked, and understanding this connection is vital for protecting your heart health.
Fortunately, with advancements in continuous ECG monitoring, there’s now a way to keep tabs on your heart rhythm while you sleep – giving you and your healthcare provider critical insights into how your heart responds during the night.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. The most common type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where throat muscles intermittently relax, blocking the airway. There’s also central sleep apnea (CSA), where the brain fails to send the right signals to control breathing.
Common symptoms include:
- Loud snoring
- Episodes of stopped breathing (often noticed by a partner)
- Waking up gasping or choking
- Heart palpitations at night
- Morning headaches
- Daytime fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
Sleep problems like apnea don’t just rob you of rest – they can strain the heart and increase the risk of arrhythmias, heart failure, and even stroke.
The Sleep Apnea–Arrhythmia Connection
Research shows that sleep apnea significantly raises the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, particularly in those with atrial fibrillation (AFib) and ventricular arrhythmias.
Here’s why:
- Interrupted breathing drops oxygen levels, triggering the heart to beat irregularly.
- Apnea episodes activate stress hormones, increasing heart rate variability and cardiac strain.
- Repeated nighttime awakenings cause sudden spikes in blood pressure and sympathetic nervous system activity, leading to erratic heart rhythms during sleep.
In fact, a large portion of nocturnal arrhythmias – including AFib, premature ventricular complexes (PVCs), and ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach) – are linked to sleep conditions like apnea.
Signs Your Heart May Be Struggling at Night
How can you tell if sleep apnea is affecting your heart? Common red flags include:
- Palpitations when lying down
- A feeling of a sudden rapid heartbeat during the night
- Heart arrhythmias detected during sleep studies
- Frequent nighttime awakenings
- Shortness of breath when waking up
- Dizziness or fainting in the morning
If you have any of these symptoms, you may be dealing with both sleep apnea and arrhythmia, putting you at higher risk of heart failure, stroke, or sudden cardiac arrest.
The Role of Continuous ECG Monitoring
Traditional sleep studies or Holter exams capture just a snapshot of your heart’s activity. But arrhythmias linked to sleep apnea often happen sporadically – making them easy to miss in short-term tests.
That’s where continuous ECG monitors make a difference.
How Continuous ECG Monitoring Helps:
- Monitors heart rhythm overnight, detecting both common and rare arrhythmias
- Tracks changes in heart rate during sleep, including sudden drops or spikes
- Identifies AFib episodes, PVCs, or other abnormal beats even when you’re unaware
- Helps correlate arrhythmias with sleep apnea events
- Provides long-term data for your cardiologist or sleep specialist to review
- Alerts you to early warning signs of heart failure or cardiac strain
By wearing a personal ECG device, you can monitor your ventricular rhythm types and supraventricular rhythms in real time – without needing to be in a clinic.
Sleep Apnea and AFib: A Dangerous Duo
One of the most researched links is between sleep apnea and atrial fibrillation (AFib). Sleep apnea can:
- Double or triple the risk of AFib
- Trigger recurrent episodes even after treatment
- Make AFib medication less effective if sleep apnea is untreated
- Increase the risk of stroke due to blood pooling in the atria during arrhythmic events
In many patients, treating sleep apnea improves AFib management. But you need continuous monitoring to know how your heart responds at night.
Ventricular Arrhythmias: A Hidden Threat
Sleep apnea doesn’t just affect the atria – it can also cause ventricular arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach) or ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib). These are potentially life-threatening conditions where the heart’s lower chambers beat too fast or out of sync.
Increased ventricular activity during sleep can lead to:
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Heart failure
- Dangerous drops in blood pressure
Continuous ECG monitors provide vital data on ventricular tachycardia ablation success rate by showing how effective treatments are in reducing nighttime arrhythmias.
How to Improve Your Sleep and Heart Health
Managing sleep conditions like apnea is essential for both heart health and overall well-being. Here’s how you can start:
Lifestyle Tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight – Excess weight is a major risk factor for apnea.
- Avoid alcohol before bed – Alcohol relaxes throat muscles, worsening apnea.
- Sleep on your side – This position reduces airway obstruction.
- Practice good sleep hygiene – Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Use a CPAP machine or other apnea appliances as prescribed.
- Monitor your heart rate while sleeping to catch early issues.
If you’re experiencing sleep disturbances alongside heart rhythm problems, don’t ignore them. Combining sleep health management with continuous ECG monitoring can help prevent dangerous complications.
When to See a Specialist
Consider seeing a sleep specialist or cardiologist if you:
- Have diagnosed sleep apnea and experience palpitations at night
- Wake up gasping or with chest discomfort
- Notice an irregular heartbeat after exercise or during sleep
- Have AFib or V-Tach that’s difficult to control despite medication
- Are seeking to improve both your sleep health and heart health
The Takeaway: Protect Your Heart While You Sleep
Sleep is when your body should recover – not a time when your heart is under threat. By addressing sleep apnea and using continuous ECG monitoring, you can protect yourself from the dangerous cycle of sleep-related arrhythmias.
Whether you’re managing AFib, V-Tach, or simply want to improve your sleep, tracking your heart rate during sleep can give you life-saving insights. With the right tools and proactive care, you can sleep well – and keep your heart healthy.
FAQs
Q: Can sleep apnea cause heart arrhythmias?
A: Yes, sleep apnea increases the risk of arrhythmias such as AFib, PVCs, and V-Tach due to oxygen drops and stress on the heart.
Q: How do I know if I have arrhythmias during sleep?
A: A continuous ECG monitor can track your heart rhythm overnight, detecting irregular beats that you may not feel.
Q: Does treating sleep apnea reduce arrhythmia risk?
A: Yes, using CPAP machines or other apnea appliances can lower the frequency of nighttime arrhythmias.
Q: What’s the benefit of a personal ECG device?
A: Unlike short-term monitors, personal ECG devices offer continuous heart monitoring – helping catch arrhythmias during sleep or daily life.
Sleep isn’t just about rest – it’s about survival. While you sleep, your heart, brain, and body repair and recalibrate themselves. Chronic sleep deprivation disrupts this process, and in some cases, it can do more than just leave you groggy. It can spark atrial fibrillation (AFib) – a dangerous heart rhythm disturbance that increases your risk of stroke, heart failure, and other serious complications.
In this article, we’ll explore the connection between sleep conditions and heart health, how lack of sleep can trigger atrial arrhythmias, and what you can do to reduce your risk.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is a type of atrial arrhythmia where the upper chambers of your heart (atria) beat irregularly and often rapidly. Instead of a steady “lub-dub,” the heart quivers or flutters, which can cause blood to pool and clot. AFib can be occasional (paroxysmal) or persistent, and symptoms range from palpitations to fatigue, chest discomfort, and shortness of breath.
But here’s the catch – not all AFib events happen when you’re awake. Many occur at night, sometimes without obvious warning signs. This makes it important to understand the role that sleep conditions play in heart rhythm stability.
Sleep Deprivation and Your Heart
Sleep deprivation is more than just “being tired.” It’s a form of stress that affects almost every system in your body. If you regularly get less than the recommended 7–9 hours of quality sleep, you’re not just risking mental fatigue – you’re putting your heart health on the line.
Research shows that sleep deprivation can:
- Raise blood pressure, which strains the heart.
- Increase inflammation, which damages blood vessels.
- Disrupt the autonomic nervous system, which regulates your heart rhythm.
- Elevate stress hormones like cortisol, which make arrhythmias more likely.
Chronic poor sleep doesn’t just set the stage for heart problems – it can trigger them.
Does Lack of Sleep Cause Heart Problems?
The short answer is yes – and atrial fibrillation is one of the most concerning.
When you’re sleep deprived:
- Your heart’s electrical signals become unstable.
The delicate balance between sympathetic (“fight or flight”) and parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) nervous system activity gets disrupted. This can cause irregular electrical firing in the atria. - Oxygen supply can be reduced.
If you also suffer from conditions like sleep apnea, the heart may repeatedly experience dips in oxygen levels at night, which strain heart tissue. - Blood pressure remains high at night.
Normally, blood pressure dips while sleeping, but with insufficient rest, this “nocturnal dipping” doesn’t happen, keeping the cardiovascular system under constant stress.
The combination of these factors means that a single sleepless night might not trigger AFib, but chronic sleep deprivation significantly increases the risk.
AFib While Sleeping: Why It Happens
AFib isn’t just a daytime condition. Many people experience atrial fibrillation during sleep, often waking up with a racing or fluttering heartbeat.
Possible nighttime triggers include:
- Sleep apnea: Strongly linked to AFib events, as repeated oxygen drops cause heart strain.
- High nighttime blood pressure: Maintains stress on heart muscles and conduction pathways.
- Alcohol before bed: Can irritate heart tissue and trigger nighttime arrhythmias.
- Late-night caffeine or stimulant use: Disrupts natural heart rhythm control.
Even without obvious symptoms, AFib at night can silently increase stroke and heart failure risk.
Insomnia and AFib Risk
Insomnia – difficulty falling or staying asleep – is another risk factor for AFib. Studies have shown that people with insomnia have higher rates of arrhythmias, possibly because prolonged wakefulness alters heart rate variability and increases sympathetic nervous system activity.
The double burden of heart failure and insomnia can be especially dangerous. Poor sleep worsens heart function, while heart failure symptoms such as shortness of breath make sleep harder to achieve. This vicious cycle can make AFib episodes more frequent and harder to control.
How to Reduce Your Risk of AFib from Sleep Problems
The good news? Improving sleep quality can reduce the risk of heart disease and help stabilize your heart rhythm.
Here are steps to protect your heart:
- Get tested for sleep disorders – Especially sleep apnea, which is treatable and reduces AFib recurrence risk.
- Stick to a sleep schedule – Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day.
- Limit stimulants – Avoid caffeine and alcohol in the hours before bedtime.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment – Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
- Practice stress reduction – Meditation, gentle stretching, or deep breathing can calm the nervous system before bed.
Long-term ECG Monitoring for Sleep-Related AFib Risks
If you have sleep problems and are prone to AFib, it’s important to detect irregular rhythms early – even while sleeping. Long-term ECG monitors, such as the FDA-cleared Frontier X Plus, provide high-fidelity ECG data for extended periods, making it possible to catch nighttime AFib episodes you may not feel. Unlike spot-check devices, these monitors track your heart rhythm continuously, helping you and your doctor link arrhythmias to sleep conditions, assess AFib triggers, and adjust treatment plans before a small problem becomes a major one.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep deprivation can destabilize the heart’s electrical system and trigger atrial fibrillation.
- Poor sleep quality increases inflammation, blood pressure, and stress hormones, all of which make arrhythmias more likely.
- AFib while sleeping often goes unnoticed without continuous monitoring.
- Addressing sleep conditions like insomnia and sleep apnea can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and help maintain normal rhythm.
- Continuous ECG monitoring can give early warnings and support proactive treatment.
Your heart needs the same thing you do after a long day: rest. Prioritizing good sleep may be one of the simplest – and most effective – steps you can take to keep your rhythm steady and your heart strong.
FAQs About Sleep Deprivation and AFib
- Does lack of sleep cause heart problems?
Yes. Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and abnormal heart rhythms like AFib. - Can you get AFib while sleeping?
Absolutely. Many people experience AFib at night, often due to changes in heart rate and oxygen levels during sleep. - How is AFib during sleep diagnosed?
Continuous ECG monitoring or overnight heart rhythm tracking is often needed to detect nighttime AFib episodes. - Is insomnia linked to atrial fibrillation?
Yes. Research shows people with chronic insomnia have a higher likelihood of developing AFib compared to those with healthy sleep patterns. - How can I reduce my risk of AFib if I have trouble sleeping?
Focus on improving sleep hygiene, treating any underlying sleep disorders, and monitoring heart health with tools like continuous ECG devices.