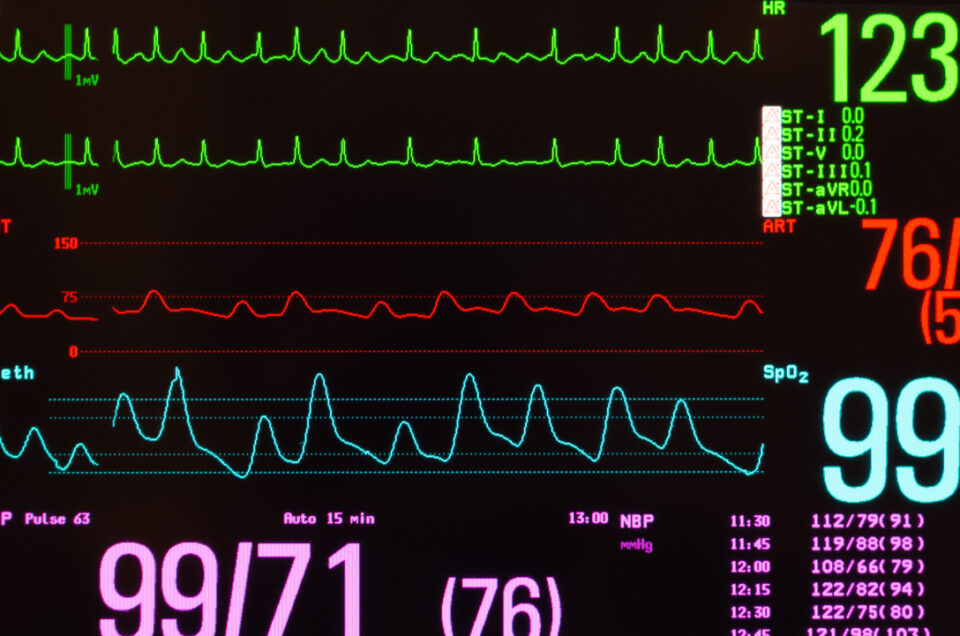
What is Myocarditis?
Myocarditis is a rare medical condition when the heart muscle becomes inflamed, causing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat. Viral or bacterial infection, exposure to toxins or chemicals, or an autoimmune reaction can cause myocarditis. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. Coping strategies and support systems can help patients manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
What are some basic strategies to cope with Myocarditis?
Follow Your Treatment Plan
Following your treatment plan is the first and most important step in coping with myocarditis. This may include medications, rest, and lifestyle changes. Taking your medications as prescribed and attending all scheduled appointments with your healthcare provider is crucial for managing your symptoms and preventing complications. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants, or medications to control your heart rate or blood pressure.
In addition to medications, your healthcare provider may recommend rest and limiting physical activity until your symptoms improve. This may mean taking time off work or school or reducing your usual amount of physical activity. It’s essential to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard, as this can exacerbate your symptoms and prolong your recovery.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend lifestyle changes to promote heart health. This may include eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise (as recommended by your healthcare provider), quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing heart-related complications.
Seek Emotional Support
Living with a chronic condition like myocarditis can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to seek emotional support from loved ones, friends, or a mental health professional. Sharing your feelings and experiences with someone who understands can help you feel less alone and more empowered to manage your condition.
Talking with a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can also provide a safe space to explore your emotions and learn coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety. Your healthcare provider may be able to refer you to a mental health professional who specializes in working with patients with chronic medical conditions.
Connect with Support Groups
Support groups can be a valuable resource for people living with myocarditis. These groups provide an opportunity to connect with others who are going through a similar experience, share coping strategies, and learn from each other. Support groups can be found online or in person through local hospitals, community centers, or advocacy organizations.
Support groups can also provide a sense of community and social support, which can help reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness. Additionally, support groups can provide information about resources and services that may be helpful, such as financial assistance or transportation services.
Stay Informed
Staying informed about your condition and treatment options can help you feel more in control of your health. Ask your healthcare provider about your condition, treatment plan, and potential complications. Research credible sources of information, such as the American Heart Association or the National Institutes of Health, to learn more about myocarditis and available treatments.
It’s essential to keep in mind that medical information can be overwhelming, so it’s important to find a balance between staying informed and not becoming consumed by your condition. Consider setting aside specific times to research and learn about your condition rather than constantly checking the internet for updates.
Practice Self-Care
Self-care generally refers to practices and activities individuals can undertake to promote their physical and emotional well-being. For patients of myocarditis 3 aspects of self-care are the most important- Rest, Diet and staying active.
Rest
Rest is an important aspect of self-care for patients with myocarditis. Getting adequate sleep is essential to allow the body to heal and recover. Patients with myocarditis may experience fatigue, so listening to the body and rest when needed is important. Taking short naps during the day and maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help ensure that the body gets the rest it needs.
Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet is essential for patients with myocarditis. This means consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Patients should aim to limit their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats. A healthy diet can help improve overall health, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications associated with myocarditis.
Stay Active
Physical activity is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health, but patients with myocarditis may need to limit their activity during the acute phase of the condition. Patients should follow the guidance of their healthcare provider and gradually increase their activity level as symptoms improve. Gentle exercises such as walking, yoga, or tai chi can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce stress.
Educate Your Loved Ones
Educating your loved ones about your condition can help them understand your needs and provide support when you need it. Consider sharing information about myocarditis, your treatment plan, and potential complications. Encourage your loved ones to ask questions and be involved in your care.
Living with myocarditis can be challenging, but by following a treatment plan, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, seeking emotional support, connecting with support groups, staying informed, practicing self-care, and educating your loved ones, you can manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle.
Make a smart investment in your heart health by choosing a top-notch heart rate monitor like the Frontier X2 to track heart rate and ECG during exercise.
Frequently Asked Questions :
What is Myocarditis?
Myocarditis is a medical condition in which the heart muscle, or myocardium, becomes inflamed. It can affect individuals of any age and may be caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection, or by an autoimmune reaction. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, fever, and irregular heartbeat. The severity of the condition can vary from mild to life-threatening, and in some cases, it can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle or lead to heart failure. Treatment may involve medications to manage symptoms and address the underlying cause, as well as lifestyle adjustments to support heart health.
What can I do to take care of myself while living with myocarditis?
Self-care is an essential aspect of managing myocarditis. This may include following a heart-healthy diet, getting enough rest, avoiding strenuous physical activity, and managing stress levels. It is also important to attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and take any medications as prescribed.
Can I still work with myocarditis?
This will depend on the severity of your condition and the type of work you do. If your job involves physical labor or significant stress, your healthcare provider may recommend taking time off work or reducing your workload until your symptoms improve.
Can I still have an active social life with myocarditis?
Yes, it is possible to maintain an active social life with myocarditis. However, listening to your body and avoiding activities that may exacerbate your symptoms is important. You may need to make some lifestyle adjustments, such as limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding late nights or other activities that can be stressful on the heart.
How can I explain myocarditis to my family and friends?
It can be helpful to educate your family and friends about myocarditis so they understand what you are going through. You can explain that it is a condition that affects the heart muscle and can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Let them know that you may need lifestyle adjustments and ask for their support and understanding.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Healthy Heart Diet | Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation | Heart Palpitation Causes | Running Heart Rate Zones | Low Heart Rate | Best ECG Monitors. | AFib Risk Factors| | Acid Reflux | Increased Heart Rate
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. When the blood supply is restricted, the heart muscle in that area is deprived of oxygen and nutrients and starts to die. This can cause chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and other symptoms. The severity of a heart attack can vary depending on the extent of the blockage and how quickly it is treated. It is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to restore blood flow and minimize damage to the heart muscle. Without treatment, a heart attack can lead to heart failure, arrhythmia, or even death. It is important to recognize the symptoms of a heart attack and seek immediate medical attention if experiencing them.
Duration of Heart Attacks :
Knowing the duration of a heart attack is crucial because it can determine the outcome of a patient’s recovery. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, which can cause damage to the heart muscle. The longer the heart attack lasts, the more damage can occur. Therefore, it is important to know the duration of a heart attack so that prompt medical attention can be sought. Early treatment can help to minimize the damage to the heart and increase the chances of a successful recovery. Additionally, knowing the duration of a heart attack can also help doctors to determine the best course of treatment and to monitor the patient’s progress during recovery. In summary, recognizing the signs of a heart attack and seeking medical attention promptly is essential to minimize damage to the heart muscle, improve outcomes and prevent future heart attacks.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack :
Some of the signs to look out for are chest pain or discomfort, which can feel like pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, sweating, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or lightheadedness, and pain or discomfort in the arms, neck, jaw, or back. In some cases, people may experience only mild symptoms or no symptoms at all, which is known as a silent heart attack. It is important to note that the symptoms of a heart attack can differ between men and women, and may also vary based on age, health history, and other factors. If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as prompt treatment can help to minimize damage to the heart and improve outcomes.
Types of Heart Attacks :
It is also integral to understand the different types of heart attacks when diagnosing your symptoms. There are three main types of heart attacks: STEMI, NSTEMI, and silent heart attacks. STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) is the most severe type of heart attack, which occurs when there is a complete blockage of a coronary artery, leading to a large area of heart muscle being damaged. NSTEMI (non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction) is a less severe type of heart attack, which occurs when there is a partial blockage of a coronary artery, leading to a smaller area of heart muscle being damaged. Silent heart attacks are heart attacks that occur without any obvious symptoms, but can still cause damage to the heart muscle. They are often discovered during routine medical tests or when investigating other health issues. Silent heart attacks can be just as serious as symptomatic heart attacks, and people who have had a silent heart attack are at an increased risk of future heart problems. The type of heart attack a person experiences can impact their treatment options and their long-term prognosis, so timing is truly critical – it is important for doctors to determine the type of heart attack as early as possible to provide the most effective treatment.
Factors influencing duration of a Heart Attack :
The duration of a heart attack can be influenced by several factors. One of the most significant factors is the location and severity of the blockage in the coronary artery. If the blockage is complete, the heart attack may be more severe and last longer. The size of the affected area of the heart also plays a role, as a larger area of damage may take longer to heal. Additionally, the duration of the heart attack can be affected by the individual’s overall health and medical history, as well as their age and lifestyle habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical activity levels. The timing of treatment can also impact the duration of a heart attack, as early intervention can help to minimize the damage to the heart and reduce the overall duration of the event. Furthermore, the type of treatment used can affect the duration of the heart attack. For example, some treatments may help to dissolve the blockage in the coronary artery more quickly, while others may take longer to take effect.
Stages of a Heart Attack :
The time frame for each stage of a heart attack can vary from person to person, but generally, there are three stages of a heart attack: the initial stage, the acute stage, and the healing stage. The initial stage occurs when a coronary artery becomes partially or completely blocked, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This stage can last for several minutes or hours, during which time a person may experience mild or no symptoms. The acute stage occurs when the blockage becomes severe enough to cause significant damage to the heart muscle, which can lead to symptoms such as chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and nausea or vomiting. This stage can last for several hours or longer, during which time emergency medical treatment is necessary to restore blood flow to the heart muscle and minimize damage. The healing stage occurs after emergency treatment, during which time the damaged heart muscle begins to repair itself. This stage can last for several weeks or months, during which time a person may need ongoing medical care and rehabilitation to recover fully. The duration of each stage of a heart attack can impact the severity of the heart attack and the long-term prognosis, so it is important for people to seek prompt medical attention if they experience any symptoms of a heart attack.
Recovery Post Heart Attack :
It is important to remember that recovery after a heart attack is a challenging but important phase in a patient’s journey towards regaining their health and wellness. Depending on the severity of the heart attack, recovery can take several weeks to several months, and in some cases, ongoing lifestyle changes may be necessary to prevent future heart problems. The initial phase of recovery often involves hospitalization, where doctors can monitor the patient’s condition and provide necessary treatments, such as medications or procedures to open blocked arteries. After being discharged from the hospital, patients may require additional care, such as cardiac rehabilitation, which involves supervised exercise and education on heart-healthy lifestyle changes. Additionally, patients may need to make lifestyle changes, such as following a heart-healthy diet, quitting smoking, managing stress, and taking medications as prescribed. It is important for patients to follow their doctor’s recommendations for recovery to prevent future heart problems and to improve their overall health and quality of life. With proper care and lifestyle changes, many people can recover fully from a heart attack and lead healthy, active lives.
Make sure you get accurate heart rate and ECG monitoring during physical activity by investing in a heart rate monitor of the highest quality, such as the Frontier X2.
Frequently Asked Questions :
How long does a heart attack typically last?
The duration of a heart attack can vary from person to person and depends on factors such as the severity of the blockage and the time it takes to receive medical treatment. Generally, a heart attack can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
Is it possible to have a heart attack that lasts for days?
While it is rare for a heart attack to last for several days, it is possible for a person to experience ongoing symptoms after the initial event. This is known as a “stuttering” heart attack, which can occur when a blood clot partially blocks a coronary artery, causing intermittent symptoms.
Can the duration of a heart attack be shortened with treatment?
Yes, receiving prompt medical treatment can help to shorten the duration of a heart attack and minimize damage to the heart muscle. Treatments such as medications, procedures to open blocked arteries, and cardiac rehabilitation can all contribute to a faster and more complete recovery.
How does the duration of a heart attack impact recovery?
The duration of a heart attack can impact the extent of damage to the heart muscle and the patient’s long-term prognosis. A longer heart attack can cause more damage and increase the risk of complications, so it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to minimize the duration of the heart attack.
Can lifestyle changes impact the duration of a heart attack?
While lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, following a heart-healthy diet, and managing stress may not impact the actual duration of a heart attack, they can improve overall heart health and reduce the risk of future heart problems. Making these changes after a heart attack can contribute to a faster and more complete recovery.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Running Heart Rate | Heart Attack causes | Wearable ECG Monitor | Cardio Exercise | Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation | Stress Test for Heart | Heart Attack Symptoms | Heart Palpitations Causes | Low Carb Diet | Healthy Heart Tips
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. When a heart attack occurs, the blood flow to the heart muscle is blocked, which can lead to damage to the heart and even death. Therefore, it is essential to stop a heart attack as quickly as possible to minimize the damage to the heart muscle and improve the chances of survival. One of the primary reasons for the urgency of stopping a heart attack is the potential for complications. If a heart attack is not treated promptly, it can lead to further damage to the heart muscle and cause life-threatening complications. Complications of a heart attack can include heart failure, abnormal heart rhythms, and cardiac arrest.
What is cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating, and it is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment with CPR and an AED. Additionally, there is potential for long-term damage to the heart muscle. When a heart attack occurs, the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen, which can cause it to be permanently damaged. This damage can lead to a weaker heart, which can impact the patient’s ability to perform physical activities and decrease their overall quality of life.
Moreover, a heart attack can be a sign of underlying heart disease. If left untreated, heart disease can lead to a range of serious health problems, including heart failure, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Treating a heart attack promptly can not only save the patient’s life but also provide an opportunity to identify and treat underlying heart disease before it leads to further complications.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
Understanding the warning signs of a heart attack is crucial for early detection and treatment. The classic symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and pain in the arm or jaw. However, it is essential to note that not all heart attacks present with these typical symptoms. In some cases, a heart attack can present with less common symptoms, such as nausea, indigestion, extreme fatigue, and lightheadedness. These symptoms can be easily dismissed or attributed to other causes, such as stress or a stomach virus. It is crucial to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, especially if they occur suddenly or are severe. Delaying treatment can lead to further damage to the heart muscle and increase the risk of complications, such as heart failure or cardiac arrest. Calling emergency services or going to the hospital as soon as possible is the best course of action.
Immediate steps to minimize heart damage
In addition to seeking prompt medical attention, there are steps that can be taken to stop a heart attack quickly. It is important to note that stopping a heart attack in 30 seconds is not always possible, and seeking medical attention as soon as possible is the best course of action. However, there are steps that can be taken to potentially reduce the damage to the heart muscle and improve the chances of survival.
- The first step to take in the event of a heart attack is to call emergency services or go to the hospital as soon as possible. Every minute counts, and delaying treatment can lead to further damage to the heart muscle and increase the risk of complications. It is important to stay as calm as possible and follow the instructions of the emergency services operator.
- Chewing and swallowing aspirin can help prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the severity of a heart attack. Aspirin works by inhibiting the formation of platelets, which can contribute to the formation of blood clots. It is important to use only aspirin that is recommended by a doctor, as not all types of aspirin are suitable for heart attack treatment.
- Performing CPR on someone experiencing a heart attack can help maintain blood flow to the heart and improve the chances of survival. CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths, and it is important to receive proper training before attempting to perform CPR.
- Using an automated external defibrillator (AED) can help restore the heart’s normal rhythm and improve the chances of survival. AEDs are portable devices that can deliver an electric shock to the heart, and they are commonly found in public places such as airports, shopping centers, and schools. It is important to receive proper training before attempting to use an AED.
It is important to note that the steps to take to stop a heart attack can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the heart attack. Seeking medical attention as soon as possible and following the instructions of emergency services personnel is crucial for the best possible outcome.
Preventing a heart attack
In addition to recognizing the warning signs of a heart attack, it is essential to be aware of the risk factors that can increase the likelihood of a heart attack. These risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, physical inactivity, and a family history of heart disease. Addressing these risk factors through lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet, can help reduce the risk of a heart attack.
It is also important to note that the warning signs of a heart attack can differ between men and women. Women are more likely to experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, and back or jaw pain, in addition to the classic symptoms of chest pain or discomfort. However, these symptoms are often ignored or attributed to other causes, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the warning signs of a heart attack is essential for early detection and treatment. Recognizing the less common symptoms of a heart attack, seeking medical attention promptly, and addressing risk factors can help prevent a heart attack and reduce the risk of complications. It is crucial to listen to your body and seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a heart attack, even if they are not typical or seem mild. Taking action quickly can save your life and prevent long-term damage to your heart.
Enhance your workout routine by investing in a heart rate monitor that accurately tracks heart rate and ECG, such as the Frontier X2.
Frequently Asked Questions :
Is it really possible to stop a heart attack in 30 seconds?
Stopping a heart attack in 30 seconds is not always possible, and seeking medical attention as soon as possible is the best course of action. However, there are steps that can be taken to potentially reduce the damage to the heart muscle and improve the chances of survival.
What is the first step to take in the event of a heart attack?
The first step to take in the event of a heart attack is to call emergency services or go to the hospital as soon as possible. Every minute counts, and delaying treatment can lead to further damage to the heart muscle and increase the risk of complications.
Can chewing and swallowing aspirin really help during a heart attack?
Chewing and swallowing aspirin can help prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the severity of a heart attack. Aspirin works by inhibiting the formation of platelets, which can contribute to the formation of blood clots. It is important to use only aspirin that is recommended by a doctor, as not all types of aspirin are suitable for heart attack treatment.
What is CPR, and how does it help during a heart attack?
Performing CPR on someone experiencing a heart attack can help maintain blood flow to the heart and improve the chances of survival. CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths, and it is important to receive proper training before attempting to perform CPR.
How do I use an automated external defibrillator (AED) to stop a heart attack?
Using an AED can help restore the heart’s normal rhythm and improve the chances of survival. AEDs are portable devices that can deliver an electric shock to the heart, and they are commonly found in public places such as airports, shopping centers, and schools. It is important to receive proper training before attempting to use an AED.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Diet For Heart Health | Heart Attack Symptoms | Running Heart Rate | Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms | Heart Palpitations Causes | Exercise for Heart Health | Cardio Exercises | Heart Rate Zones | Post Covid Fatigue | Best Heart Rate Monitor
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Running is a great way to improve your cardiovascular fitness, lose weight, and reduce stress. However, if you want to get the most out of your running workouts, you need to train in the right heart rate zone. Zone 2 training is a popular method that can help you improve your aerobic fitness and endurance. We’ll discuss how heart rate monitors can help you maximize Zone 2 training for running.
What is Zone 2 Training?
Zone 2 training is a type of training that targets your aerobic energy system. This means that you’re primarily burning fat for fuel and training your cardiovascular system to work more efficiently. Zone 2 training is typically done at a moderate intensity, where you can comfortably carry on a conversation without gasping for air.
How Heart Rate Monitors Work
Heart rate monitors are useful devices that can help you monitor your heart rate during exercise. They work by detecting the electrical signals generated by the heart and calculating your heart rate in real-time. There are three main types of heart rate monitors: chest strap monitors, wristwatch monitors, and optical monitors. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that works best for you.
Anatomy of the Heart
Before we dive into how heart rate monitors work, it’s important to understand the anatomy of the heart. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. The heart is controlled by an electrical system that regulates the rhythm and rate of heartbeats.
How Heart Rate is Measured
Heart rate is measured in beats per minute (BPM). The most common way to measure heart rate is by using a heart rate monitor. Heart rate monitors work by detecting the electrical signals generated by the heart. These signals cause the heart muscles to contract, which creates a pulse. By detecting these pulses, heart rate monitors can determine your heart rate.
Types of Heart Rate Monitors
There are three main types of heart rate monitors: chest strap heart rate monitors, wristwatch heart rate monitors, and optical heart rate monitors.
Chest Strap Heart Rate Monitors:
Chest strap heart rate monitors consist of a strap that is worn around the chest and a sensor that is placed on the strap. The sensor detects the electrical signals generated by the heart and transmits the data to a display unit, which shows your heart rate in real-time. Chest strap heart rate monitors are known for their accuracy, but some people find them uncomfortable to wear.
Wristwatch Heart Rate Monitors:
Wristwatch heart rate monitors are similar to chest strap monitors, but the sensor is placed on the wristwatch instead of the chest strap. These monitors use light sensors to detect changes in blood flow and calculate your heart rate. Wristwatch heart rate monitors are convenient to wear, but they may not be as accurate as chest strap monitors.
Optical Heart Rate Monitors:
Optical heart rate monitors are becoming increasingly popular, as they don’t require a chest strap or wristwatch. These monitors use light sensors to detect changes in blood flow and calculate your heart rate. They are typically worn on the arm, and some models are even built into clothing. Optical heart rate monitors are convenient to wear, but they may not be as accurate as chest strap monitors.
Heart rate monitors are useful devices that can help you monitor your heart rate during exercise. They work by detecting the electrical signals generated by the heart and calculating your heart rate in real-time. There are three main types of heart rate monitors: chest strap monitors, wristwatch monitors, and optical monitors. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that works best for you.
Benefits of Zone 2 Training with Heart Rate Monitors
Training in Zone 2 with a heart rate monitor can provide a number of benefits for runners, including:
Improved Aerobic Fitness:
Training in Zone 2 can improve your aerobic fitness, which is the ability of your body to use oxygen to produce energy. This can lead to improvements in your running performance, such as increased speed and endurance.
Increased Fat Burning:
Training in Zone 2 can also help you burn more fat, which is an important fuel source for endurance athletes. By improving your body’s ability to burn fat for fuel, you can improve your endurance and delay the onset of fatigue.
Reduced Risk of Overtraining:
Overtraining can lead to injuries, burnout, and decreased performance. By using a heart rate monitor to train in Zone 2, you can ensure that you are training at a safe and sustainable intensity. This can help you avoid overtraining and stay healthy throughout your training.
How to Determine Your Zone 2 Heart Rate:
The best way to determine your Zone 2 heart rate is to use a heart rate monitor during a graded exercise test. This involves starting at a low intensity and gradually increasing the intensity until you reach your maximum heart rate. Your Zone 2 heart rate is typically around 60-70% of your maximum heart rate. If you don’t have access to a graded exercise test, you can estimate your Zone 2 heart rate using the Karvonen formula.
Tips for Zone 2 Training with Heart Rate Monitors
Here are some tips to help you make the most of your Zone 2 training with heart rate monitors:
Monitor Your Heart Rate:
During your workout, it’s important to monitor your heart rate and stay within your target heart rate zone. If you go above or below your target heart rate zone, you may need to adjust your intensity to stay within the zone.
Pay Attention to How You Feel:
Heart rate monitors can provide valuable data, but it’s also important to pay attention to how you feel during your workout. If you’re struggling to carry on a conversation or feeling fatigued, you may need to decrease your intensity to stay within your target heart rate zone.
Adjust Your Intensity as Needed:
Your heart rate can fluctuate during your workout, so it’s important to adjust your intensity as needed to stay within your target heart rate zone. This may mean slowing down or speeding up depending on how you feel and what your heart rate is telling you.
Using a heart rate monitor during Zone 2 training can help you train more efficiently and effectively. By training in the right heart rate zone, you can improve your aerobic fitness, burn more fat, and reduce your risk of injury and burnout. If you’re looking to take your running performance to the next level, consider incorporating Zone 2 training with a heart rate monitor into your routine. So, get started and pair your new and improved workout routine with the use of a heart monitoring device to make the most out of your Zone 2 Training. Purchase the revolutionary Frontier X2 (ref. link) to get visually represented post-activity insights into the time spent in each HR zone so you can be on your way to a healthier tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions :
How can heart rate monitors help with Zone 2 training?
Heart rate monitors can help you track your heart rate during exercise and ensure that you’re working in the correct heart rate zone for Zone 2 training. This can help you avoid overtraining and maximize the benefits of your workout.
How do I determine my heart rate zones?
You can determine your heart rate zones by calculating your maximum heart rate and using a percentage of that number to determine your target heart rate zones. A common formula for calculating maximum heart rate is 220 minus your age.
Do I need a heart rate monitor for Zone 2 training?
While a heart rate monitor isn’t necessary for Zone 2 training, it can be a useful tool for ensuring that you’re working in the correct heart rate zone. It can also help you track your progress over time and make adjustments to your training plan as needed.
How often should I do Zone 2 training?
The frequency of your Zone 2 training will depend on your individual fitness goals and training plan. However, it’s generally recommended to incorporate Zone 2 training into your workout routine 1-3 times per week.
Are there any risks associated with using a heart rate monitor for Zone 2 training?
As long as you use the heart rate monitor correctly and follow a safe and effective training plan, there are no significant risks associated with using a heart rate monitor for Zone 2 training. However, if you have any pre-existing medical conditions, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Healthy Heart Diet | Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation | Heart Palpitation Causes | Running Heart Rate Zones | Low Heart Rate | Best ECG Monitors. | AFib Risk Factors| | Acid Reflux | Increased Heart Rate
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Cardiovascular fitness is a key component of overall health, as it refers to the ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues during physical activity. One effective way to improve cardiovascular fitness is through Zone 2 running, which involves maintaining a heart rate at around 60-70% of your maximum heart rate. This type of training has been shown to provide significant benefits for heart health, including increased oxygen delivery, improved heart function, and reduced risk of heart disease. We will explore the benefits of Zone 2 running for heart health, as well as tips for improving cardiovascular fitness through this type of exercise.
What is Zone 2 running and its relation to heart rate?
Zone 2 running refers to running at a moderate intensity that allows you to maintain a heart rate of approximately 60-70% of your maximum heart rate (ref. link). This heart rate zone is considered optimal for improving cardiovascular fitness and providing a number of health benefits. Your maximum heart rate can be estimated by subtracting your age from 220, and your Zone 2 heart rate can be calculated as a percentage of your maximum heart rate.
How to Determine Your Zone 2 Heart Rate
There are several methods for determining your Zone 2 heart rate, including:
- Using a heart rate monitor: A heart rate monitor can provide real-time feedback on your heart rate during exercise, making it easy to maintain a heart rate in Zone 2.
- Taking a heart rate test: A heart rate test involves running at gradually increasing speeds while monitoring your heart rate, until you reach your lactate threshold heart rate (the point at which muscles begin producing lactic acid).Your Zone 2 heart rate is typically about 15-20 beats per minute below your lactate threshold heart rate.
- Using a calculator: There are several online calculators that can help you determine your Zone 2 heart rate based on your age, gender, and fitness level.
Zone 2 running is an effective and efficient way to improve cardiovascular fitness and promote overall health. By maintaining a heart rate in the optimal Zone 2 range, you can reap the benefits of improved oxygen delivery, heart function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
How Zone 2 Running Improves Heart Health?
The cardiovascular system is responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues, and is critical for overall health and wellbeing. Regular exercise, including Zone 2 running, can help to improve the function of the cardiovascular system and provide a number of heart health benefits.
The Cardiovascular System and Exercise
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, and is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. During exercise, the cardiovascular system responds by increasing the heart rate and expanding blood vessels to deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the muscles.
Benefits of Zone 2 Running for the Heart and Cardiovascular System
Zone 2 running provides several benefits for the heart and cardiovascular system, including:
- Increased oxygen delivery: By maintaining a heart rate in Zone 2, you can improve the delivery of oxygen-rich blood to the muscles. This helps to increase endurance and overall cardiovascular health.
- Improved heart function: Consistent Zone 2 training can help to strengthen the heart and improve its ability to pump blood more efficiently. This can reduce the likelihood of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Reduced risk of heart disease: Regular Zone 2 running has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease by improving cardiovascular health (ref. link), reducing inflammation, and promoting healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Improved recovery: Zone 2 running helps to improve the body’s ability to recover after exercise, which can reduce the risk of injury and improve overall performance.
By incorporating Zone 2 running into your exercise routine, you can improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease, while also enjoying the benefits of increased endurance, improved recovery, and overall fitness.
Tips for Improving Cardiovascular Fitness with Zone 2 Running
Zone 2 running is an effective way to improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of heart disease. To maximize the heart health benefits of Zone 2 running, it’s important to structure your workouts properly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your runs.
Structuring Zone 2 Running Workouts
To structure effective Zone 2 running workouts, consider the following tips:
- Warm up: Start with a 5-10 minute warm-up at an easy pace to prepare your body for the workout.
- Maintain a consistent pace: Keep your heart rate in Zone 2 by maintaining a consistent pace throughout your run. Avoid sudden bursts of speed or intensity that can push you out of the target heart rate zone.
- Gradually increase duration and intensity: Over time, gradually increase the duration and intensity of your Zone 2 running workouts. Start with shorter runs at a lower intensity, and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your cardiovascular fitness improves.
Monitoring and Adjusting Intensity
To monitor and adjust the intensity of your Zone 2 running workouts, consider the following tips:
- Use a heart rate monitor: A heart rate monitor is an effective tool for monitoring your heart rate during exercise and ensuring that you stay within the target Zone 2 heart rate range.
- Adjust intensity as needed: If you find that you’re consistently falling outside of the target heart rate zone, adjust the intensity of your workout as needed. This may mean slowing down or taking breaks as needed to bring your heart rate back into the optimal range.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to your body during your workouts and adjust your intensity as needed based on how you’re feeling. If you’re feeling overly fatigued or experiencing any discomfort, slow down or take a break to prevent injury.
Zone 2 running is an effective way to improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of heart disease. By structuring your workouts properly, monitoring and adjusting intensity, and gradually increasing duration and intensity over time, you can maximize the heart health benefits of your Zone 2 running routine. With consistent effort and dedication, you can improve your overall cardiovascular fitness and enjoy the many benefits of a healthy heart.
Finally, pair your new and improved workout routine with the use of a heart monitoring device to make the most out of your Zone 2 Training. Purchase the revolutionary Frontier X2 (ref. link) to get visually represented post-activity insights into the time spent in each HR zone so you can be on your way to a healthier tomorrow!
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is Zone 2 running?
Zone 2 running refers to aerobic exercise performed at an intensity that corresponds to a heart rate of approximately 60-70% of your maximum heart rate.
How can I determine my Zone 2 heart rate?
You can determine your Zone 2 heart rate by using a heart rate monitor and calculating your maximum heart rate, then determining 60-70% of that value.
What are the benefits of Zone 2 running for heart health?
Zone 2 running can improve cardiovascular fitness, increase oxygen delivery to the body, improve heart function, reduce the risk of heart disease, and enhance overall health and well-being.
How frequently should I perform running workouts in Zone 2?
It is recommended to perform Zone 2 running workouts 2-3 times per week to maximize heart health benefits.
Can I continue to engage in other forms of exercise in addition to running in Zone 2?
Yes, it is beneficial to include a variety of exercise types in your routine, including strength training, high-intensity interval training, and other aerobic activities, to maximize overall health and fitness.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Diet For Heart Health | Heart Attack Symptoms | Running Heart Rate | Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms | Heart Palpitations Causes | Exercise for Heart Health | Cardio Exercises | Heart Rate Zones | Post Covid Fatigue | Best Heart Rate Monitor
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Heart rate variability (HRV) (ref. link) is the measure of the variation in time between successive heartbeats. HRV has become an increasingly popular metric for assessing overall health, as it has been linked to a wide range of health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression, and anxiety.
There are several ways to measure HRV, ranging from simple techniques that can be performed at home to more advanced methods that require specialized equipment. We will discuss some of the most common ways to measure HRV :
Clinical Tests :
If you have concerns about your heart health, your doctor may recommend clinical tests to measure your HRV. Your doctor may recommend clinical tests to measure your HRV, which can provide a more detailed assessment of your heart function and identify any underlying heart conditions that may be affecting your health.
ECG:
One common clinical test used to measure HRV is an electrocardiogram (ECG). During an ECG, electrodes are attached to the skin of your chest, arms, and legs to measure the electrical activity in your heart. This test is non-invasive and provides accurate HRV readings (ref. link).
Holter monitor:
Another test that may be recommended is a Holter monitor, which is a portable device that records your heart activity for 24 to 48 hours. This device is typically worn during your normal daily activities and can provide a more comprehensive picture of your heart function than a single ECG reading.
Both the ECG and Holter monitor tests can help identify any underlying heart conditions that may be affecting your health. If you have any concerns about your heart health or are experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations, it is important to speak with your doctor and undergo any necessary testing to ensure your heart is functioning properly.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices, such as heart rate monitors and smartwatches, have become increasingly popular for measuring HRV. These devices use sensors to track your heart rate and calculate your HRV based on the time between each heartbeat.
Benefits of Using Wearable Devices for HRV Monitoring
Wearable devices can provide continuous HRV monitoring throughout the day and offer insights into your overall health and fitness.
Types of Wearable Devices for HRV Monitoring
- Heart Rate Monitors: These devices typically consist of a chest strap or wristband that monitors your heart rate and calculates HRV based on the time between each beat.
- Smartwatches: Many smartwatches now include HRV monitoring as a feature, allowing users to track their HRV throughout the day and during exercise.
- Other Wearable Devices: There are other wearable heart rate devices, such as fitness trackers and heart rate variability sensors, that can also be used to measure HRV.
Accuracy of Wearable Devices for HRV Monitoring
While wearable devices can provide convenient and continuous HRV monitoring, it’s important to note that the accuracy of these devices can vary. Some factors that can affect accuracy include the quality of the sensors and the device’s algorithms for calculating HRV.
A 2017 study (ref. link) involving 50 healthy adults found that chest straps provide more accurate results than wrist-worn heart rate monitors and fitness trackers. Consequently, they are the preferred method for measuring heart rate and HRV outside of clinical settings.
Given all this information, one of the best ways to measure your Heart Rate Variability is by using a Frontier X2. This smart heart monitor gives you detailed, accurate data that you can only otherwise get at a clinic, while allowing you to workout as it collects data, unlike most medical grade devices. Strap on a Frontier X2 across your chest so you can measure your cardiac activity when it’s most relevant, ensuring you get fitter and healthier by the day!
Heart Rate Variability Apps
There are several apps available that use the camera on your smartphone to measure your HRV. These apps work by using photoplethysmography (PPG), a non-invasive method of measuring blood flow, to track the changes in blood volume that occur with each heartbeat.
Factors Affecting HRV
Several factors can affect HRV, including age, gender, physical activity level, stress levels, and certain medical conditions. It’s important to keep these factors in mind when interpreting your HRV results.
Interpreting HRV Results
Interpreting HRV results can be complicated, as there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Your HRV results will vary depending on several factors, including your age, gender, and overall health.
However, in general, a higher HRV is typically associated with better health outcomes, while a lower HRV may be a sign of poor health or underlying medical conditions.
Improving HRV
If your HRV results are lower than you’d like, there are several ways to improve your HRV, including regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and healthy lifestyle habits.
Consult your doctor before making any changes to your health routine based on HRV measurements. Your doctor can help you interpret your HRV results and develop a personalized plan to improve your overall health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions :
What is heart rate variability (HRV)?
Heart rate variability refers to the variation in time between each heartbeat. It is a measure of the autonomic nervous system’s ability to regulate the heart rate and respond to stress.
Why is HRV important?
HRV is an indicator of overall health and fitness, as it reflects the body’s ability to adapt to stressors and recover from exertion. Low HRV is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, while high HRV is associated with improved performance and resilience.
How can I check my HRV?
There are several ways to check your HRV, including using specialized heart rate monitors, smartphone apps, or wearable fitness trackers. These devices use sensors to measure heart rate variability and provide real-time feedback on your overall health and fitness.
What factors can affect HRV?
HRV can be affected by various factors, including stress, sleep quality, physical activity, and nutrition. By monitoring HRV regularly, you can identify patterns and adjust your lifestyle to optimize your health and fitness.
When should I check my HRV?
It is recommended to check your HRV first thing in the morning, as soon as you wake up. This provides a baseline measurement of your autonomic nervous system’s activity and reflects your overall recovery from the previous day’s activities. Consistent monitoring can help you track your progress over time and adjust your training and lifestyle accordingly.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore :
Heart Palpitations After Covid | Silent Heart Attack | Meditation and Heart Health | Heart Stress Test | Heart Rate Monitor | Diabetes Impact on Heart Health | Post Covid Fatigue | Irregular Heartbeat | Normal Resting Heart Rate | Heart Health Monitor Device
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Resting heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute when at rest. A lower resting heart rate is generally considered a sign of good health and cardiovascular fitness. The optimal resting heart rate (bpm) for the majority of individuals should be between 60 and 100 (ref. link). If your resting heart rate is higher than you would like, there are lifestyle changes you can make to help lower it.
Why is a lower resting heart rate good for you?
Lower workload on the heart:
A lower resting heart rate means that your heart doesn’t have to work as hard to pump blood through your body. This can reduce the workload on your heart and may lower your risk of developing heart disease.
Improved Cardiovascular Fitness:
A lower resting heart rate can also indicate that you have better cardiovascular fitness. This means that your heart is strong and efficient, and can deliver oxygen and nutrients to your body more efficiently.
Better Recovery Time:
Individuals with a lower resting heart rate may also have a shorter recovery time after physical activity. This is because their heart is more efficient at returning to its resting state after being elevated during exercise.
Lower risk of Hypertension:
Having a lower resting heart rate may also lower your risk of developing hypertension (high blood pressure). This is because a lower resting heart rate can indicate that your blood vessels are more relaxed, allowing blood to flow more easily.
Reduced Stress on the Body:
A lower resting heart rate may also reduce stress on the body, as a higher resting heart rate can be a sign of stress or anxiety. By keeping your heart rate lower, you may be able to manage stress and anxiety more effectively.
Overall, having a lower resting heart rate is a sign of good cardiovascular health and can help lower your risk of developing heart disease and other health conditions.
Factors That Affect Resting Heart Rate:
There are many factors affecting the resting heart rate, like:
Age: As we age, our resting heart rate may increase slightly.
Gender: Women tend to have a slightly higher resting heart rate than men.
Physical fitness level: Individuals who are physically fit tend to have lower resting heart rates.
Medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, can lower the resting heart rate.
Medical conditions: Medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, anemia, and sleep apnea can impact the resting heart rate.
Ways to lower your resting Heart Rate:
Regular Exercise:
2018 meta-analysis (ref. link) found that regular exercise can reduce resting heart rate consistently. Regular exercise, particularly cardiovascular exercise, can help improve cardiovascular fitness and lower the resting heart rate. On most days of the week, try to get in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Staying Hydrated:
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy heart rate. Dehydration can cause the heart to work harder, leading to an increase in heart rate. By drinking enough water and staying hydrated, you can help your body maintain a healthy heart rate during physical activity and reduce the risk of dehydration-related complications. A 2017 study (ref. link) discovered that a 335 ml of water can reduce resting heart rate for a 30-minute period.
Healthy Diet:
Eating a healthy, balanced diet can also help lower the resting heart rate. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and limit processed and high-fat foods. A diet rich in Antioxidants, dietary fiber, Vitamin A, Vitamin C promotes heart health according to a study (ref. link).
Stress Management:
Stress can increase the resting heart rate, so finding ways to manage stress can be beneficial. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress and lower the resting heart rate.
Quality Sleep:
Getting enough quality sleep is essential for overall health and can also impact the resting heart rate. Establish a regular sleep schedule and aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking can increase resting heart rate and put additional strain on the heart. Quitting smoking can help lower your resting heart rate and improve your overall health. Research from 2020 (ref. link) found that people’s resting heart rates increase when they change their regular bedtimes.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
If your resting heart rate remains consistently high, despite lifestyle changes, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Additionally, if you experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, it is important to seek medical attention.
Lowering your resting heart rate can be beneficial for overall health and can reduce your risk of heart disease. By making lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating, stress management, quality sleep, and quitting smoking, you can help lower your resting heart rate and improve cardiovascular fitness. One of the best ways to ensure the changes you are making are positively impacting your heart is by monitoring it. Purchase the Frontier X2 smart heart monitor, and gain access to a multitude of heart health metrics including heart rate, so that you can stay on top of your heart health always. If you have concerns about your resting heart rate, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How can I reduce my resting heart rate?
There are a number of ways to reduce your resting heart rate, including regular aerobic exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and getting sufficient sleep.
What is a good resting heart rate by age?
A healthy resting heart rate for adults is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute. However, the ideal resting heart rate can vary depending on age, fitness level, and overall health. For example, a resting heart rate of 50-60 beats per minute may be considered healthy for athletes or individuals who exercise regularly.
Why is my resting heart rate so high?
Several factors can contribute to a high resting heart rate, like stress and anxiety, a lack of physical activity, dehydration, certain medications, or medical conditions. If you have concerns about your resting heart rate, it’s important to speak with your doctor to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
How fast can I lower my resting heart rate?
The speed at which you can lower your resting heart rate depends on various factors, including your current heart rate, overall health, and lifestyle habits. Engaging in regular physical activity, practicing relaxation techniques, and getting enough sleep can help lower your resting heart rate over time. However, it’s important to make lifestyle changes gradually and work with your healthcare provider to develop a safe and effective plan to lower your heart rate.
What are some lifestyle changes that can lower my resting heart rate?
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep can all help lower your resting heart rate.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Heart Palpitations After Covid | Silent Heart Attack | Meditation and Heart Health | Heart Stress Test | Heart Rate Monitor | Diabetes Impact on Heart Health | Post Covid Fatigue | Irregular Heartbeat | Normal Resting Heart Rate | Heart Health Monitor Device
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
What is considered a Normal Heart Rate?
A normal heart rate refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. The normal heart rate range for adults is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute (ref. link). However, the normal range can vary based on age, gender, and overall health status. For children, the normal range is typically higher, between 70 and 100 beats per minute.
Factors Affecting Normal Heart Rate:
Here are some factors that can affect normal heart rate:
Age: As a person ages, their heart rate tends to decrease. For example, newborns have a heart rate of about 100-160 bpm, while adults generally have a heart rate of 60-100 bpm.
Physical activity: When a person engages in physical activity, their heart rate increases to deliver more oxygen to the body’s muscles. During exercise, it is normal for the heart rate to be higher than the resting heart rate.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can cause the heart rate to increase. This is due to the release of adrenaline, which stimulates the heart to beat faster.
Medications: Some medications, such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, can affect the heart rate.
Normal Heart Rate Ranges by Age :
As mentioned earlier, a normal heart rate varies depending on age. Here are the average heart rate ranges for different age groups:
Newborns (0-1 months) : 70-190 bpm
Infants (1 to 11 months) : 80-160 bpm
Toddlers (1-3 years) : 80-130 bpm
Preschoolers (3-5 years) : 80-120 bpm
Children (5-6 years) : 75 to 115 bpm
(7-9 years) : 70 to 110 bpm
(10-15 years) : 60 to 100bpm
Adults (15 and older) : 60-100 bpm
What is Maximum Heart rate?
Maximum heart rate is the highest number of times your heart can beat in one minute during exercise. It is influenced by age, fitness level, and genetics. Monitoring your heart rate during exercise helps you determine the appropriate intensity level and avoid injury or overexertion. You can calculate your Maximum heart rate by subtracting your age from 220. For example, if you are 30 years old, your estimated maximum heart rate would be 190 beats per minute. The most accurate method for determining maximum heart rate is a stress test or heart rate monitor. Understanding the factors that affect maximum heart rate can help you make adjustments to your exercise routine and stay healthy.
Abnormal Heart Rate
What is Considered an Abnormal Heart Rate?
An abnormal heart rate is typically considered to be below 60 or above 100 beats per minute for adults. However, the normal range can vary based on age, gender, and overall health status. For children, the normal range is typically higher, between 70 and 100 beats per minute. A heart rate that is consistently outside the normal range can indicate an underlying heart condition and may require medical attention.
Types of Abnormal Heart Rates
There are several types of abnormal heart rates, including:
Tachycardia (ref. link): A condition where the heart rate is faster than the normal range, typically above 100 beats per minute. This can occur during physical activity or as a result of an underlying medical condition.
Bradycardia: A condition where the heart rate is slower than the normal range, typically below 60 beats per minute. This can occur as a result of an underlying medical condition or certain medications.
Arrhythmia: An irregular heartbeat that can be too fast, too slow, or a combination of both. This can occur as a result of an underlying medical condition, electrolyte imbalances, or other factors.
Causes of Abnormal Heart Rates
There are many potential causes of abnormal heart rates including heart disease, medication side effects, dehydration, thyroid problems, and electrical abnormalities in the heart.
How to Check Heart Rate
Find your pulse in the wrist
The easiest way to check your heart rate is to place two fingers (usually the index and middle fingers) on the wrist, just below the thumb. You can also check your heart rate by placing two fingers on the neck, just to the side of the windpipe. Count the number of beats you feel in 15 seconds, then multiply by four to get the beats per minute. Another option is to use a heart rate monitor device.
Devices for Monitoring Heart Rate
There are several devices available for monitoring heart rate, including wearable fitness trackers, smartwatches, and heart rate monitors. These devices can track heart rate continuously and provide data on heart rate variability, exercise performance, and overall heart health.
How Often to Monitor Heart Rate
The frequency of monitoring the heart rate can vary based on age, overall health status, and any underlying heart conditions. In general, it is recommended to monitor heart rate at least once a day, particularly during physical activity or exercise. If you have a history of heart problems or are experiencing symptoms of an abnormal heart rate, more frequent monitoring may be necessary.
Maintaining a Healthy Heart Rate
Maintaining a healthy heart rate is important for overall heart health. Here are some lifestyle changes that can help maintain a healthy heart rate:
Regular exercise: Exercise can help strengthen the heart and improve cardiovascular health.
Balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy heart rate.
Stress management: High levels of stress can impact heart rate, so it is important to find ways to manage stress, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have negative impacts on heart health and heart rate.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Abnormal Heart Rate?
If you experience persistent symptoms of an abnormal heart rate, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or dizziness, it is important to seek medical attention. Additionally, if you have a history of heart disease or other underlying heart conditions, regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider may be necessary.
A normal heart rate can vary based on several factors, including age, gender, and overall health status. For adults, a resting heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute is generally considered normal. However, it is important to note that individual factors may impact what is considered normal for each person. Monitoring heart rate regularly and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help ensure overall heart health and identify potential heart problems. The best way to do so is by using a smart heart monitor like the Frontier X2. If you experience persistent symptoms of an abnormal heart rate, it is important to seek medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions :
Does age affect a normal heart rate?
Yes, age can affect a normal heart rate. As we age, our heart rate at rest may decrease slightly.
Does gender affect the normal heart rate?
Gender can also affect the normal heart rate. In general, women tend to have a slightly higher resting heart rate than men.
Can physical fitness level impact a normal heart rate?
Yes, physical fitness level can impact normal heart rate. Regular exercise can help lower resting heart rate over time.
Are there any medical conditions that can impact normal heart rate?
Yes, medical conditions such as thyroid problems, heart disease, and certain medications can impact normal heart rate.
Can stress or anxiety impact normal heart rate?
Yes, stress or anxiety can impact normal heart rate, potentially causing it to increase temporarily.
How often should I check my heart rate?
The frequency of checking heart rate can vary based on individual factors. In general, checking heart rate at least once a day, particularly during physical activity or exercise, can be helpful for maintaining heart health.
When should I seek medical attention for abnormal heart rate
If you experience persistent symptoms of an abnormal heart rate, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or dizziness, it is important to seek medical attention. Additionally, if you have a history of heart disease or other underlying heart conditions, regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider may be necessary.
Can lifestyle changes impact normal heart rate?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management can all help maintain a healthy heart rate.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
Heart Rate While Running | Silent heart attack | Heart Attack Symptoms | Heart Palpitations Causes | Increased Heart Rate | Healthy Heart Tips | Running Heart Rate Zones | Heart Attack causes | Wearable ECG Monitor | Cardio Exercise
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Your heart rate is a crucial indicator of overall health, and it’s important to understand what factors can affect it. A normal heart rate at rest is between 60-100 beats per minute (ref. link). However, did you know that several factors can affect heart rate? From physical activity to emotional states, medication to medical conditions, the list is diverse and extensive. We will explore the various factors that can influence heart rate and the implications of each of these factors.
Physical Activity:
Physical activity is one of the most well-known factors that affect heart rate. Your exercise-induced heart rate response is one of the best indicators of cardiovascular fitness.
How physical activity affects heart rate
Physical activity affects heart rate by increasing the demand for oxygen and nutrients in the body. As physical activity (ref. link) increases, the body needs to pump more blood and oxygen to the working muscles, leading to an increase in heart rate. The heart rate increases in proportion to the intensity of the exercise
The difference between resting heart rate and exercise heart rate
Resting heart rate is the heart rate when the body is at rest. It is usually measured first thing in the morning, before getting out of bed, and is a good indicator of overall cardiovascular health. Exercise heart rate, on the other hand, is the heart rate during physical activity. It can vary depending on the type and intensity of the exercise.
Activities that can increase heart rate
Activities that can increase heart rate include cardio exercises such as running, cycling, swimming, and aerobics. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) (ref. link) is also an effective way to increase heart rate quickly. Weightlifting and resistance training can also increase heart rate, but not to the same extent as cardio exercises.
Emotional State:
How emotions can affect heart rate
Different emotions can lead to changes in heart rate. For instance, anxiety and fear can cause an increase in heart rate, while feelings of relaxation and calm can lead to a decrease in heart rate. The autonomic nervous system regulates the heart rate response to different emotions.
The relationship between stress and heart rate
Stress can be a significant factor that affects heart rate. When a person experiences stress (ref. link), the body’s “fight or flight” response is triggered, leading to an increase in heart rate, among other physiological responses. Chronic stress can also have long-term effects on the heart, leading to cardiovascular disease.
Emotions that can increase or decrease heart rate
Emotions (ref. link) that can increase heart rate include fear, anxiety, anger, and excitement. On the other hand, emotions that can decrease heart rate include relaxation, calmness, and meditation.
It’s essential to manage our emotional states to maintain a healthy heart rate. By practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga, we can help reduce stress levels and keep our heart rate within a healthy range.
Body Position:
The difference between standing, sitting, and lying down heart rate
Heart rate can vary depending on body position. When we change our body position, our heart has to work differently to pump blood throughout the body. As a result, our heart rate can change. When we are lying down, our heart doesn’t have to work as hard to pump blood throughout the body, so our heart rate tends to be lower. When we are sitting or standing, our heart rate is higher because our heart has to work harder to pump blood against gravity.
How body position changes affect heart rate
When we stand up suddenly from a lying position, we experience a phenomenon called orthostatic hypotension. This sudden change in body position can cause a decrease in blood pressure, which in turn can cause an increase in heart rate. Similarly, when we lie down after standing for a long time, our heart rate can decrease as our heart doesn’t have to work as hard to pump blood.
It’s important to be aware of how changes in body position can affect heart rate, especially for individuals with cardiovascular disease or orthostatic hypotension. By making gradual changes in body position, such as sitting up slowly or taking breaks during prolonged standing, we can help maintain a healthy heart rate.
Medications and other substances:
Medications and substances can also affect heart rate, sometimes with significant implications for overall cardiovascular health.
How Medications and substances can affect heart rate
Medications and other substances (like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol) can affect heart rate by altering the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which controls the heart rate. Some medications can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, leading to an increase in heart rate, while others can depress the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a decrease in heart rate.
The relationship between caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol consumption and heart rate
Caffeine (ref. link) and nicotine are stimulants that can increase heart rate by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system. Alcohol, on the other hand, can depress the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a decrease in heart rate.
Medications that can increase or decrease heart rate
Examples of medications that can increase heart rate include beta-blockers (ref. link), which block the effects of adrenaline on the heart and slow down heart rate, and some asthma medications, which stimulate the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of medications that can decrease heart rate include calcium channel blockers, which slow down heart rate by blocking the movement of calcium ions into the heart muscle, and some antidepressants, which depress the sympathetic nervous system.
Medical Conditions:
Several medical conditions can affect heart rate, often with significant implications for overall cardiovascular health.
How medical conditions can affect heart rate
Medical conditions can affect heart rate by altering the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which controls the heart rate. Some medical conditions can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, leading to an increase in heart rate, while others can depress the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a decrease in heart rate.
The relationship between hypertension, arrhythmia, and heart rate
Hypertension, or high blood pressure (ref. link), can lead to an increase in heart rate as the heart works harder to pump blood through the arteries. Arrhythmia (ref. link), or an irregular heartbeat, can also lead to changes in heart rate, depending on the specific type of arrhythmia.
Medical conditions that can affect heart rate
Examples of medical conditions that can increase heart rate include hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid gland that can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, and fever, which can increase heart rate by increasing metabolic demand. Examples of medical conditions that can decrease heart rate include hypothyroidism, an underactive thyroid gland that can depress the sympathetic nervous system, and sleep apnea, which can depress the parasympathetic nervous system.
Heart rate is affected by a variety of factors including physical activity, emotional state, medication use, caffeine intake, body temperature, and overall health status. By understanding the factors that affect heart rate, individuals can better monitor their own heart health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices. It is important to maintain a healthy heart rate within the normal range to reduce the risk of heart disease and other health complications.
Your Heart Rate is one of many heart health related metrics that you can pay attention to. Purchase the Frontier X2 smart heart monitor and get access to detailed, accurate data on these metrics so that you can know what is affecting your heart and how. Stay vigilant and stay healthy!
Frequently Asked Questions:
How does physical activity affect heart rate?
Physical activity increases heart rate by increasing the demand for oxygen and nutrients in the body. This increase in heart rate is a normal and healthy response to exercise.
Can emotional state affect heart rate?
Yes, emotional state can affect heart rate. Stress, anxiety, and fear can all cause an increase in heart rate. On the other hand, relaxation and meditation can help lower heart rate.
Can medication affect heart rate?
Yes, medication can affect heart rate. Some medications can cause an increase or decrease in heart rate as a side effect. It is important to discuss any medication concerns with a healthcare provider.
Does caffeine intake affect heart rate?
Yes, caffeine intake can affect heart rate. Caffeine is a stimulant that can elevate the heart rate. Individuals who are sensitive to caffeine may experience a more significant increase in heart rate than those who are not.
Can body temperature affect heart rate?
Yes, body temperature can affect heart rate. An increase in body temperature, such as during a fever, can cause an increase in heart rate. Similarly, a decrease in body temperature, such as during hypothermia, can cause a decrease in heart rate.
Why is it important to monitor heart rate?
Monitoring heart rate can provide important information about overall heart health. An abnormal heart rate can indicate a heart condition or other health complications. By monitoring heart rate, individuals can take steps to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Other Heart Health Topics To Explore:
How To Improve Heart Health | Heart Arrhythmia | Heart Palpitations Causes | AFib Risk Factors | Heart Attack Causes | Low Heart Rate | Atrial Fibrillation | Stress Test for Heart | Endurance Training | Best Heart Rate Monitor
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK
Heart Rate is the measure of the number of times your heart beats per minute, and it can provide valuable insights into your overall health and fitness. By monitoring your heart rate, you can track changes in your cardiovascular health, measure the intensity of your workouts, and identify potential health risks. Recording your heart rate is a simple and quick process that can be done using your fingertips or a heart rate monitor. We’ll provide step-by-step instructions for taking your heart rate, as well as information on why it’s important to do so. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or simply looking to improve your overall health, tracking your heart rate can be an effective tool for achieving your goals.
Normal Range of Heart Rate
To measure your heart rate, you can take your pulse (ref. link) by placing your fingertips on your wrist or neck and counting the number of beats you feel in a set amount of time, such as 15 or 30 seconds.
The normal range of heart rate varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and fitness level. At rest, a normal heart rate (ref. link) for adults is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute. During exercise, the heart rate can increase significantly, depending on the intensity of the activity. For example, a moderate-intensity workout may cause the heart rate to reach 50-70% (ref. link) of the maximum heart rate, while a high-intensity workout may cause the heart rate to reach 70-85% of the maximum heart rate.
How is Heart Rate affected by Exercise
During exercise, the heart rate increases to deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the working muscles. The heart rate is affected by the intensity and duration of the exercise (ref. link), as well as individual factors such as age, fitness level, and overall health. For example, an athlete may have a lower resting heart rate and a higher maximum heart rate compared to a sedentary person of the same age. It’s important to monitor your heart rate during exercise to ensure you’re working at the right intensity level and to avoid overexertion, which can lead to injury or other health problems.
How is Heart Rate affected by Stress and Other Factors
Heart rate is also affected by stress and other factors, such as caffeine intake, medication use, and illness. When the body is under stress, the heart rate can increase as part of the body’s fight-or-flight response. Chronic stress can lead to a higher resting heart rate and may increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems. Conversely, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can help lower the heart rate and reduce stress.
Why Measure Your Heart Rate?
Monitoring your heart rate is important for several reasons. Your heart rate can provide valuable information about your overall health, fitness level, and response to stress and other factors. Monitoring your heart rate allows you to:
Identify potential health problems: An unusually high or low heart rate at rest or during exercise can indicate potential health problems, such as arrhythmias, heart disease, or overtraining.
Prevent health problems: Regular monitoring of your heart rate can help you identify potential health problems early and take preventive measures, such as adjusting your lifestyle habits or seeking medical attention.
Optimize your fitness routine: Tracking your heart rate during exercise can help you determine the intensity level of your workout and adjust it accordingly. This can help you avoid overtraining or not working out hard enough.
Measure progress: By monitoring your heart rate over time, you can track your progress and set achievable fitness goals.
Benefits of Tracking Heart Rate During Exercise
Tracking your heart rate during exercise can provide several benefits, such as:
Better workout efficiency: By tracking your heart rate, you can ensure that you’re working out at the appropriate intensity level for your fitness goals. This can help you optimize your workout and achieve better results.
Improved cardiovascular health: Regular exercise can help improve cardiovascular health. By tracking your heart rate during exercise, you can ensure that you’re exercising at the appropriate intensity level to reap these benefits.
Reduced risk of injury: Overtraining can lead to injuries. By tracking your heart rate during exercise, you can ensure that you’re not overtraining and risking injury.
How to Take Your Heart Rate :
There are two main methods for taking your heart rate: manually and using a heart rate monitor.
To take your heart rate manually, you can follow these steps:
Find your pulse: As mentioned earlier, you can find your pulse at your wrist, neck, or on the top of your foot.
Count the beats: Using a watch or clock with a second hand, count the number of beats you feel in 60 seconds. You can also count the beats for 15 seconds and multiply by four to get your beats per minute.
To take your heart rate using a heart rate monitor, you can follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your particular device.
Tips for Accurate Measurement :
To get an accurate heart rate reading, it’s important to:
Take measurements in a relaxed, quiet environment: Avoid talking or moving during the measurement.
Take multiple measurements at different times: This can ensure consistency and accuracy.
Use the same method each time: Whether you use a manual or heart rate monitor method, use the same method each time you measure your heart rate to ensure consistency.
Interpreting Your Heart Rate :
Interpreting your heart rate readings can provide valuable information about your overall health and fitness. A high or low heart rate at rest or during exercise may indicate potential health problems or training needs.
For example, a high heart rate during exercise may indicate that you’re working too hard, which can increase the risk of injury or overtraining. A low heart rate during exercise may indicate that you’re not working hard enough to achieve your fitness goals.
If you’re concerned about your heart rate readings, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance. They can help you determine whether your heart rate is within a healthy range and provide recommendations for improving your heart health and fitness.
Heart rate is an important measure of cardiovascular health and fitness. It’s affected by a variety of factors, including exercise, stress, and other lifestyle factors. By monitoring your heart rate regularly, you can gain valuable insights into your overall health and make informed decisions about your fitness routine and lifestyle choices.
Your Heart Rate is one of many heart health metrics that the Frontier X2 gives you access to. Monitoring your cardiac function allows you to make the most out of your workouts so that your health and fitness goals can be achieved as efficiently as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How can I measure my heart rate without a heart rate monitor?
You can measure your heart rate manually by taking your pulse on your wrist, neck or chest. Count the number of beats you feel within a 15-second period and multiply by four to get your heart rate per minute.
How can I measure my heart rate during exercise?
You can use a heart rate monitor to measure your heart rate during exercise. These devices can be worn on your wrist or chest and provide a continuous readout of your heart rate.
How accurate are heart rate monitors?
When used properly, heart rate monitors are generally accurate. However, factors such as movement, position of the device, and interference from other electronic devices can affect accuracy.
How often should I measure my heart rate?
The frequency of measuring heart rate depends on the reason for monitoring. For general health and fitness purposes, measuring once a day or a few times a week is sufficient. For specific medical conditions, a healthcare professional may recommend more frequent monitoring.
When should I seek medical attention based on my heart rate?
If you notice a significant increase or decrease in your heart rate, or if your heart rate consistently falls outside of the normal range, you should consult a healthcare professional. Other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness should also prompt medical attention.
Other Heart Health Options To Explore:
Heart Palpitations Causes | Increased Heart rate | Healthy Heart Tips | Arrhythmia Causes | Running Heart Rate | Heart Attack Causes | Best ECG Monitors | Heart Rate While Running | Mental Stress | Heart Attack Symptoms
Frontier X2:
Smart Heart ECG Monitor in USA | ECG Machine Price in India | Best Heart Rate Monitor UK